 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Gingivitis
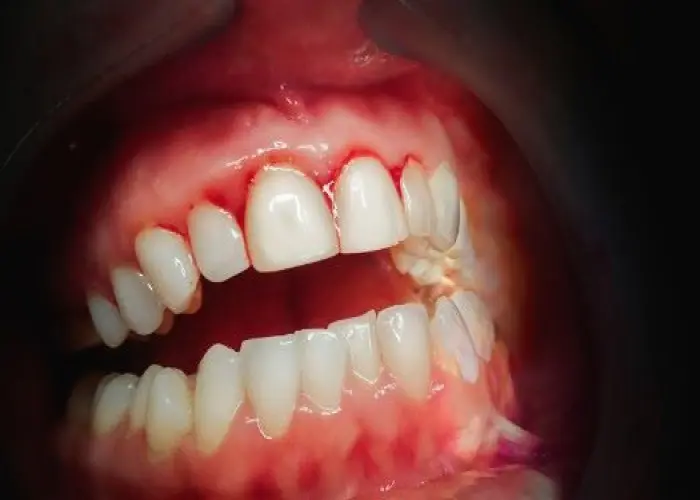
Gingivitis is a common form of gum disease that causes inflammation and irritation of the gums. It is usually caused by a buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth and gums. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to a more serious form of gum disease called periodontitis, which can lead to tooth loss and other complications.
Symptoms of gingivitis may include redness, swelling, tenderness, and bleeding of the gums, especially during brushing or flossing. Bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth may also be present.
Prevention and treatment of gingivitis involve good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing and flossing regularly and using an antiseptic mouthwash. Regular dental checkups and professional cleanings are also important to remove any plaque or tartar buildup and to monitor the health of the gums.
If left untreated, gingivitis can lead to more serious complications, including periodontitis and tooth loss. In some cases, it can also increase the risk of other health problems, such as heart disease, stroke, and respiratory infections.
If you suspect you have gingivitis, it is important to see a dentist for a proper diagnosis and treatment. With proper care and treatment, most cases of gingivitis can be reversed and the health of the gums can be restored.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Swollen gums
- Dark red gums
- Bleeding from gums
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- Tender gums
- Gums that bleed easily when you brush or floss
Disease Causes
Gingivitis
The most common cause of gingivitis is poor oral hygiene that encourages plaque to form on teeth, causing inflammation of the surrounding gum tissues. Here's how plaque can lead to gingivitis:
- Plaque forms on your teeth. Plaque is an invisible, sticky film composed mainly of bacteria that forms on your teeth when starches and sugars in food interact with bacteria normally found in your mouth. Plaque requires daily removal because it re-forms quickly.
- Plaque turns into tartar. Plaque that stays on your teeth can harden under your gumline into tartar (calculus), which collects bacteria. Tartar makes plaque more difficult to remove, creates a protective shield for bacteria and causes irritation along the gumline. You need professional dental cleaning to remove tartar.
- Gingiva become inflamed (gingivitis). The longer that plaque and tartar remain on your teeth, the more they irritate the gingiva, the part of your gum around the base of your teeth, causing inflammation. In time, your gums become swollen and bleed easily. Tooth decay (dental caries) also may result. If not treated, gingivitis can advance to periodontitis and eventual tooth loss.
Disease Prevents
Gingivitis
- Good oral hygiene. That means brushing your teeth for two minutes at least twice daily — in the morning and before going to bed — and flossing at least once a day. Better yet, brush after every meal or snack or as your dentist recommends. Flossing before you brush allows you to clean away the loosened food particles and bacteria.
- Regular dental visits. See your dentist or dental hygienist regularly for cleanings, usually every six to 12 months. If you have risk factors that increase your chance of developing periodontitis — such as having dry mouth, taking certain medications or smoking — you may need professional cleaning more often. Annual dental X-rays can help identify diseases that are not seen by a visual dental examination and monitor for changes in your dental health.
- Good health practices. Practices such as healthy eating and managing blood sugar if you have diabetes also are important to maintain gum health.
Disease Treatments
Prompt treatment usually reverses symptoms of gingivitis and prevents its progression to more serious gum disease and tooth loss. You have the best chance for successful treatment when you also adopt a daily routine of good oral care and stop tobacco use.
Professional gingivitis care includes:
- Professional dental cleaning. Your initial professional cleaning will include removing all traces of plaque, tartar and bacterial products — a procedure known as scaling and root planing. Scaling removes tartar and bacteria from your tooth surfaces and beneath your gums. Root planning removes the bacterial products produced by inflammation, smooths the root surfaces, discouraging further buildup of tartar and bacteria, and allows proper healing. The procedure may be performed using instruments, a laser or an ultrasonic device.
