Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
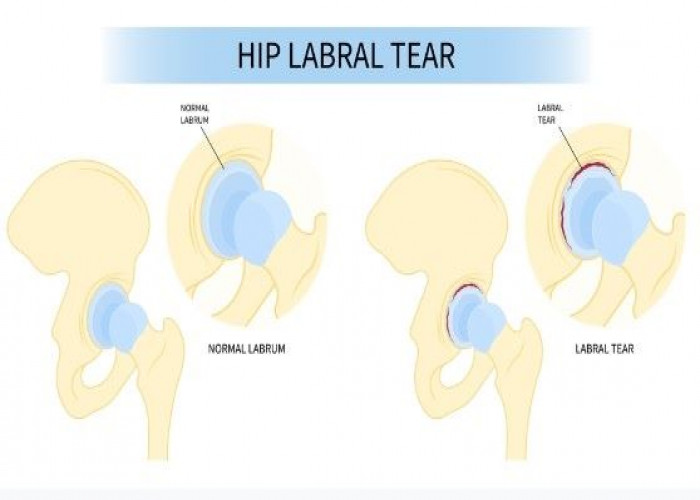
Hip labral tear
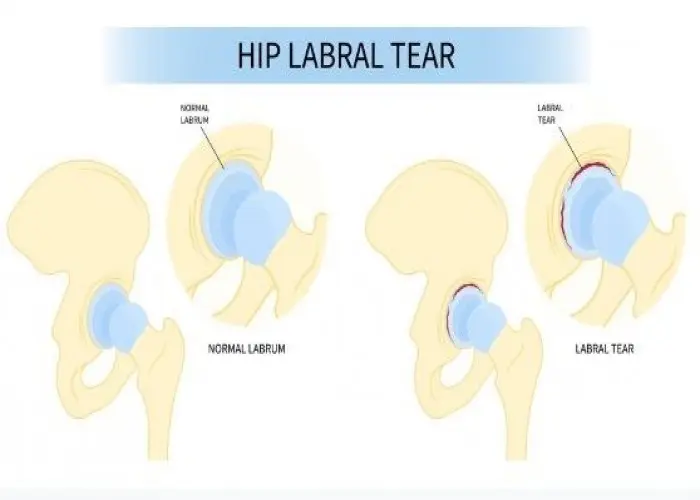
A hip labral tear is an injury to the ring of cartilage (the labrum) that surrounds the hip joint. The labrum helps to provide stability to the joint and cushion the hip joint as it moves. A labral tear can occur as a result of a sudden injury or due to overuse or degeneration of the joint.
Symptoms of a hip labral tear can include pain in the groin area or hip, clicking or popping in the hip joint, stiffness, and decreased range of motion. These symptoms may be worsened by certain activities, such as twisting or pivoting.
Diagnosis of a hip labral tear may involve a physical exam, imaging studies such as an MRI or CT scan, and possibly an arthroscopy (a minimally invasive surgical procedure) to visualize and repair the tear.
Treatment for a hip labral tear may include rest, physical therapy, and medications to manage pain and inflammation. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or remove the torn labrum.
Prevention of a hip labral tear may involve taking measures to reduce stress on the hip joint, such as proper warm-up and cool-down before exercise, and avoiding repetitive activities that strain the hip joint.
If you are experiencing symptoms of a hip labral tear, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the cause of your symptoms and the appropriate treatment.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Hip joint disease
- Groin pain or hip pain
Disease Causes
Hip labral tear
The cause of a hip labral tear might be:
- Trauma. Injury to or dislocation of the hip joint — which can occur during car accidents or from playing contact sports such as football or hockey — can cause a hip labral tear.
- Structural problems. Some people are born with hip issues that can accelerate wear and tear of the joint and eventually cause a hip labral tear. This can include having a socket that doesn't fully cover the ball portion of the upper thigh bone (dysplasia) or a shallow socket, which can put more stress on the labrum.
- Extra bone in the hip, called femoroacetabular impingement (FAI), can also cause pinching of the labrum, which can lead to tearing over time.
- Repetitive motions. Sports-related and other physical activities — including long-distance running and the sudden twisting or pivoting motions common in golf or softball — can lead to joint wear and tear that ultimately result in a hip labral tear.
Disease Prevents
Hip labral tear
If the sports you play put a lot of strain on your hips, condition the surrounding muscles with strength and flexibility exercises.
Disease Treatments
Treatment depends on how severe your symptoms are. Some people recover in a few weeks with conservative treatments, including rest and modified activities; others need arthroscopic surgery to repair the torn portion of the labrum.
Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve), can relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Pain can also be controlled temporarily with an injection of corticosteroids into the joint.
Therapy
A physical therapist can teach you exercises to increase your hip's range of motion and build hip and core strength and stability. Therapists can also teach you to avoid movements that put stress on your hip joint.
Surgical and other procedures
If conservative treatments don't relieve your symptoms, your health care provider might recommend arthroscopic surgery — in which a fiber-optic camera and surgical tools are inserted via small incisions in your skin.
Depending on the cause and extent of the tear, the surgeon might remove the torn piece of labrum or repair the torn tissue by sewing it back together.
Complications of surgery can include infection, bleeding, nerve injury and recurrent symptoms if the repair doesn't heal properly. A return to sports usually takes 3-6 months.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Hip labral tear and Learn More about Diseases

Broken hand

Trichotillomania (hair-pulling disorder)
Kidney stones

Cold sore

Intermittent explosive disorder

Klinefelter syndrome

Hypothermia
Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors
hip labral tear, হিপ ল্যাব্রাল টিয়ার
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.