 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
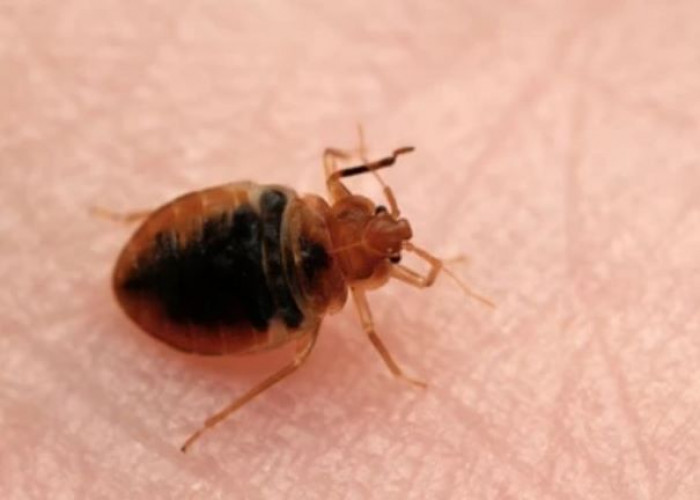
Bedbugs

Bedbugs are small, flat, reddish-brown insects that feed on the blood of animals and humans. They are often found in and around bedding, mattresses, and other furniture, and can be easily transported from place to place, such as in luggage or clothing. Bedbug bites may appear as small, itchy red bumps often arranged in a line or cluster. Infestations can be difficult to eliminate and may require professional pest control services. Preventative measures may include regular vacuuming, sealing cracks and crevices, and inspecting secondhand furniture and clothing before bringing them into the home. Bedbugs do not transmit diseases, but their bites can be irritating and may cause allergic reactions in some people.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Red spots in skin
- Itching
- Red, often with a darker red spot in the middle
Disease Causes
Bedbugs
Bedbug infestations may be linked to:
- Increased international travel
- Changes in pest control practices
- Insecticide resistance
Disease Prevents
Bedbugs
Preventing bites
- Cover up. Because bedbugs don't tend to burrow under clothing, you may be able to avoid bites by wearing pajamas that cover as much skin as possible.
- Bug spray. Insect repellents designed to protect against mosquitoes or ticks aren't very effective against bedbugs.
- Mosquito netting. Bed nets impregnated with the pesticide permethrin may help protect sleepers against bedbug bites. However, this practice may be helping bedbugs develop resistance to this pesticide.
Preventing infestations
- Secondhand items. Inspect used bedding items and upholstered furniture carefully before bringing them into your home.
- Hotel precautions. Check mattress seams for bedbug excrement and place your luggage on tables or dressers instead of on the floor.
- Birds and bats. Eliminate any neighboring bird and bat habitats that may serve as a refuge for bedbugs.
Disease Treatments
The itchy red spots associated with bedbug bites usually disappear on their own within a week or two. You might speed your recovery by using:
- A skin cream containing hydrocortisone (Cortaid)
- An oral antihistamine, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
If you develop a skin infection from scratching bedbug bites, your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic.
Treating your home
Once your symptoms are treated, you must tackle the underlying infestation. This can be difficult because bedbugs hide so well and can live several months without eating. Your best bet may be to hire a professional exterminator, who may use a combination of pesticides and nonchemical treatments.
Nonchemical treatments may include:
- Vacuuming. A thorough vacuuming of cracks and crevices can physically remove bedbugs from an area. Empty the vacuum after each use.
- Laundering. Washing and drying items in a dryer on a high setting will kill bedbugs in clothing or linens.
- Freezing. Bedbugs are also vulnerable to temperatures below 32 F (0 C), but you'd need to leave the items outdoors or in the freezer for several days.
Some professional exterminators use portable devices to raise the temperature of a room to a lethal temperature. All stages of bedbugs can be killed at 122 F (50 C). In some cases, you may have to throw out heavily infested items such as mattresses or couches.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Bedbugs and Learn More about Diseases