- Dental restoration, if needed. Misaligned teeth or poorly fitting crowns, bridges or other dental restorations may irritate your gums and make it harder to remove plaque during daily oral care. If problems with your teeth or dental restorations contribute to your gingivitis, your dentist may recommend fixing these problems.
- Ongoing care. Gingivitis usually clears up after a thorough professional cleaning — as long as you continue good oral hygiene at home. Your dentist will help you plan an effective at-home program and a schedule of regular professional checkups and cleaning.
If you're consistent with your home oral hygiene, you should see the return of pink, healthy gum tissue within days or weeks.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Gingivitis and Learn More about Diseases
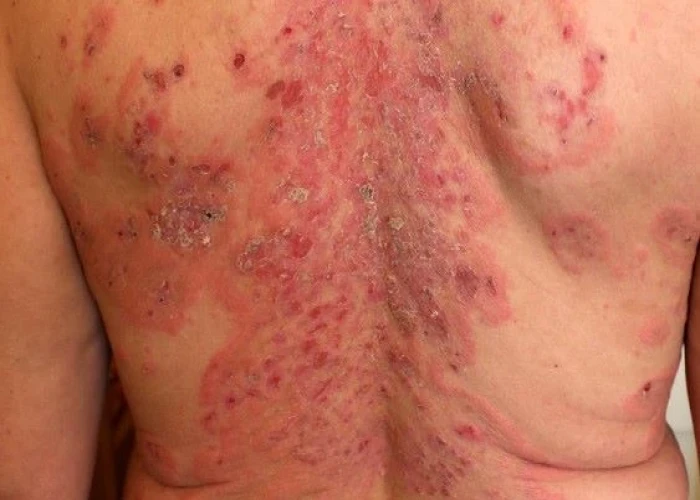
Pemphigus
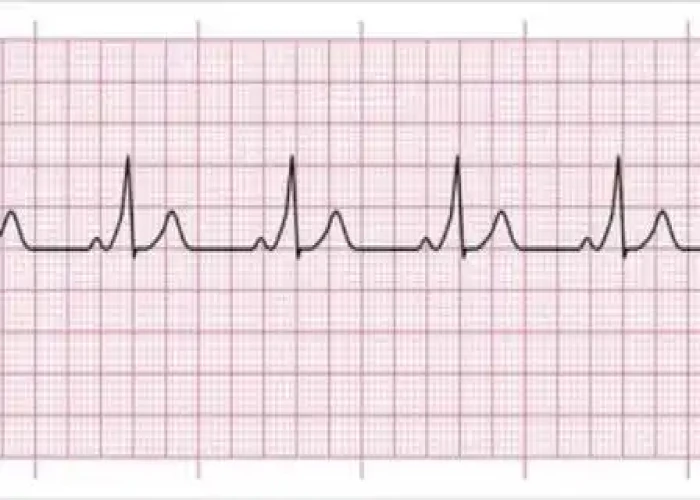
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome

Vascular dementia
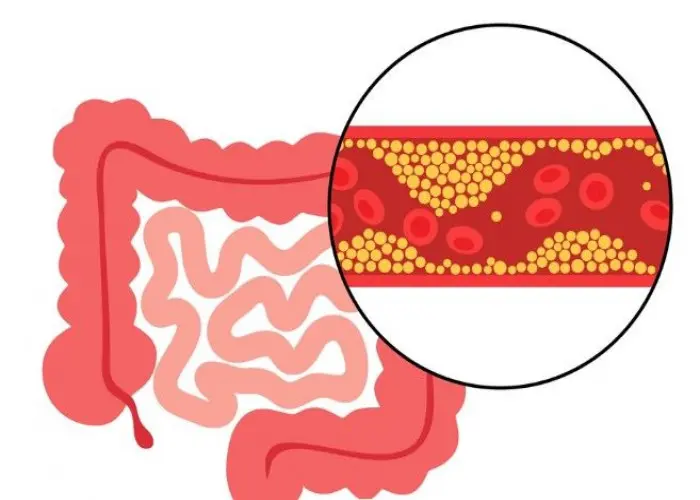
Intestinal ischemia
Posterior vaginal prolapse (Rectocele)

Toothache
Ataxia
Coronary artery disease
gingivitis, জিংজিভাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
