Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
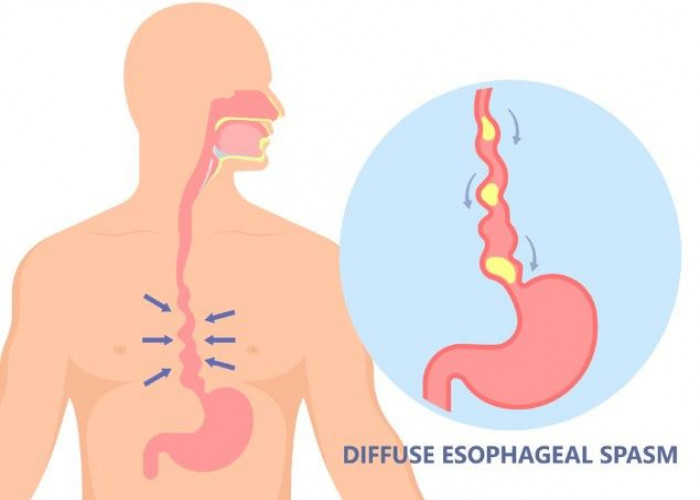
Esophageal spasms

Esophageal spasms are sudden, involuntary contractions of the muscles in the esophagus, the muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. These spasms can cause chest pain, difficulty swallowing, and a feeling of tightness or constriction in the chest. The exact cause of esophageal spasms is not fully understood, but certain factors can trigger or worsen symptoms, including hot or cold foods or drinks, acid reflux, and anxiety.
Esophageal spasms can be diagnosed through tests such as an upper endoscopy or esophageal manometry, which measures the pressure in the esophagus during swallowing. Treatment options may include medications to relax the esophagus, such as nitrates or calcium channel blockers, as well as botulinum toxin injections or surgery in more severe cases.
In addition to medical treatment, making certain lifestyle changes may also help reduce symptoms of esophageal spasms. These can include avoiding trigger foods or drinks, eating smaller, more frequent meals, and managing stress and anxiety. If acid reflux is present, treating this condition may also help reduce symptoms of esophageal spasms.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Chest pain
- Heart pain (Angina)
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Backflow of undigested food (regurgitation)
- The feeling that an object is stuck in the throat
Disease Causes
Esophageal spasms
It's not clear what causes esophageal spasms. However, they appear to be related to abnormal functioning of nerves that control the muscles you use when you swallow.
A healthy esophagus normally moves food into your stomach through a series of coordinated muscle contractions. Esophageal spasms make it difficult for the muscles in the walls of your lower esophagus to coordinate in order to move food to your stomach.
There are two types of esophageal spasms — distal esophageal spasm and hypercontractile esophagus, also referred to as jackhammer esophagus.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Treatment depends on the frequency and severity of your esophageal spasms.
If your spasms are occasional, your doctor might first recommend avoiding extremely hot or cold foods to see if that relieves your symptoms.
If your spasms make it difficult to eat or drink, your doctor might recommend:
- Managing any underlying conditions. Esophageal spasms are sometimes associated with conditions such as heartburn or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Your doctor might recommend a proton pump inhibitor to treat GERD, or an antidepressant, such as imipramine (Tofranil), which may help reduce the sensation of pain in the esophagus.
- Medications to relax your swallowing muscles. Peppermint oil, onabotulinumtoxin A (Botox) injections or calcium channel blockers, such as diltiazem (Cardizem, Tiazac, others), can reduce the severity of spasms.
- Surgery (myotomy). If medication doesn't work, your doctor might recommend a procedure that involves cutting the muscle at the lower end of the esophagus to weaken esophageal contractions. Long-term studies of this approach aren't available, so myotomy generally isn't recommended for esophageal spasms. However, it might be considered if other treatments don't work.
- Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM). In this new minimally invasive technique, an endoscope inserted through your mouth and down your throat allows a surgeon to make an incision in the inside lining of your esophagus. Then, as in standard myotomy, the surgeon cuts the muscle at the lower end of the esophagus. Like standard myotomy, POEM is usually considered only if other treatments don't work.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Esophageal spasms and Learn More about Diseases

Movement disorders

Precocious puberty
Placenta previa
Rectal cancer

Common variable immunodeficiency
Neurodermatitis

Cavernous malformations
Postpartum preeclampsia
esophageal spasms, এসোফিজিয়াল স্প্যামস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.