Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Diabetes
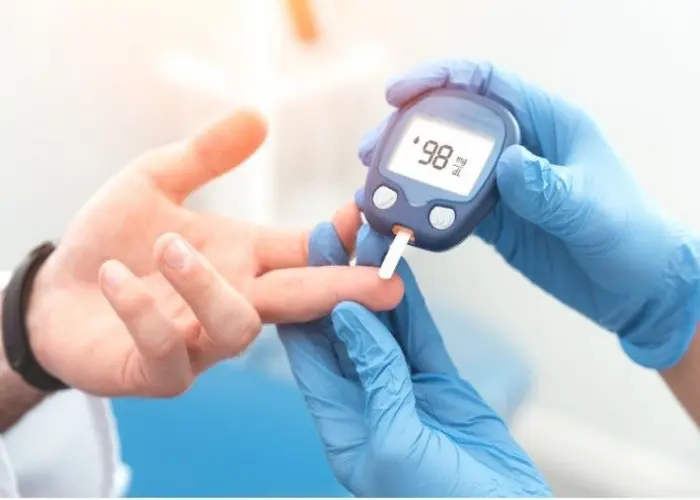
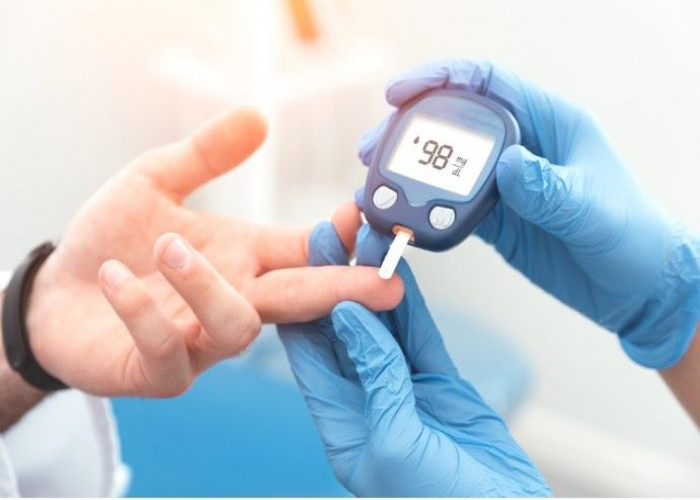
Diabetes is a chronic disease characterized by high levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. It is caused by the body's inability to produce or use insulin, a hormone that regulates the amount of glucose in the bloodstream. There are several types of diabetes, including type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This type of diabetes typically develops in childhood or adolescence and requires lifelong insulin therapy.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for approximately 90% of all cases. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels. Type 2 diabetes is often linked to obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, and poor dietary choices.
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy. It usually develops in the second or third trimester and typically goes away after the baby is born. Women who have had gestational diabetes are at higher risk for developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Symptoms of diabetes may include frequent urination, excessive thirst, hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts or wounds. If left untreated, diabetes can lead to serious complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and blindness.
The diagnosis of diabetes is typically made through a blood test that measures glucose levels. Treatment for diabetes involves managing blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and medication (such as insulin or oral medications). Lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, quitting smoking, and reducing stress, can also help manage diabetes.
Preventing diabetes involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and maintaining a healthy weight. Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources can help prevent or manage diabetes.
In conclusion, diabetes is a chronic disease that requires lifelong management. Proper diagnosis, treatment, and lifestyle changes can help prevent or manage this condition and reduce the risk of serious complications. If you are experiencing symptoms of diabetes, speak with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate course of action.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent infections, such as gums or skin infections and vaginal infections
- Frequent infections
- Blurred vision of eye
- Irritability
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Weight loss
- Extreme hunger
- Frequent urination
- Diabetes
Disease Causes
Diabetes
To understand diabetes, first you must understand how glucose is normally processed in the body.
How insulin works
Insulin is a hormone that comes from a gland situated behind and below the stomach (pancreas).
- The pancreas secretes insulin into the bloodstream.
- The insulin circulates, enabling sugar to enter your cells.
- Insulin lowers the amount of sugar in your bloodstream.
- As your blood sugar level drops, so does the secretion of insulin from your pancreas.
The role of glucose
Glucose — a sugar — is a source of energy for the cells that make up muscles and other tissues.
- Glucose comes from two major sources: food and your liver.
- Sugar is absorbed into the bloodstream, where it enters cells with the help of insulin.
- Your liver stores and makes glucose.
- When your glucose levels are low, such as when you haven't eaten in a while, the liver breaks down stored glycogen into glucose to keep your glucose level within a normal range.
Causes of type 1 diabetes
The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is unknown. What is known is that your immune system — which normally fights harmful bacteria or viruses — attacks and destroys your insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This leaves you with little or no insulin. Instead of being transported into your cells, sugar builds up in your bloodstream.
Type 1 is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic susceptibility and environmental factors, though exactly what those factors are is still unclear. Weight is not believed to be a factor in type 1 diabetes.
Causes of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes
In prediabetes — which can lead to type 2 diabetes — and in type 2 diabetes, your cells become resistant to the action of insulin, and your pancreas is unable to make enough insulin to overcome this resistance. Instead of moving into your cells where it's needed for energy, sugar builds up in your bloodstream.
