Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
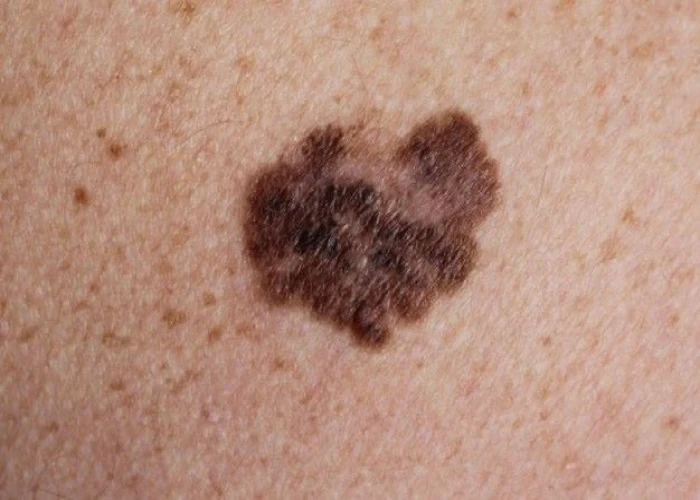
Melanoma

Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that develops from pigment-containing cells called melanocytes. It is the most dangerous form of skin cancer and can spread to other parts of the body if not detected and treated early.
Risk factors for melanoma include:
- Exposure to UV radiation from the sun or tanning beds
- Fair skin, freckles, and light-colored eyes
- History of sunburns, especially early in life
- Family history of melanoma
- Weakened immune system
Symptoms of melanoma may include:
- A new or changing mole on the skin
- An irregular or asymmetrical mole with an uneven color or border
- A mole that is larger than a pencil eraser
- A mole that itches or bleeds
To diagnose melanoma, a healthcare provider may perform a skin exam and biopsy, which involves removing a small sample of skin to test for cancer cells. Imaging tests such as CT scans or MRIs may also be performed to determine if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Treatment for melanoma typically involves surgery to remove the cancerous area, followed by further treatment such as radiation therapy or chemotherapy, depending on the extent of the cancer. Immunotherapy, which uses the body's own immune system to fight cancer cells, may also be recommended.
Prevention of melanoma involves protecting the skin from UV radiation by wearing protective clothing, using sunscreen with a high SPF, avoiding tanning beds, and seeking shade during peak sun hours. Regular skin exams with a healthcare provider can also help detect and treat melanoma early.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Brown skin
- Acral-lentiginous melanoma can occur under a fingernail or toenail. It can also be found on the palms of the hands or the soles of the feet.
- Look for new growth in a mole larger than 1/4 inch (about 6 millimeters).
- Look for moles with irregular, notched or scalloped borders characteristics of melanomas.
- Look for moles with irregular shapes, such as two very different-looking halves.
- Moles may change in appearance over time and some may even disappear with age.
- They're oval or round and usually smaller than 1/4 inch (about 6 millimeters) in diameter the size of a pencil eraser.
- These hidden melanomas are more common in people with darker skin.
- They most often develop in areas that have had exposure to the sun, such as your back, legs, arms and face.
- The development of a new pigmented or unusual-looking growth on the skin
- Dermatitis
- Melanoma
Disease Causes
Melanoma
Melanoma occurs when something goes wrong in the melanin-producing cells (melanocytes) that give color to your skin.
Normally, skin cells develop in a controlled and orderly way — healthy new cells push older cells toward your skin's surface, where they die and eventually fall off. But when some cells develop DNA damage, new cells may begin to grow out of control and can eventually form a mass of cancerous cells.
Just what damages DNA in skin cells and how this leads to melanoma isn't clear. It's likely that a combination of factors, including environmental and genetic factors, causes melanoma. Still, doctors believe exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun and from tanning lamps and beds is the leading cause of melanoma.
UV light doesn't cause all melanomas, especially those that occur in places on your body that don't receive exposure to sunlight. This indicates that other factors may contribute to your risk of melanoma.
Disease Prevents
Melanoma
You can reduce your risk of melanoma and other types of skin cancer if you:
- Avoid the sun during the middle of the day. For many people in North America, the sun's rays are strongest between about 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Schedule outdoor activities for other times of the day, even in winter or when the sky is cloudy.
- You absorb UV radiation year-round, and clouds offer little protection from damaging rays. Avoiding the sun at its strongest helps you avoid the sunburns and suntans that cause skin damage and increase your risk of developing skin cancer. Sun exposure accumulated over time also may cause skin cancer.
