 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Metabolic syndrome

Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of medical conditions that increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease, stroke, and diabetes. The underlying cause of metabolic syndrome is insulin resistance, which is a condition where the body is unable to effectively use insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels.
Metabolic syndrome is defined by the presence of three or more of the following conditions:
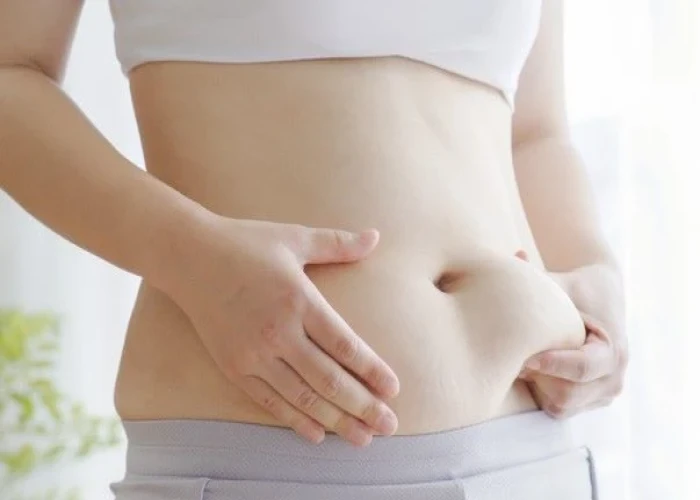
- Abdominal obesity: a waist circumference of greater than 40 inches for men and 35 inches for women
- High blood pressure: a systolic blood pressure of 130 mm Hg or higher, or a diastolic blood pressure of 85 mm Hg or higher
- High fasting blood sugar levels: a fasting blood sugar level of 100 mg/dL or higher
- High triglyceride levels: triglyceride levels of 150 mg/dL or higher
- Low HDL cholesterol levels: HDL cholesterol levels of less than 40 mg/dL for men and less than 50 mg/dL for women
The risk factors for metabolic syndrome include obesity, physical inactivity, insulin resistance, aging, and a family history of type 2 diabetes or cardiovascular disease. Lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, weight loss, and smoking cessation can help manage metabolic syndrome. Medications may also be prescribed to help manage individual components of metabolic syndrome, such as high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Blurred vision of eye
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- High blood sugar
- High cholesterol
Disease Causes
Metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is closely linked to overweight or obesity and inactivity.
It's also linked to a condition called insulin resistance. Normally, your digestive system breaks down the foods you eat into sugar. Insulin is a hormone made by your pancreas that helps sugar enter your cells to be used as fuel.
In people with insulin resistance, cells don't respond normally to insulin and glucose can't enter the cells as easily. As a result, your blood sugar levels rise even as your body churns out more and more insulin to try to lower your blood sugar.
Disease Prevents
Metabolic syndrome
A lifelong commitment to a healthy lifestyle may prevent the conditions that cause metabolic syndrome. A healthy lifestyle includes:
- Getting at least 30 minutes of physical activity most days
- Eating plenty of vegetables, fruits, lean protein and whole grains
- Limiting saturated fat and salt in your diet
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Not smoking
Disease Treatments
If aggressive lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise aren't enough, your doctor might suggest medications to help control your blood pressure, cholesterol and blood sugar levels.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Metabolic syndrome and Learn More about Diseases

Muscular dystrophy

Teen depression
Autonomic neuropathy
Congenital myasthenic syndromes
Pediatric obstructive sleep apnea
Vitamin deficiency anemia
Cervical cancer

Reye's syndrome
metabolic syndrome, বিপাকীয় সিন্ড্রোম
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