Exactly why this happens is uncertain, although it's believed that genetic and environmental factors play a role in the development of type 2 diabetes too. Being overweight is strongly linked to the development of type 2 diabetes, but not everyone with type 2 is overweight.
Causes of gestational diabetes
During pregnancy, the placenta produces hormones to sustain your pregnancy. These hormones make your cells more resistant to insulin.
Normally, your pancreas responds by producing enough extra insulin to overcome this resistance. But sometimes your pancreas can't keep up. When this happens, too little glucose gets into your cells and too much stays in your blood, resulting in gestational diabetes.
Disease Prevents
Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes can't be prevented. However, the same healthy lifestyle choices that help treat prediabetes, type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes can also help prevent them:
- Eat healthy foods. Choose foods lower in fat and calories and higher in fiber. Focus on fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Strive for variety to prevent boredom.
- Get more physical activity. Aim for about 30 minutes of moderate aerobic activity on most days of the week, or at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity a week.
- Lose excess pounds. If you're overweight, losing even 7% of your body weight — for example, 14 pounds (6.4 kilograms) if you weigh 200 pounds (90.7 kilograms) — can reduce the risk of diabetes.
- Don't try to lose weight during pregnancy, however. Talk to your doctor about how much weight is healthy for you to gain during pregnancy.
- To keep your weight in a healthy range, focus on permanent changes to your eating and exercise habits. Motivate yourself by remembering the benefits of losing weight, such as a healthier heart, more energy and improved self-esteem.
Sometimes medication is an option as well. Oral diabetes drugs such as metformin (Glumetza, Fortamet, others) may reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes — but healthy lifestyle choices remain essential. Have your blood sugar checked at least once a year to check that you haven't developed type 2 diabetes.
Disease Treatments
Depending on what type of diabetes you have, blood sugar monitoring, insulin and oral medications may play a role in your treatment. Eating a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight and participating in regular activity also are important factors in managing diabetes.
Treatments for all types of diabetes
An important part of managing diabetes — as well as your overall health — is maintaining a healthy weight through a healthy diet and exercise plan:
- Healthy eating. Contrary to popular perception, there's no specific diabetes diet. You'll need to center your diet on more fruits, vegetables, lean proteins and whole grains — foods that are high in nutrition and fiber and low in fat and calories — and cut down on saturated fats, refined carbohydrates and sweets. In fact, it's the best eating plan for the entire family. Sugary foods are OK once in a while, as long as they're counted as part of your meal plan.
- Yet, understanding what and how much to eat can be a challenge. A registered dietitian can help you create a meal plan that fits your health goals, food preferences and lifestyle. This will likely include carbohydrate counting, especially if you have type 1 diabetes or use insulin as part of your treatment.
- Physical activity. Everyone needs regular aerobic exercise, and people who have diabetes are no exception. Exercise lowers your blood sugar level by moving sugar into your cells, where it's used for energy. Exercise also increases your sensitivity to insulin, which means your body needs less insulin to transport sugar to your cells.
- Get your doctor's OK to exercise. Then choose activities you enjoy, such as walking, swimming or biking. What's most important is making physical activity part of your daily routine.
- Aim for at least 30 minutes or more of aerobic exercise most days of the week, or at least 150 minutes of moderate physical activity a week. Bouts of activity can be as brief as 10 minutes, three times a day. If you haven't been active for a while, start slowly and build up gradually. It's also a good idea to avoid sitting for too long — aim to get up and move if you've been sitting for more than 30 minutes.
Treatments for type 1 and type 2 diabetes
Treatment for type 1 diabetes involves insulin injections or the use of an insulin pump, frequent blood sugar checks, and carbohydrate counting. Treatment of type 2 diabetes primarily involves lifestyle changes, monitoring of your blood sugar, along with diabetes medications, insulin or both.
- Monitoring your blood sugar. Depending on your treatment plan, you may check and record your blood sugar as many as four times a day or more often if you're taking insulin. Careful monitoring is the only way to make sure that your blood sugar level remains within your target range. People with type 2 diabetes who aren't taking insulin generally check their blood sugar much less frequently.
- People who receive insulin therapy also may choose to monitor their blood sugar levels with a continuous glucose monitor. Although this technology hasn't yet completely replaced the glucose meter, it can significantly reduce the number of fingersticks necessary to check blood sugar and provide important information about trends in blood sugar levels.
- Even with careful management, blood sugar levels can sometimes change unpredictably. With help from your diabetes treatment team, you'll learn how your blood sugar level changes in response to food, physical activity, medications, illness, alcohol, stress — and for women, fluctuations in hormone levels.
- In addition to daily blood sugar monitoring, your doctor will likely recommend regular A1C testing to measure your average blood sugar level for the past two to three months.
- Compared with repeated daily blood sugar tests, A1C testing better indicates how well your diabetes treatment plan is working overall. An elevated A1C level may signal the need for a change in your oral medication, insulin regimen or meal plan.
- Your target A1C goal may vary depending on your age and various other factors, such as other medical conditions you may have. However, for most people with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends an A1C of below 7%. Ask your doctor what your A1C target is.
