Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Granuloma annulare
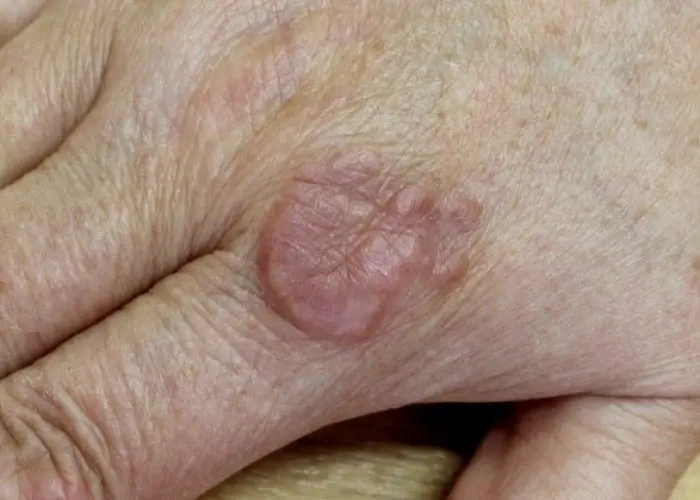
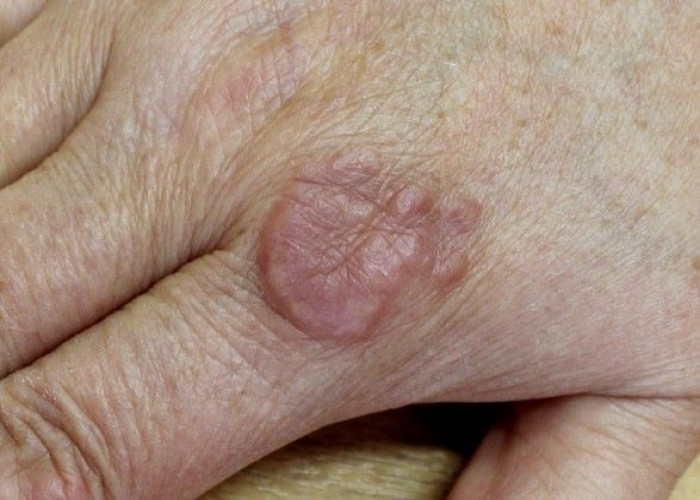
Granuloma annular is a chronic skin condition that causes small, raised, reddish or skin-colored bumps that form rings on the skin. The condition can occur anywhere on the body but is most commonly found on the hands, feet, wrists, and ankles.
The exact cause of granuloma annulare is unknown, but it is thought to be related to a dysfunction in the immune system. The condition is not contagious and is not associated with any other health conditions.
Granuloma annulare is typically painless and does not cause any other symptoms, although some people may experience mild itching or burning. In most cases, the condition will resolve on its own without treatment, although this can take several months or even years.
For those who seek treatment, topical or oral steroids, cryotherapy, or phototherapy may be recommended to reduce inflammation and speed up the healing process. In some cases, other medications, such as retinoids or immune-suppressing drugs, may be prescribed.
While granuloma annulare is not harmful, it can be unsightly and may cause concern for those affected. If you suspect you may have granuloma annulare, it is important to see a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and to discuss treatment options.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Skin bumps
- Skin lesions
- Skin rash
Disease Causes
Granuloma annulare
It's not clear what causes granuloma annulare. Sometimes it's triggered by:
- Animal or insect bites
- Infections, such as hepatitis
- Tuberculin skin tests
- Vaccinations
- Sun exposure
- Minor skin injuries
- Drugs
Granuloma annulare is not contagious.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Granuloma annulare can clear on its own over time. Treatment might help clear the skin faster than if left untreated, but recurrence is common. The lesions that return after treatment tend to appear at the same spots, and 80% of those usually clear within two years.
Untreated, the lesions might last a few weeks or decades.
Treatment options include:
- Corticosteroid creams or ointments. Prescription-strength products may help improve the appearance of the bumps and help them disappear faster. Your doctor may direct you to cover the cream with bandages or an adhesive patch, to increase the effectiveness of this treatment.
- Corticosteroid injections. If the skin lesions aren't clearing up with topical treatment, your doctor may suggest a corticosteroid injection. Repeat injections may be needed every 6 to 8 weeks until the condition clears up.
- Freezing. Applying liquid nitrogen to the affected area may help remove the lesions.
- Light therapy. Exposing the lesions to certain types of light, including lasers, is sometimes helpful.
- Oral medications. When the lesions are widespread, your doctor might prescribe drugs taken by mouth, such as antibiotics, antimalarials or drugs used to prevent immune system reactions.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Granuloma annulare and Learn More about Diseases
Filaria
Seborrheic keratosis

Orthostatic hypotension (postural hypotension)

Menopause
Diabetic nephropathy
Oral lichen planus

Systemic capillary leak syndrome

Narcissistic personality disorder
granuloma annulare, গ্রানুলোমা অ্যানুলার
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.