- Wear sunscreen year-round. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, even on cloudy days. Apply sunscreen generously, and reapply every two hours — or more often if you're swimming or perspiring.
- Wear protective clothing. Cover your skin with dark, tightly woven clothing that covers your arms and legs, and a broad-brimmed hat, which provides more protection than does a baseball cap or visor.
- Some companies also sell protective clothing. A dermatologist can recommend an appropriate brand. Don't forget sunglasses. Look for those that block both types of UV radiation — UVA and UVB rays.
- Avoid tanning lamps and beds. Tanning lamps and beds emit UV rays and can increase your risk of skin cancer.
- Become familiar with your skin so that you'll notice changes. Examine your skin often for new skin growths or changes in existing moles, freckles, bumps and birthmarks. With the help of mirrors, check your face, neck, ears and scalp.
- Examine your chest and trunk and the tops and undersides of your arms and hands. Examine both the front and back of your legs and your feet, including the soles and the spaces between your toes. Also check your genital area and between your buttocks.
Disease Treatments
The best treatment for your melanoma depends on the size and stage of cancer, your overall health, and your personal preferences.
Treatment for small melanomas
Treatment for early-stage melanomas usually includes surgery to remove the melanoma. A very thin melanoma may be removed entirely during the biopsy and require no further treatment. Otherwise, your surgeon will remove the cancer as well as a border of normal skin and a layer of tissue beneath the skin. For people with early-stage melanomas, this may be the only treatment needed.
Treating melanomas that have spread beyond the skin
If melanoma has spread beyond the skin, treatment options may include:
- Surgery to remove affected lymph nodes. If melanoma has spread to nearby lymph nodes, your surgeon may remove the affected nodes. Additional treatments before or after surgery also may be recommended.
- Immunotherapy. Immunotherapy is a drug treatment that helps your immune system to fight cancer. Your body's disease-fighting immune system might not attack cancer because the cancer cells produce proteins that help them hide from the immune system cells. Immunotherapy works by interfering with that process.
- Immunotherapy is often recommended after surgery for melanoma that has spread to the lymph nodes or to other areas of the body. When melanoma can't be removed completely with surgery, immunotherapy treatments might be injected directly into the melanoma.
- Targeted therapy. Targeted drug treatments focus on specific weaknesses present within cancer cells. By targeting these weaknesses, targeted drug treatments can cause cancer cells to die. Cells from your melanoma may be tested to see if targeted therapy is likely to be effective against your cancer.
- For melanoma, targeted therapy might be recommended if the cancer has spread to your lymph nodes or to other areas of your body.
- Radiation therapy. This treatment uses high-powered energy beams, such as X-rays and protons, to kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy may be directed to the lymph nodes if the melanoma has spread there. Radiation therapy can also be used to treat melanomas that can't be removed completely with surgery.
- For melanoma that spreads to other areas of the body, radiation therapy can help relieve symptoms.
- Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy can be given intravenously, in pill form or both so that it travels throughout your body.
- Chemotherapy can also be given in a vein in your arm or leg in a procedure called isolated limb perfusion. During this procedure, blood in your arm or leg isn't allowed to travel to other areas of your body for a short time so that the chemotherapy drugs travel directly to the area around the melanoma and don't affect other parts of your body.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Melanoma and Learn More about Diseases
Acute lymphocytic leukemia
Invasive lobular carcinoma

Hives (Cold urticaria)
Neurofibromatosis

POEMS syndrome
Poison ivy rash

Pneumothorax

Chondrosarcoma
melanoma, মেলানোমা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.