Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Noonan syndrome
Noonan syndrome is a genetic disorder that affects multiple parts of the body. It is caused by mutations in certain genes that play a role in the normal development and function of cells and tissues. The specific gene mutations associated with Noonan syndrome can vary, but many affect a pathway known as the RAS-MAPK pathway, which is important for cell growth and division.
Some common signs and symptoms of Noonan syndrome include:
- Facial features that may include a broad forehead, widely spaced eyes, and a small jaw
- Short stature
- Congenital heart defects, such as pulmonary valve stenosis or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Abnormalities of the lymphatic system, such as lymphedema or lymphangiectasia
- Developmental delays or intellectual disability
- Eye problems, such as strabismus or amblyopia
- Hearing loss
- Blood clotting disorders
- Increased risk of certain cancers, such as leukemia and neuroblastoma
Diagnosis of Noonan syndrome is usually based on clinical features and genetic testing to confirm the presence of gene mutations associated with the condition. There is no cure for Noonan syndrome, but treatment may involve management of symptoms and complications, such as surgery to correct heart defects, physical therapy to improve motor skills and strength, and speech therapy to address communication difficulties. Long-term follow-up and monitoring is important to detect and manage any potential complications, including an increased risk of cancer.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Large head
- The face may appear droopy and expressionless.
- Teeth may be crooked, the inside roof of the mouth (palate) may be highly arched and the lower jaw may be small.
- Nose is depressed at the top, with a wide base and bulbous tip.
- Ears are low-set and rotated backward.
- Rapid movement of eyeballs (Nystagmus)
- Short neck
- Poor growth or weight gain
- Irregular heartbeats (arrhythmia)
- Heart valve problems
- Skin may appear thin and transparent with age.
- Head may appear large with a prominent forehead and a low hairline on the back of the head.
Disease Causes
Noonan syndrome
Noonan syndrome is caused by a genetic mutation. These mutations can occur in multiple genes. Defects in these genes cause the production of proteins that are continually active. Because these genes play a role in the formation of many tissues throughout the body, this constant activation of proteins disrupts the normal process of cell growth and division.
The mutations that cause Noonan syndrome can be:
- Inherited. Children who have one parent with Noonan syndrome who carries the defective gene (autosomal dominant) have a 50 percent chance of developing the disorder.
- Random. Noonan syndrome can develop because of a new mutation in children who don't have a genetic predisposition for the disorder (de novo).
Disease Prevents
Noonan syndrome
Because some cases of Noonan syndrome occur spontaneously, there's no known way to prevent it. However, if you have a family history of this syndrome, talk to your doctor about the benefits of genetic counseling before you have children. Noonan syndrome can be detected with molecular genetic testing.
If Noonan syndrome is detected early, it's possible that ongoing and comprehensive care may lessen some of its complications, such as heart disease.
Disease Treatments
Although there's no way to repair the gene changes that cause Noonan syndrome, treatments can help minimize its effects. The earlier a diagnosis is made and treatment is started, the greater the benefits.
Treatment of the symptoms and complications that occur with Noonan syndrome depends on type and severity. Many of the health and physical issues associated with this syndrome are treated as they would be for anyone with a similar health problem. Taken together, though, the many problems of this disorder require a coordinated team approach.
Recommended approaches may include:
- Heart treatment. Certain drugs may be effective in treating some kinds of heart problems. If there's a problem with the heart's valves, surgery may be necessary. The doctor also may recommend that heart function be evaluated periodically.
- Treating low growth rate. Height should be measured three times a year until 3 years of age and then once every year until adulthood to make sure he or she is growing. To evaluate nutrition, the doctor will likely request blood tests. If your child's growth hormone levels are insufficient, growth hormone therapy may be a treatment option.
- Addressing learning disabilities. For early childhood developmental delays, ask the doctor about infant stimulation programs. Physical and speech therapies may be helpful for addressing a variety of possible issues. In some cases special education or individualized teaching strategies may be appropriate.
- Vision and hearing treatments. Eye exams are recommended at least every two years. Most eye issues can be treated with glasses alone. Surgery may be needed for some conditions, such as cataracts. Hearing screenings are recommended annually during childhood.
- Treatment for bleeding and bruising. If there's a history of easy bruising or excessive bleeding, avoid aspirin and aspirin-containing products. In some cases, doctors may prescribe drugs that help the blood to clot. Notify your doctor before any procedures.
- Treatment for lymphatic problems. Lymphatic problems can occur in many ways and may not require treatment. If they do require treatment, your doctor can suggest appropriate measures.
- Treatment for genital problems. If one or both testicles haven't moved into proper position within the first few months of life (undescended testicle), surgery may be needed.
Other evaluations and regular follow-up care may be recommended depending on specific issues, for example, regular dental care. Children, teens and adults should continue to have ongoing, periodic evaluations by their health care professional.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Noonan syndrome and Learn More about Diseases

Bipolar disorder
Dry socket
Salivary gland tumors
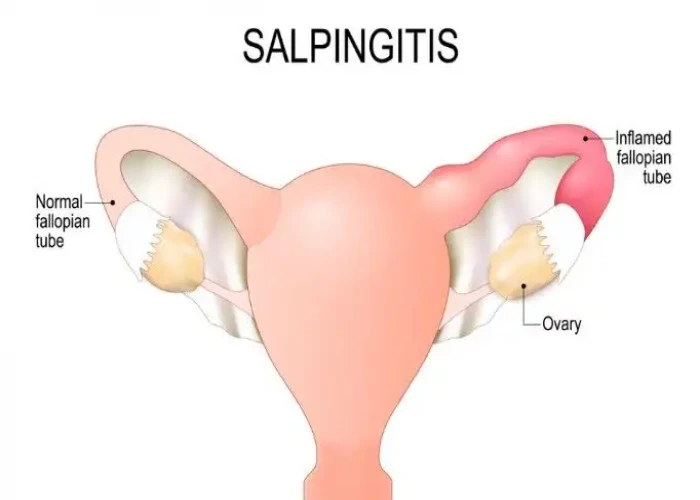
Salpingitis

Ulnar wrist pain
Peritonitis
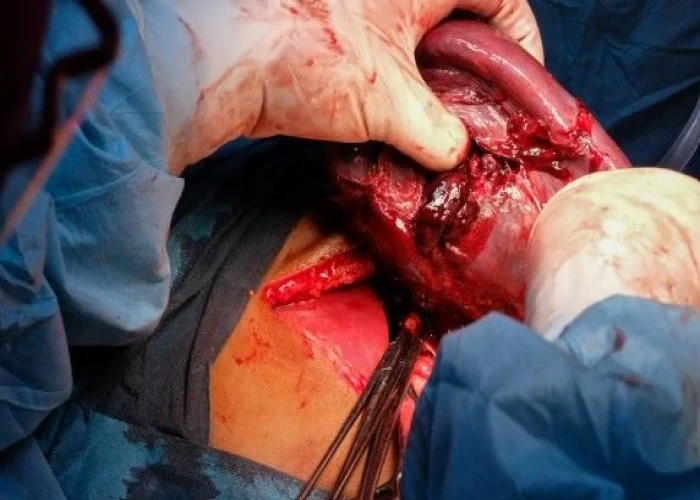
Ruptured spleen

Rett syndrome
noonan syndrome, নুনান সিনড্রোম
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.