Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
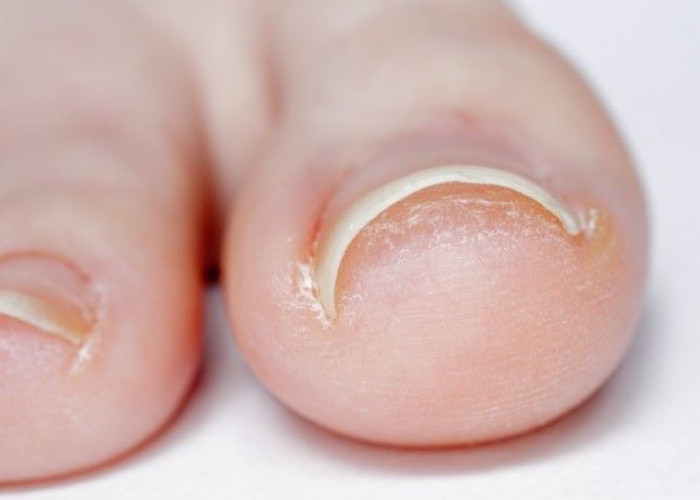
Ingrown toenails

Ingrown toenails are a common condition in which the edge of the toenail grows into the surrounding skin, causing pain, swelling, redness, and sometimes infection. Ingrown toenails most commonly affect the big toe, but can occur on any toe.
Ingrown toenails can be caused by a variety of factors, including improperly trimmed nails, shoes that are too tight or narrow, injury to the toe, or genetic factors that cause the nail to grow abnormally. People with diabetes or poor circulation are at a higher risk of developing complications from ingrown toenails.
Treatment for ingrown toenails typically involves soaking the affected foot in warm water several times a day to reduce inflammation, and gently pushing the skin away from the nail to allow it to grow out. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Wearing open-toed shoes or sandals can also help to reduce pressure on the affected toe.
In more severe cases, a doctor or podiatrist may need to perform a procedure to remove the ingrown portion of the nail. This may involve trimming the nail or using a chemical or laser treatment to prevent the nail from growing back into the skin. In rare cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected nail or a portion of the nail bed.
To prevent ingrown toenails, it is important to trim toenails straight across and avoid trimming them too short or too close to the skin. Wearing shoes that fit properly and are not too tight or narrow can also help to prevent ingrown toenails.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Swollen skin
- Redness around your toenail
- Infection of the tissue around your toenail
- Toe pain
- Swollen toe
Disease Causes
Ingrown toenails
Causes of ingrown toenails include:
- Wearing shoes that crowd the toenails
- Cutting toenails too short or not straight across
- Injuring a toenail
- Having very curved toenails
- Nail infections
- Certain medical conditions
Disease Prevents
Ingrown toenails
To help prevent an ingrown toenail:
- Trim your toenails straight across. Don't curve your nails to match the shape of the front of your toe. If you get a pedicure, ask the person doing it to trim your nails straight across. If you have a condition that causes poor blood flow to the feet and you can't trim your nails, see a podiatrist regularly to have your nails trimmed.
- Keep toenails at a moderate length. Trim toenails so they're even with the tips of your toes. If you trim your toenails too short, the pressure from your shoes on your toes may direct a nail to grow into the tissue.
- Wear shoes that fit properly. Shoes that place too much pressure on your toes or pinch them may cause a nail to grow into surrounding tissue. If you have nerve damage to the feet, you may not be able to sense if your shoes fit too tightly.
- Wear protective footwear. If your activities put you at risk of injuring your toes, wear protective footwear, such as steel-toed shoes.
- Check your feet. If you have diabetes, check your feet daily for signs of ingrown toenails or other foot problems.
Disease Treatments
If home remedies haven't helped your ingrown toenail, your health care provider may recommend:
- Lifting the nail. For a slightly ingrown nail, your health care provider may carefully lift the ingrowing nail edge and place cotton, dental floss or a splint under it. This separates the nail from the overlying skin and helps the nail grow above the skin edge, usually in 2 to 12 weeks. At home, you'll need to soak the toe and replace the material daily. Your health care provider might also prescribe a corticosteroid cream to apply after soaking.
- Another approach, which minimizes the need for daily replacement, uses cotton coated with a solution that fixes it in place and makes it waterproof (collodion).
- Taping the nail. With this method, your health care provider pulls the skin away from the ingrown nail with tape.
- Placing a gutter splint under the nail. With this method, your health care provider numbs the toe and slips a tiny slit tube underneath the embedded nail. This splint stays in place until the nail has grown above the skin edge. This method helps ease the pain of an ingrown nail as well.
- Partially removing the nail. For a more severe ingrown toenail (inflamed skin, pain and pus), your health care provider may numb the toe and trim or remove the ingrown portion of the nail. It could take 2 to 4 months for your toenail to grow back.
- Removing the nail and tissue. If you have the problem repeatedly on the same toe, your health care provider may suggest removing a portion of the nail along with the underlying tissue (nail bed). This procedure may prevent that part of the nail from growing back. Your health care provider will numb the toe and use a chemical, a laser or other methods.
After a nail-removal procedure, you can take a pain reliever as needed. It might help to apply a wet compress for a few minutes for a few days, until the swelling has gone down. And rest and elevate the toe for 12 to 24 hours. When you resume moving about, avoid activities that hurt your toe, and don't swim or use a hot tub until your health care provider tells you it's okay to do so. It's okay to shower the day after surgery. Call your health care provider if the toe isn't healing.
Sometimes, even with successful surgery, the problem occurs again. Surgical approaches are better at preventing recurrence than are nonsurgical methods.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Ingrown toenails and Learn More about Diseases

Stuttering
Burns
Pink eye (conjunctivitis)

Bacillary Dysentry

Moyamoya disease
Earwax blockage

Plague

Spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD)
ingrown toenails, অন্তর্বর্ধিত পায়ের নখ
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.