 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Cataracts
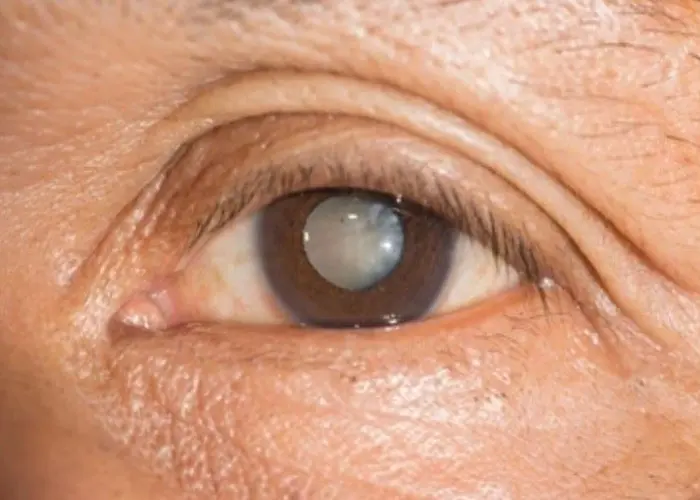
Cataracts are a common eye condition that causes clouding of the natural lens of the eye, which can affect vision. The clouding is caused by changes in the proteins in the lens that occur as a part of the normal aging process. Other risk factors for cataracts include genetics, certain medical conditions such as diabetes, and prolonged exposure to sunlight or radiation. Symptoms of cataracts may include blurred vision, sensitivity to light, and difficulty seeing at night. Treatment for cataracts usually involves surgery to remove the cloudy lens and replace it with an artificial lens. Cataract surgery is a safe and effective procedure that can improve vision and quality of life for people with cataracts. It is important to work with your eye doctor to monitor changes in your vision and develop a personalized treatment plan for cataracts.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Eye pain or burning
- Weakness, numbness, difficulty speaking, difficulty understanding others, unsteadiness, vision changes or severe headache.
- It clouds the lens and distorts the light passing through the lens.
- Frequent changes in eyeglass or contact lens prescription
- Need for brighter light for reading and other activities
- Double vision (diplopia)
- Seeing halos around lights
- Difficulty with night vision
- Blurred vision of eye
- Cataracts
Disease Causes
Cataracts
Most cataracts develop when aging or injury changes the tissue that makes up the eye's lens. Proteins and fibers in the lens begin to break down, causing vision to become hazy or cloudy.
Some inherited genetic disorders that cause other health problems can increase your risk of cataracts. Cataracts can also be caused by other eye conditions, past eye surgery or medical conditions such as diabetes. Long-term use of steroid medications, too, can cause cataracts to develop.
How a cataract forms
A cataract is a cloudy lens. The lens is positioned behind the colored part of your eye (iris). The lens focuses light that passes into your eye, producing clear, sharp images on the retina — the light-sensitive membrane in the eye that functions like the film in a camera.
As you age, the lenses in your eyes become less flexible, less transparent and thicker. Age-related and other medical conditions cause proteins and fibers within the lenses to break down and clump together, clouding the lenses.
As the cataract continues to develop, the clouding becomes denser. A cataract scatters and blocks the light as it passes through the lens, preventing a sharply defined image from reaching your retina. As a result, your vision becomes blurred.
Cataracts generally develop in both eyes, but not always at the same rate. The cataract in one eye may be more advanced than the other, causing a difference in vision between eyes.
Types of cataracts
Cataract types include:
- Cataracts affecting the center of the lens (nuclear cataracts). A nuclear cataract may at first cause more nearsightedness or even a temporary improvement in your reading vision. But with time, the lens gradually turns more densely yellow and further clouds your vision.
- As the cataract slowly progresses, the lens may even turn brown. Advanced yellowing or browning of the lens can lead to difficulty distinguishing between shades of color.
- Cataracts that affect the edges of the lens (cortical cataracts). A cortical cataract begins as whitish, wedge-shaped opacities or streaks on the outer edge of the lens cortex. As it slowly progresses, the streaks extend to the center and interfere with light passing through the center of the lens.
