 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
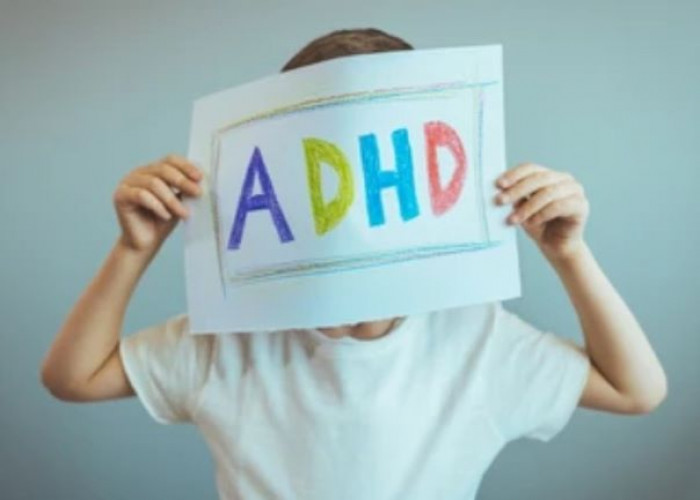
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children

Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects children and adolescents and can continue into adulthood. It is characterized by inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
The exact causes of ADHD are not yet fully understood, but a combination of genetic, neurobiological, and environmental factors is thought to play a role.
Common symptoms of ADHD in children include:
- Difficulty paying attention or staying focused
- Easily distracted
- Fidgeting or squirming
- Difficulty staying seated
- Excessive talking
- Interrupting others
- Impulsive behavior (such as acting without thinking)
Diagnosis of ADHD in children typically involves a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional, including a medical history, behavioral assessment, and sometimes neuropsychological testing.
Treatment for ADHD in children typically involves a combination of medication, behavioral therapy, and lifestyle changes. Medications such as stimulants and non-stimulants can be effective in managing symptoms of inattention and hyperactivity/impulsivity. Behavioral therapy can help children learn coping strategies and improve their behavior and social skills. Lifestyle changes, such as getting regular exercise, eating a balanced diet, and getting enough sleep, can also help manage symptoms.
It's important to remember that every child with ADHD is unique and may require a personalized approach to treatment. If your child has been diagnosed with ADHD, it's important to work with a healthcare professional to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to your child's individual needs.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Talk too much
- Have difficulty waiting for his or her turn
- Blurt out answers, interrupting the questioner
- Have trouble playing or doing an activity quietly
- Difficulty staying seated in the classroom or in other situations
- Lose items needed for tasks or activities, for example, toys, school assignments, pencils
- Avoid or dislike tasks that require focused mental effort, such as homework
- Have trouble organizing tasks and activities
- Difficulty following through on instructions and fail to finish schoolwork or chores
- Trouble staying focused in tasks or play
- Fail to pay close attention to details or make careless mistakes
- A mix of inattentive symptoms and hyperactive/impulsive symptoms.
- The majority of symptoms are hyperactive and impulsive.
- Interrupt or intrude on others' conversations, games or activities
Disease Causes
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children
While the exact cause of ADHD is not clear, research efforts continue. Factors that may be involved in the development of ADHD include genetics, the environment or problems with the central nervous system at key moments in development.
Disease Prevents
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children
To help reduce your child's risk of ADHD:
- During pregnancy, avoid anything that could harm fetal development. For example, don't drink alcohol, use recreational drugs or smoke cigarettes.
- Protect your child from exposure to pollutants and toxins, including cigarette smoke and lead paint.
- Limit screen time. Although still unproved, it may be prudent for children to avoid excessive exposure to TV and video games in the first five years of life.
Disease Treatments
Standard treatments for ADHD in children include medications, behavior therapy, counseling and education services. These treatments can relieve many of the symptoms of ADHD, but they don't cure it. It may take some time to determine what works best for your child.
Stimulant medications
Currently, stimulant drugs (psychostimulants) are the most commonly prescribed medications for ADHD. Stimulants appear to boost and balance levels of brain chemicals called neurotransmitters. These medications help improve the signs and symptoms of inattention and hyperactivity — sometimes effectively in a short period of time.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and Learn More about Diseases

Hiccups

Peanut allergy
Trachoma
Posterior vaginal prolapse (Rectocele)
Barrett's esophagus

Prader-Willi syndrome

Tuberculosis
Cradle cap
attention deficit, hyperactivity disorder adhd in children, ADHD, শিশুদের মধ্যে মনোযোগ-ঘাটতি, হাইপার্যাকটিভিটি ডিসঅর্ডার এডিএইচডি, এডিএইচডি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
