 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Nightmare disorder
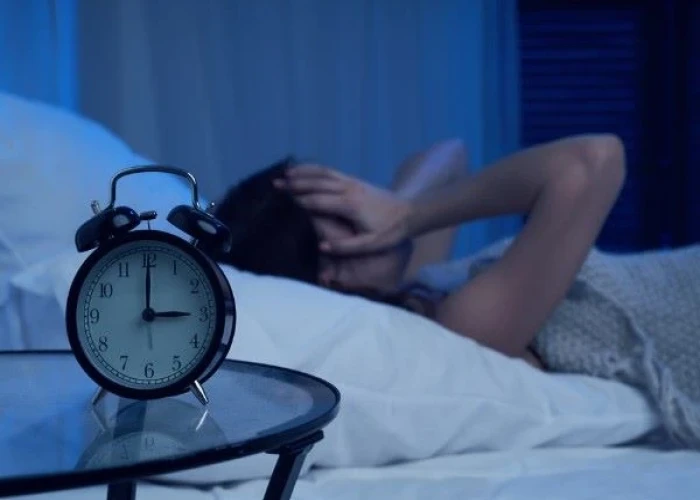

Nightmare disorder is a sleep disorder characterized by repeated and frequent nightmares that significantly disrupt a person's sleep and cause distress or impairment in daily functioning. Nightmare disorder is a type of parasomnia, which is a sleep disorder that involves abnormal behaviors or experiences during sleep.
Nightmares are vivid and disturbing dreams that often involve threats to personal safety or feelings of helplessness, and they can cause a person to wake up feeling anxious, frightened, or upset. Nightmare disorder is more common in children, but it can also affect adults.
The exact causes of nightmare disorder are not fully understood, but factors that may contribute to the disorder include:
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Anxiety disorders
- Depression
- Medications that affect the central nervous system
- Substance abuse
- Sleep deprivation
Treatment for nightmare disorder may include a combination of therapies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), relaxation techniques, and medication. CBT involves working with a therapist to identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to nightmares. Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and progressive muscle relaxation, can help reduce anxiety and promote better sleep. Medications, such as antidepressants and antipsychotics, may be prescribed in some cases to reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- Daytime fatigue or low energy
- Feel scared, anxious, angry, sad or disgusted as a result of the dream
- Can think clearly upon awakening and can recall details of the dream
- Problems with concentration or memory, or can't stop thinking about images from dreams
- Problems functioning at work or school or in social situations
- Behavior problems related to bedtime or fear of the dark
- Enlarged blood vessels just beneath the skin's surface
Disease Causes
Nightmare disorder
Nightmare disorder is referred to by doctors as a parasomnia — a type of sleep disorder that involves undesirable experiences that occur while you're falling asleep, during sleep or when you're waking up. Nightmares usually occur during the stage of sleep known as rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. The exact cause of nightmares is not known.
Nightmares can be triggered by many factors, including:
- Stress or anxiety. Sometimes the ordinary stresses of daily life, such as a problem at home or school, trigger nightmares. A major change, such as a move or the death of a loved one, can have the same effect. Experiencing anxiety is associated with a greater risk of nightmares.
- Trauma. Nightmares are common after an accident, injury, physical or sexual abuse, or other traumatic event. Nightmares are common in people who have post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
- Sleep deprivation. Changes in your schedule that cause irregular sleeping and waking times or that interrupt or reduce the amount of sleep you get can increase your risk of having nightmares. Insomnia is associated with an increased risk of nightmares.
- Medications. Some drugs — including certain antidepressants, blood pressure medications, beta blockers, and drugs used to treat Parkinson's disease or to help stop smoking — can trigger nightmares.
- Substance misuse. Alcohol and recreational drug use or withdrawal can trigger nightmares.
- Other disorders. Depression and other mental health disorders may be linked to nightmares. Nightmares can happen along with some medical conditions, such as heart disease or cancer. Having other sleep disorders that interfere with adequate sleep can be associated with having nightmares.
- Scary books and movies. For some people, reading scary books or watching frightening movies, especially before bed, can be associated with nightmares.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Treatment for nightmares isn't usually necessary. However, treatment may be needed if the nightmares are causing you distress or sleep disturbance and interfering with your daytime functioning.
The cause of the nightmare disorder helps determine treatment. Treatment options may include:
- Medical treatment. If the nightmares are associated with an underlying medical condition, treatment is aimed at the underlying problem.
- Stress or anxiety treatment. If a mental health condition, such as stress or anxiety, seems to be contributing to the nightmares, your doctor may suggest stress-reduction techniques, counseling or therapy with a mental health professional.
- Imagery rehearsal therapy. Often used with people who have nightmares as a result of PTSD, imagery rehearsal therapy involves changing the ending to your remembered nightmare while awake so that it's no longer threatening. You then rehearse the new ending in your mind. This approach may reduce the frequency of nightmares.
- Medication. Medication is rarely used to treat nightmares. However, medication may be recommended for severe nightmares associated with PTSD.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Nightmare disorder and Learn More about Diseases

Myoclonus
C. difficile infection
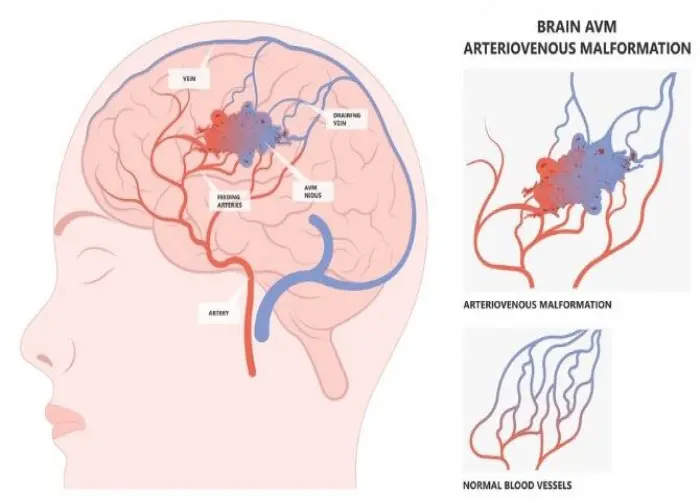
Intracranial venous malformations

Sleep terrors (night terrors)

Infant reflux

Panic attacks and panic disorder

Incompetent cervix

Spinal cord tumor
nightmare disorder, দুঃস্বপ্নের ব্যাধি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
