Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Hairy cell leukemia
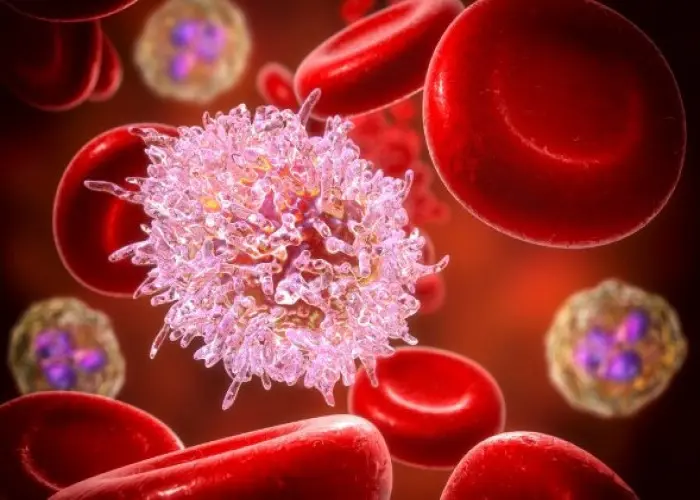
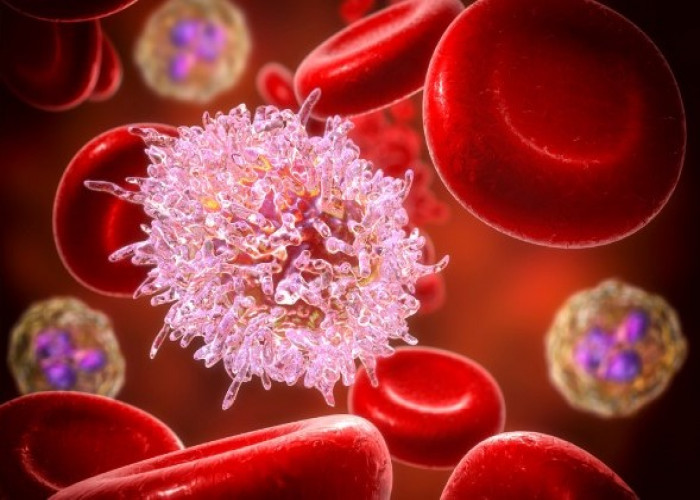
Hairy cell leukemia (HCL) is a rare type of cancer that affects the white blood cells, specifically the B cells. It is called "hairy cell" leukemia because the cancer cells have small hair-like projections on their surface when viewed under a microscope.
The cause of HCL is not well understood, but it is thought to be related to a genetic mutation that causes the abnormal growth and accumulation of hairy cells in the bone marrow and blood. HCL can also spread to the spleen, liver, and other organs.
Symptoms of HCL can include weakness, fatigue, fever, night sweats, and frequent infections, as well as an enlarged spleen and liver. HCL is often diagnosed through blood tests, bone marrow biopsy, and imaging studies.
Treatment for HCL may involve medications, such as interferon alpha and cladribine, which can help kill the abnormal cells and slow the progression of the disease. In some cases, a splenectomy (surgical removal of the spleen) may also be recommended. Stem cell transplantation may be considered for patients who do not respond to initial treatment or for those with advanced disease.
The prognosis for HCL is generally good, with many patients responding well to treatment and achieving long-term remission. However, regular follow-up and monitoring are recommended to detect any signs of relapse or progression of the disease.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Excessive bruising
- Frequent infections
- Weakness
- Weight loss
Disease Causes
Hairy cell leukemia
It's not clear what causes hairy cell leukemia.
Doctors know that cancer occurs when cells develop errors (mutations) in their DNA. In the case of hairy cell leukemia, mutations in the DNA cause your bone marrow stem cells to create too many white blood cells that don't work properly. Doctors don't know what causes the DNA mutations that lead to hairy cell leukemia.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
It's not always necessary to start treatment for hairy cell leukemia immediately after the diagnosis is confirmed. Because this cancer progresses very slowly and sometimes doesn't progress at all, treatment can be delayed.
You'll have regular follow-up appointments with your doctor to monitor for progression of the hairy cell leukemia. If you experience signs and symptoms of the cancer, you may decide to undergo treatment. The majority of people with hairy cell leukemia eventually need treatment.
There is no cure for hairy cell leukemia. But treatments are effective at putting hairy cell leukemia in remission for years.
Chemotherapy
Doctors consider chemotherapy drugs the first line of treatment for hairy cell leukemia. A great majority of people will experience complete or partial remission through the use of chemotherapy.
Two chemotherapy drugs are used in hairy cell leukemia:
- Cladribine. Treatment for hairy cell leukemia typically begins with cladribine. You may receive either a continuous infusion of the drug or daily injections into a vein over several days.
- Most people who receive cladribine experience a complete remission that can last for several years. If your hairy cell leukemia returns, you can be treated with cladribine again. Side effects of cladribine may include infection and fever.
- Pentostatin. Pentostatin (Nipent) causes remission rates similar to cladribine, but it's given on a different schedule. People who take pentostatin receive infusions every other week for three to six months. Side effects of pentostatin may include fever, nausea and infection.
Biological treatments
Biological therapy attempts to make cancer cells more recognizable to your immune system. Once your immune system identifies cancer cells as intruders, it can set about destroying your cancer.
Two types of biological treatments are used in hairy cell leukemia:
- Rituximab. Rituximab (Rituxan) is a monoclonal antibody approved to treat non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia, though it's sometimes used in hairy cell leukemia.
- If chemotherapy drugs haven't worked for you or you can't take chemotherapy, your doctor might consider rituximab. You doctor may also combine cladribine and rituximab. Side effects of rituximab include fever and infection.
