Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
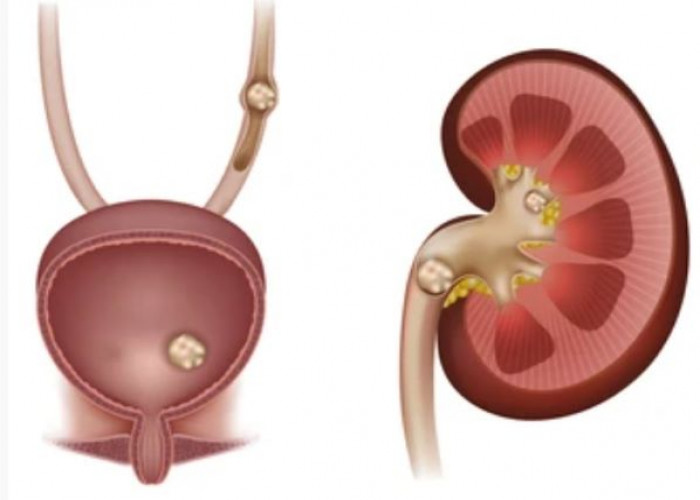
Bladder stones

Bladder stones are hard, mineral deposits that form in the bladder when urine becomes concentrated and crystallizes. They can cause symptoms such as pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen, difficulty urinating, frequent urination, and blood in the urine. Treatment for bladder stones may include medication to help dissolve the stones or surgical removal of the stones. In some cases, a procedure called lithotripsy may be used to break up the stones into smaller pieces that can be passed more easily. Preventative measures, such as drinking plenty of fluids and avoiding urinary tract infections, can help reduce the risk of bladder stones.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Abdomen pain
- Lower abdomen pain
- Burning during urination
- Frequent urination
- Difficulty urinating or interrupted urine flow
- Blood in urine (hematuria)
- Excess protein or cloudy urine (proteinuria)
Disease Causes
Bladder stones
Bladder stones can develop when your bladder doesn't empty completely. This causes urine to become concentrated urine. Concentrated urine can crystallize and form stones.
Some infections can lead to bladder stones. Sometimes an underlying condition that affects the bladder's ability to hold, store or eliminate urine can result in bladder stone formation. Any foreign materials present in the bladder tend to cause bladder stones.
The most common conditions that cause bladder stones include:
- Prostate gland enlargement. An enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hyperplasia, or BPH) can cause bladder stones in men. An enlarged prostate can obstruct the flow of urine, preventing the bladder from emptying completely.
- Damaged nerves. Normally, nerves carry messages from your brain to your bladder muscles, directing your bladder muscles to tighten or release. If these nerves are damaged — from a stroke, spinal cord injury or other health problem — your bladder may not empty completely. This is known as neurogenic bladder.
Other possible causes of bladder stones include:
- Inflammation. Bladder inflammation, sometimes caused by urinary tract infections or radiation therapy to the pelvis, can lead to bladder stones.
- Medical devices. Bladder catheters — slender tubes inserted through the urethra to help urine drain from your bladder — may cause bladder stones. So can objects that accidentally migrate to your bladder, such as a contraceptive device or urinary stent. Mineral crystals, which later become stones, tend to form on the surfaces of these devices.
- Kidney stones. Stones that form in your kidneys are not the same as bladder stones. They develop in different ways. But small kidney stones may travel down the ureters into your bladder and, if not expelled, can grow into bladder stones.
Disease Prevents
Bladder stones
Bladder stones are usually caused by an underlying condition that's hard to prevent, but you can decrease your chances of bladder stones by following these tips:
- Tell your doctor about unusual urinary symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment of an enlarged prostate or another urologic condition may reduce your risk of developing bladder stones.
- Drink plenty of fluids. Drinking more fluids, especially water, may help prevent bladder stones because fluids dilute the concentration of minerals in your bladder. How much water you should drink depends on your age, size, health and level of activity. Ask your doctor what's an appropriate amount of fluid for you.
Disease Treatments
Drinking lots of water may help a small stone pass naturally. However, because bladder stones are often caused by difficulty emptying your bladder completely, extra water may not be enough to make the stone pass.
Most of the time, you'll need to have the stones removed. There are a few ways to do this.
Breaking stones apart
In one method, you're first given numbing medication or general anesthesia to make you unconscious. After that, a small tube with a camera at the end is inserted into your bladder to let your doctor see the stone. Then, a laser, ultrasound or other device breaks the stone into small pieces and flushes them from the bladder.
Surgical removal
Occasionally, bladder stones are large or too hard to break up. In these cases, your doctor will surgically remove the stones from your bladder.
If your bladder stones are the result of a bladder outlet obstruction or an enlarged prostate, these problems need to be treated at the same time as your bladder stones, typically with surgery.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Diclofenac Sodium
Pain medication with diclofenac sodium.
Adults 50 mg 3 times a day with or after meals.
-
Diclofenac Potassium
Pain medication with diclofenac sodium. 1 3 times a day between meals or after meals.
-
Ranitidine Hydrochloride
Medicines containing ranitidine to prevent acid or gas in the stomach.
1 pill in the morning and at night after food.
-
Drotaverine
1 ampoule should be injected very slowly into the flesh or vein.
-
Pethidine Hydrochloride
Medicines containing pethidine hydrochloride for severe pain.
Adults 50/100mg should be injected intramuscularly. It can be given again after 6 hours if necessary.
-
Ampicillin Sodium
Ampicillin is a drug for bacterial infections.
1/2 capsule every 6 hours.
-
Cotrimoxazole
1 pill 2 times a day for 7-10 days.
-
Amoxicillin Trihydrate
1 capsule 3 times a day. 1 capsule every 6 hours according to the severity of the disease.
-
Ciprofloxacin
1 pill 2 times a day for 10 days.
-
Monosemicarbazone Adrenochrome
Blood clots with urine.
1 injection in the morning and 1 injection in the evening.
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
-
Lycopodium clavatum
6, 30, 200 power.
-
Berberis vulgaris
Q power.
-
Lithium carbonicum
3X power.
-
Acidum benzoicum
30 strength.
-
Triticum repens
30, 200 strength.
-
Cannabis sativa
6, 30 strength.
Disease yoga
Bladder stones and Learn More about Diseases
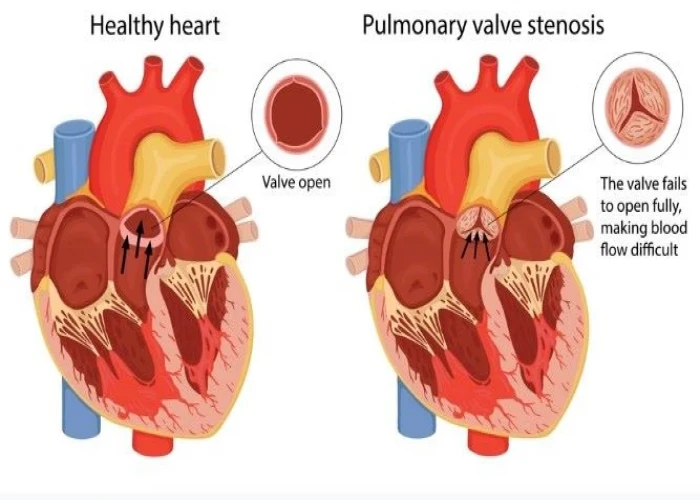
Pulmonary valve stenosis
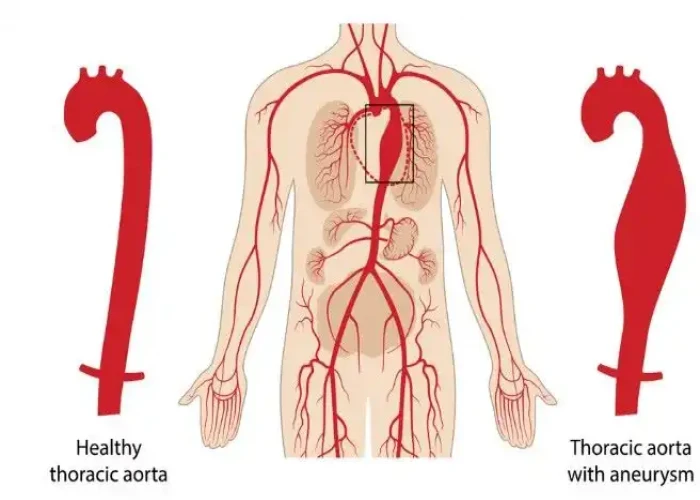
Thoracic aortic aneurysm