- Cataracts that affect the back of the lens (posterior subcapsular cataracts). A posterior subcapsular cataract starts as a small, opaque area that usually forms near the back of the lens, right in the path of light. A posterior subcapsular cataract often interferes with your reading vision, reduces your vision in bright light, and causes glare or halos around lights at night. These types of cataracts tend to progress faster than other types do.
- Cataracts you're born with (congenital cataracts). Some people are born with cataracts or develop them during childhood. These cataracts may be genetic, or associated with an intrauterine infection or trauma.
- These cataracts may also be due to certain conditions, such as myotonic dystrophy, galactosemia, neurofibromatosis type 2 or rubella. Congenital cataracts don't always affect vision, but if they do, they're usually removed soon after detection.
Disease Prevents
Cataracts
No studies have proved how to prevent cataracts or slow the progression of cataracts. But doctors think several strategies may be helpful, including:
- Have regular eye examinations. Eye examinations can help detect cataracts and other eye problems at their earliest stages. Ask your doctor how often you should have an eye examination.
- Quit smoking. Ask your doctor for suggestions about how to stop smoking. Medications, counseling and other strategies are available to help you.
- Manage other health problems. Follow your treatment plan if you have diabetes or other medical conditions that can increase your risk of cataracts.
- Choose a healthy diet that includes plenty of fruits and vegetables. Adding a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables to your diet ensures that you're getting many vitamins and nutrients. Fruits and vegetables have many antioxidants, which help maintain the health of your eyes.
- Studies haven't proved that antioxidants in pill form can prevent cataracts. But a large population study recently showed that a healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals was associated with a reduced risk of developing cataracts. Fruits and vegetables have many proven health benefits and are a safe way to increase the amount of minerals and vitamins in your diet.
- Wear sunglasses. Ultraviolet light from the sun may contribute to the development of cataracts. Wear sunglasses that block ultraviolet B (UVB) rays when you're outdoors.
- Reduce alcohol use. Excessive alcohol use can increase the risk of cataracts.
Disease Treatments
When your prescription glasses can't clear your vision, the only effective treatment for cataracts is surgery.
When to consider cataract surgery
Talk with your eye doctor about whether surgery is right for you. Most eye doctors suggest considering cataract surgery when your cataracts begin to affect your quality of life or interfere with your ability to perform normal daily activities, such as reading or driving at night.
It's up to you and your doctor to decide when cataract surgery is right for you. For most people, there is no rush to remove cataracts because they usually don't harm the eyes. But cataracts can worsen faster in people with certain conditions, including diabetes, high blood pressure or obesity.
Delaying the procedure generally won't affect how well your vision recovers if you later decide to have cataract surgery. Take time to consider the benefits and risks of cataract surgery with your doctor.
If you choose not to undergo cataract surgery now, your eye doctor may recommend periodic follow-up exams to see if your cataracts are progressing. How often you'll see your eye doctor depends on your situation.
What happens during cataract surgery
Cataract surgery involves removing the clouded lens and replacing it with a clear artificial lens. The artificial lens, called an intraocular lens, is positioned in the same place as your natural lens. It remains a permanent part of your eye.
For some people, other eye problems prohibit the use of an artificial lens. In these situations, once the cataract is removed, vision may be corrected with eyeglasses or contact lenses.
Cataract surgery is generally done on an outpatient basis, which means you won't need to stay in a hospital after the surgery. During cataract surgery, your eye doctor uses a local anesthetic to numb the area around your eye, but you usually stay awake during the procedure.
Cataract surgery is generally safe, but it carries a risk of infection and bleeding. Cataract surgery increases the risk of retinal detachment.
After the procedure, you'll have some discomfort for a few days. Healing generally occurs within a few weeks.
If you need cataract surgery in both eyes, your doctor will schedule surgery to remove the cataract in the second eye after you've healed from the first surgery.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Cataracts and Learn More about Diseases

Body dysmorphic disorder
Ureteral obstruction
Pyoderma gangrenosum
Barrett's esophagus
Anal fistula

Vascular dementia
Blocked tear duct
Entropion
Cataracts, Cataract surgery, ছানি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