Irritable bowel syndrome
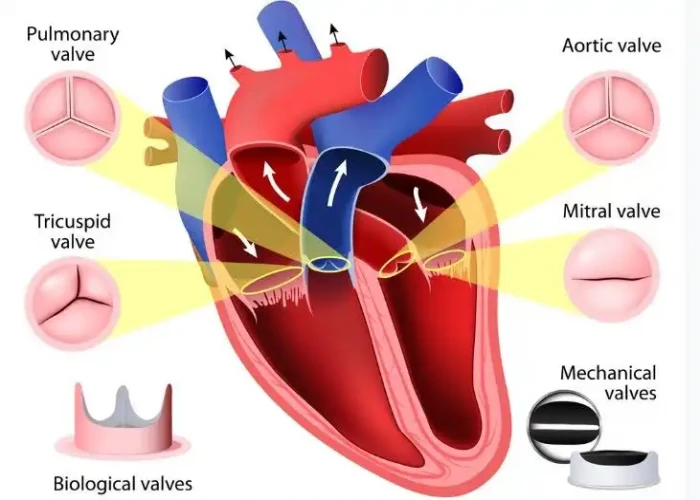
Tricuspid valve regurgitation
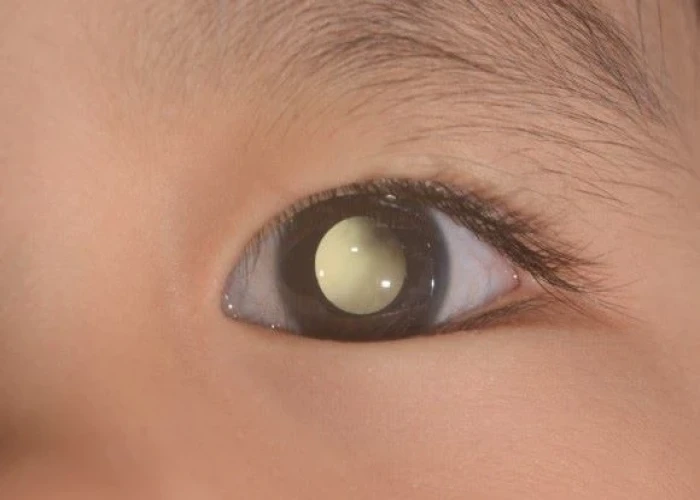
Retinoblastoma
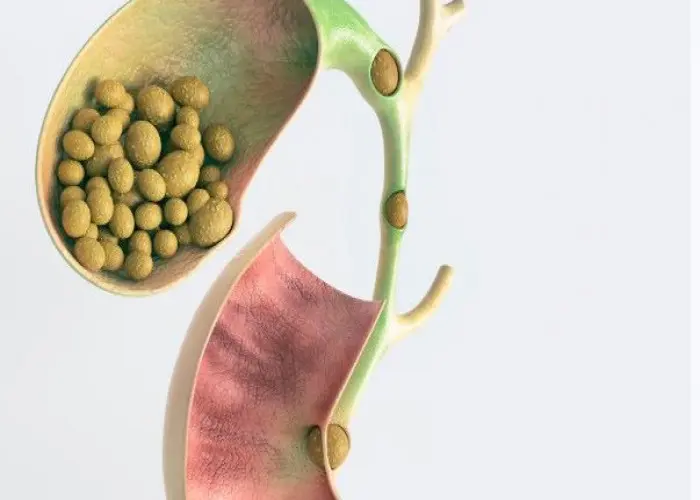
Gallstones

Worms
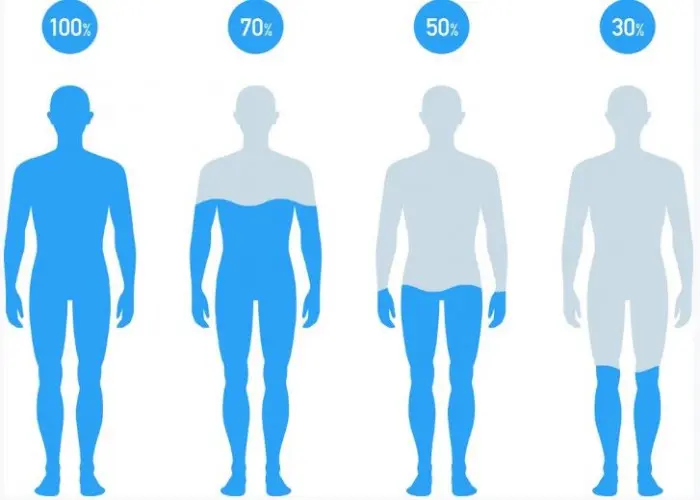
Dehydration
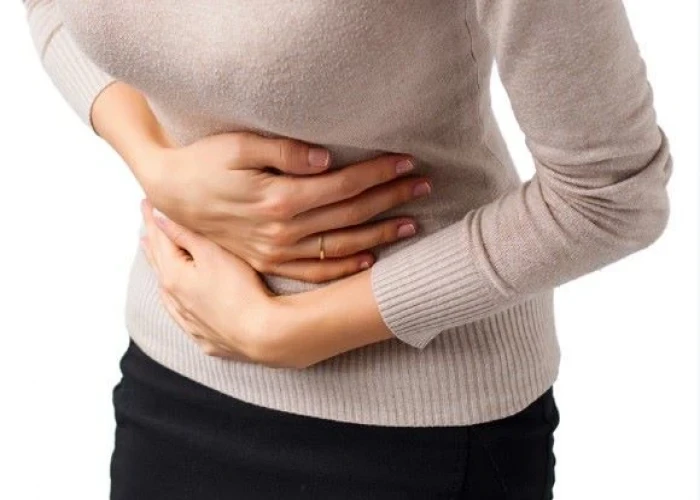

Menstrual cramps
Cystitis
Bedbugs, Bed bugs, Get rid of bed bugs, Bit by bed bugs, ছারপোকা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