- Insulin. People with type 1 diabetes need insulin therapy to survive. Many people with type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes also need insulin therapy.
- Many types of insulin are available, including short-acting (regular insulin), rapid-acting insulin, long-acting insulin and intermediate options. Depending on your needs, your doctor may prescribe a mixture of insulin types to use throughout the day and night.
- Insulin can't be taken orally to lower blood sugar because stomach enzymes interfere with insulin's action. Often insulin is injected using a fine needle and syringe or an insulin pen — a device that looks like a large ink pen.
- An insulin pump also may be an option. The pump is a device about the size of a small cellphone worn on the outside of your body. A tube connects the reservoir of insulin to a catheter that's inserted under the skin of your abdomen.
- A tubeless pump that works wirelessly is also now available. You program an insulin pump to dispense specific amounts of insulin. It can be adjusted to deliver more or less insulin depending on meals, activity level and blood sugar level.
- In September 2016, the Food and Drug Administration approved the first artificial pancreas for people with type 1 diabetes who are age 14 and older. A second artificial pancreas was approved in December 2019. Since then systems have been approved for children older than 2 years old.
- An artificial pancreas is also called closed-loop insulin delivery. The implanted device links a continuous glucose monitor, which checks blood sugar levels every five minutes, to an insulin pump. The device automatically delivers the correct amount of insulin when the monitor indicates it's needed.
- There are more artificial pancreas (closed loop) systems currently in clinical trials.
- Oral or other medications. Sometimes other oral or injected medications are prescribed as well. Some diabetes medications stimulate your pancreas to produce and release more insulin. Others inhibit the production and release of glucose from your liver, which means you need less insulin to transport sugar into your cells.
- Still others block the action of stomach or intestinal enzymes that break down carbohydrates or make your tissues more sensitive to insulin. Metformin (Glumetza, Fortamet, others) is generally the first medication prescribed for type 2 diabetes.
- Another class of medication called SGLT2 inhibitors may be used. They work by preventing the kidneys from reabsorbing sugar into the blood. Instead, the sugar is excreted in the urine.
- Transplantation. In some people who have type 1 diabetes, a pancreas transplant may be an option. Islet transplants are being studied as well. With a successful pancreas transplant, you would no longer need insulin therapy.
- But transplants aren't always successful — and these procedures pose serious risks. You need a lifetime of immune-suppressing drugs to prevent organ rejection. These drugs can have serious side effects, which is why transplants are usually reserved for people whose diabetes can't be controlled or those who also need a kidney transplant.
- Bariatric surgery. Although it is not specifically considered a treatment for type 2 diabetes, people with type 2 diabetes who are obese and have a body mass index higher than 35 may benefit from this type of surgery. People who've undergone gastric bypass have seen significant improvements in their blood sugar levels. However, this procedure's long-term risks and benefits for type 2 diabetes aren't yet known.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Glibenclamide
Take half or 1 pill every morning between breakfast.
-
Glipizide
Initially half a pill to 1 pill daily with breakfast. Thus the maximum dose can be given up to 160 mg (2 pills) in the morning.
-
Acarbose
500mg 1+1+1 (6-8 weeks) before food intake can be increased if not effective.
-
Nateglinide
The usual dose is 1 tablet of 120 mg before meals, alone or in combination with metformin.
-
Metformin Hydrochloride
Metformin Hcl of the bigunamide class when sulfonylureas cannot be given or are ineffective in obese diabetic patients.
Starting dose is 1+0+1 (500mg) or 850mg 1 time a day with food. It can be given as an adjunct to any other medicine.
-
Vitamin B complex
2cc medicine should be injected into the flesh after 1 day.
- Vitamin B1, B2 & B6
- Antioxidants and Micronutrients
- Super Antioxidant, Vitamins & Multimineral
- Biphasic Insulin Aspart [rDNA]
- Insulin Aspart
- Insulin Degludec
- Insulin Degludec + Insulin Aspart Premixed
- Insulin Glargine [rDNA]
- Insulin Glulisine
- Insulin Human [Long-Acting]
- Insulin Human [rDNA] + Isophane Insulin Human
- Insulin Lispro
- Insulin Lispro Protamine + Insulin Lispro
- Protamine Crystallised Insulin Aspart
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
-
Lactic acid
3, 6, 30 power.
-
Arsenicum bromatum
Q power.
-
Kreosotum
6, 30 strength.
-
Syzygium jambolanum
1X strength.
-
Acidum phosphoricum
30 strength.
-
Uranium nitricum
3X strength.
-
Argentum metallicum
3X strength.
-
Ammonium aceticum
6, 30 strength.
-
Acid aceticum
6, 30 strength.
-
Insulin
3X strength.
-
Cantharis
6, 30, 200 power.
-
Helonias
Q power.
Disease yoga
Diabetes and Learn More about Diseases

Intermittent explosive disorder
Pseudocholinesterase deficiency

Antiphospholipid syndrome
Burning mouth syndrome

Low blood pressure (hypotension)

Polymyositis
Hairy cell leukemia
Eye melanoma
diabetes, বহুমুত্র
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.