Mittelschmerz
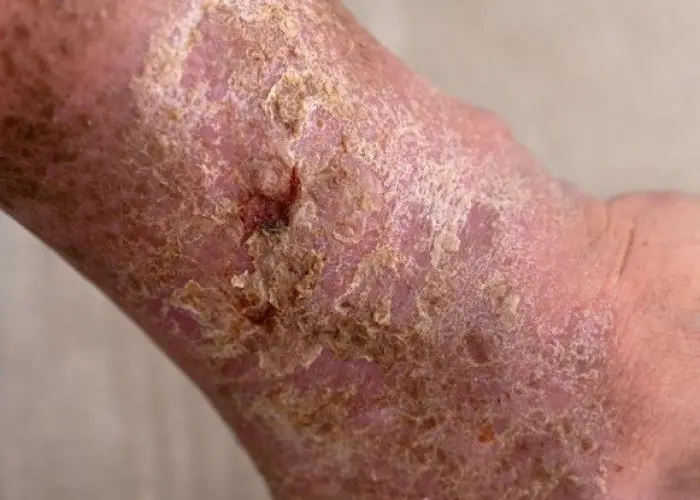
Gangrene

Mitral valve stenosis
Trichomoniasis
Neurodermatitis

Osteomyelitis
Bladder stones, Gall bladder stone, Gall bladder stone treatment, মূত্রাশয় পাথর
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.