- Interferon. Currently, the role of interferon in hairy cell leukemia treatment is limited. You might receive interferon if chemotherapy hasn't been effective or if you can't take chemotherapy.
- Most people experience partial remission with interferon, which is taken for a year. Side effects include flu-like symptoms, such as fever and fatigue.
Other drugs that target the immune system may be recommended if your cancer returns or if it doesn't respond to standard treatments. Clinical trials are studying new biological therapies and targeted therapies for treating hairy cell leukemia.
Surgery
Surgery to remove your spleen (splenectomy) might be an option if your spleen ruptures or if it's enlarged and causing pain. Though removing your spleen can't cure hairy cell leukemia, it can usually restore normal blood counts.
Splenectomy isn't commonly used to treat hairy cell leukemia, but it may be helpful in certain situations. Any surgery carries a risk of bleeding and infection.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Hairy cell leukemia and Learn More about Diseases
Neurodermatitis
Dilated cardiomyopathy
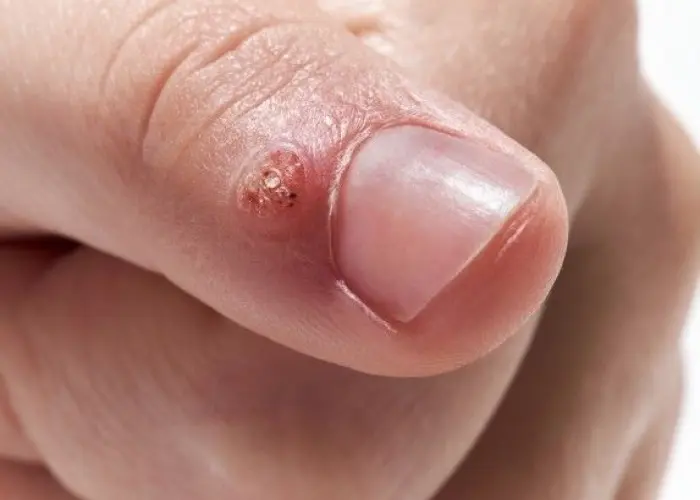
HPV infection
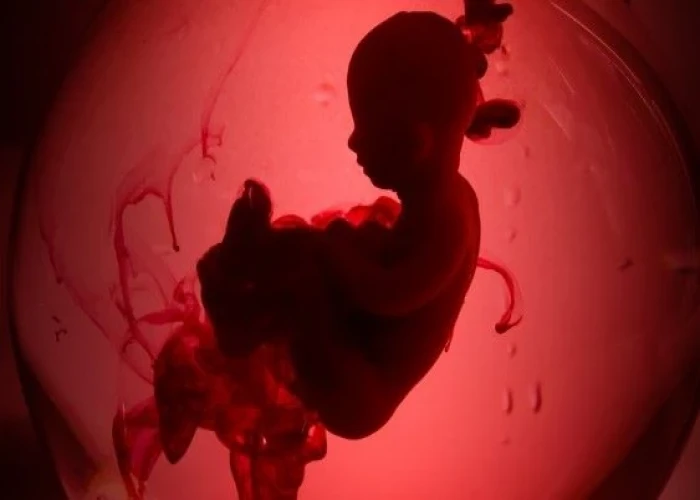
Miscarriage (Abortion)
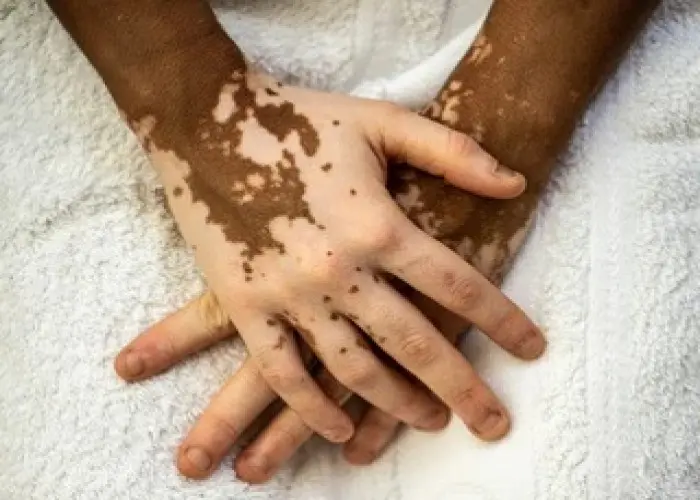

Albinism
Neuroendocrine tumors
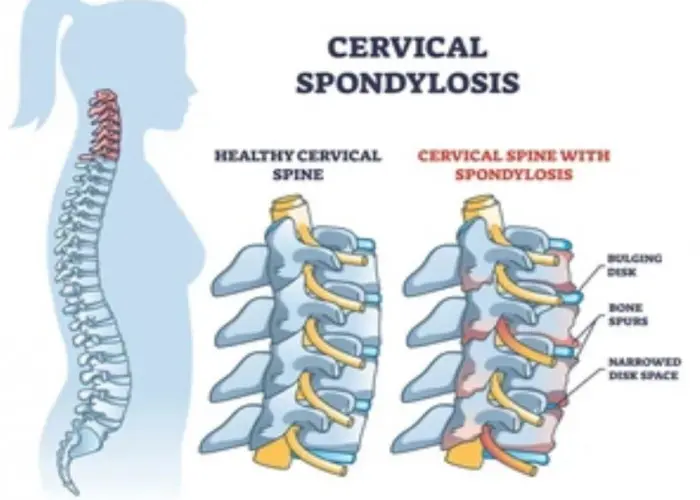
Cervical spondylosis
Folliculitis
hairy cell leukemia, হেয়ার সেল লিউকেমিয়া
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.