 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Liver hemangioma
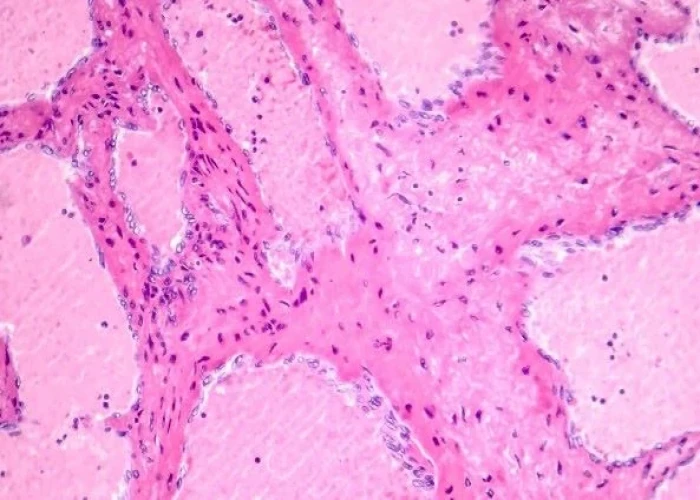
A liver hemangioma is a benign (non-cancerous) tumor that is made up of blood vessels. It is the most common type of liver tumor, and it is estimated that up to 7% of the population has one. Most liver hemangiomas are small and do not cause any symptoms. They are usually found incidentally during imaging tests done for other reasons.
Symptoms of a liver hemangioma may include pain or discomfort in the abdomen, nausea, vomiting, and a feeling of fullness after eating. However, these symptoms are rare, and most people with liver hemangiomas do not experience any symptoms.
Liver hemangiomas are usually not treated, as they are benign and do not pose a significant health risk. However, if the tumor is large or causing symptoms, treatment options may include surgery, embolization, or radiofrequency ablation.
It's important to note that a liver hemangioma is not the same as liver cancer. Liver cancer is a malignant tumor that can grow and spread to other parts of the body, whereas a liver hemangioma is a benign growth that usually does not cause any problems. If you have any concerns about a liver hemangioma, it's important to speak with your healthcare provider.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Upper abdomen pain
- Feeling bloated after eating
- Nausea or vomiting
Disease Causes
Liver hemangioma
It's not clear what causes a liver hemangioma to form. Doctors believe liver hemangiomas are present at birth (congenital).
A liver hemangioma usually occurs as a single abnormal collection of blood vessels that is less than about 1.5 inches (about 4 centimeters) wide. Occasionally liver hemangiomas can be larger or occur in multiples. Large hemangiomas can occur in young children, but this is rare.
In most people, a liver hemangioma will never grow and never cause any signs and symptoms. But in a small number of people, a liver hemangioma will grow to cause symptoms and require treatment. It's not clear why this happens.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
If your liver hemangioma is small and doesn't cause any signs or symptoms, you won't need treatment. In most cases a liver hemangioma will never grow and will never cause problems. Your doctor may schedule follow-up exams to check your liver hemangioma periodically for growth if the hemangioma is large.
Liver hemangioma treatment depends on the location and size of the hemangioma, whether you have more than one hemangioma, your overall health, and your preferences.
Treatment options may include:
- Surgery to remove the liver hemangioma. If the hemangioma can be easily separated from the liver, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove the mass.
- Surgery to remove part of the liver, including the hemangioma. In some cases, surgeons may need to remove a portion of your liver along with the hemangioma.
- Procedures to stop blood flow to the hemangioma. Without a blood supply, the hemangioma may stop growing or shrink. Two ways to stop the blood flow are tying off the main artery (hepatic artery ligation) or injecting medication into the artery to block it (arterial embolization). Healthy liver tissue is unharmed because it can draw blood from other nearby vessels.
- Liver transplant surgery. In the unlikely event that you have a large hemangioma or multiple hemangiomas that can't be treated by other means, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove your liver and replace it with a liver from a donor.
- Radiation therapy. Radiation therapy uses powerful energy beams, such as X-rays, to damage the cells of the hemangioma. This treatment is rarely used because of the availability of safer and more-effective treatments.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Liver hemangioma and Learn More about Diseases

Skin cancer

Wilson's disease
Placental abruption
Polio
Delayed ejaculation

Mammary duct ectasia
Floor of the mouth cancer

Group B strep disease
liver hemangioma, লিভার হেম্যানজিওমা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
