Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Gout
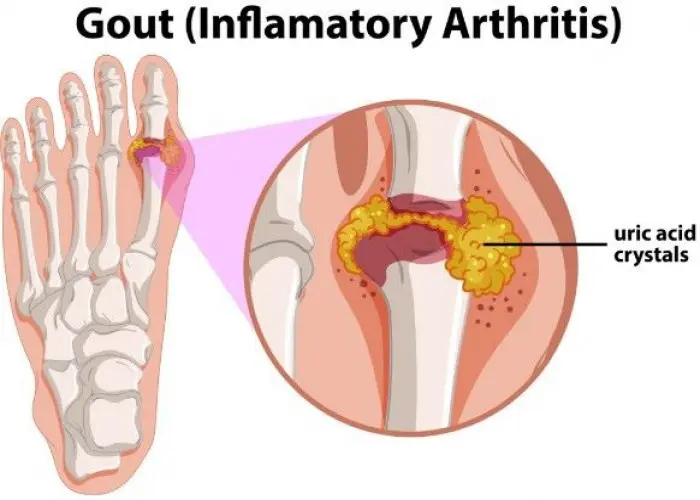
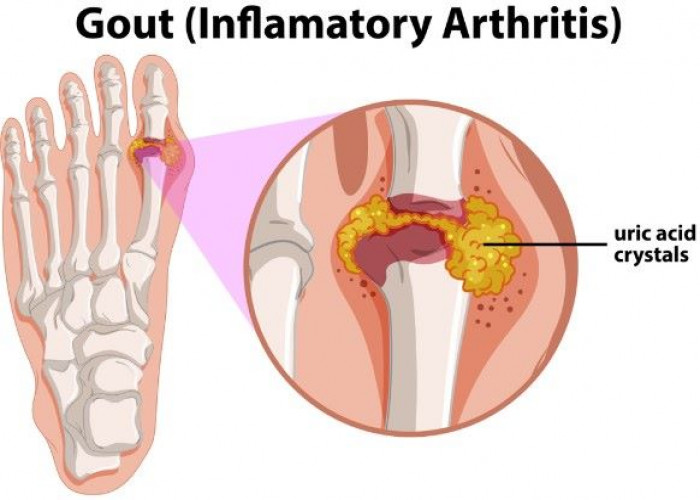
Gout is a type of arthritis that causes sudden, severe attacks of pain, tenderness, redness, warmth, and swelling in the joints, particularly in the big toe, ankle, and knee. It occurs when uric acid levels in the blood become too high, leading to the formation of uric acid crystals in the joints.
Risk factors for gout include obesity, high blood pressure, diabetes, a family history of gout, and a diet high in purines, such as red meat, shellfish, and alcohol. Certain medications, such as diuretics, can also increase the risk of developing gout.
Symptoms of gout may include sudden and severe pain in the affected joint, along with redness, warmth, and swelling. The pain and inflammation typically peak within 24-48 hours and can last for several days to weeks.
Diagnosis of gout usually involves a physical exam and joint fluid analysis to check for the presence of uric acid crystals. Blood tests may also be used to check for elevated levels of uric acid in the blood.
Treatment for gout typically involves medications to reduce pain and inflammation during acute attacks, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and colchicine. Long-term management of gout may involve medications to lower uric acid levels in the blood, such as allopurinol, febuxostat, or probenecid. Lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, limiting alcohol and high-purine foods, and staying well-hydrated, can also help to manage gout.
If you suspect you may have gout or have a family history of the condition, it is important to see a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Early detection and treatment can help to manage the condition and prevent long-term complications associated with gouts, such as joint damage and kidney stones.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Joint pain
- Joint stiffness
- Swollen joint
- The affected joint or joints become swollen, tender, warm and red.
Disease Causes
Gout
Gout occurs when urate crystals accumulate in your joint, causing the inflammation and intense pain of a gout attack. Urate crystals can form when you have high levels of uric acid in your blood. Your body produces uric acid when it breaks down purines — substances that are found naturally in your body.
Purines are also found in certain foods, including red meat and organ meats, such as liver. Purine-rich seafood includes anchovies, sardines, mussels, scallops, trout and tuna. Alcoholic beverages, especially beer, and drinks sweetened with fruit sugar (fructose) promote higher levels of uric acid.
Normally, uric acid dissolves in your blood and passes through your kidneys into your urine. But sometimes either your body produces too much uric acid or your kidneys excrete too little uric acid. When this happens, uric acid can build up, forming sharp, needlelike urate crystals in a joint or surrounding tissue that cause pain, inflammation and swelling.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Gout medications are available in two types and focus on two different problems. The first type helps reduce the inflammation and pain associated with gout attacks. The second type works to prevent gout complications by lowering the amount of uric acid in your blood.
Which type of medication is right for you depends on the frequency and severity of your symptoms, along with any other health problems you may have.
Medications to treat gout attacks
Drugs used to treat gout flares and prevent future attacks include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). NSAIDs include over-the-counter options such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve), as well as more-powerful prescription NSAIDs such as indomethacin (Indocin, Tivorbex) or celecoxib (Celebrex). NSAIDs carry risks of stomach pain, bleeding and ulcers.
- Colchicine. Your doctor may recommend colchicine (Colcrys, Gloperba, Mitigare), an anti-inflammatory drug that effectively reduces gout pain. The drug's effectiveness may be offset, however, by side effects such as nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
- Corticosteroids. Corticosteroid medications, such as prednisone, may control gout inflammation and pain. Corticosteroids may be in pill form, or they can be injected into your joint. Side effects of corticosteroids may include mood changes, increased blood sugar levels and elevated blood pressure.
Medications to prevent gout complications
If you experience several gout attacks each year, or if your gout attacks are less frequent but particularly painful, your doctor may recommend medication to reduce your risk of gout-related complications. If you already have evidence of damage from gout on joint X-rays, or you have tophi, chronic kidney disease or kidney stones, medications to lower your body's level of uric acid may be recommended.
- Medications that block uric acid production. Drugs such as allopurinol (Aloprim, Lopurin, Zyloprim) and febuxostat (Uloric) help limit the amount of uric acid your body makes. Side effects of allopurinol include fever, rash, hepatitis and kidney problems. Febuxostat side effects include rash, nausea and reduced liver function. Febuxostat also may increase the risk of heart-related death.
- Medications that improve uric acid removal. Drugs such as probenecid (Probalan) help improve your kidneys' ability to remove uric acid from your body. Side effects include a rash, stomach pain and kidney stones.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Indomethacin (Oral)
Medicines containing indomethacin for severe or severe arthritis.
2 capsules (50 mg) 3 times a day after meals, 2 days later 1 capsule 3 times a day for 7 days.
-
Celecoxib
100mg medicine 1+0+1 or 0+0+2.
-
Naproxen Sodium
Adults: 1 tablet in the morning and 1 tablet at night after meals.
-
Diclofenac Sodium
1 pill daily at night after meal for 5-7 days.
-
Allopurinol
Can be used in young and old cases of arthritis.
-
Ranitidine Hydrochloride
Whatever anti-rheumatic medicine is given, gas-destroying medicine should be given.
1 in the morning and 1 in the night after meals.
-
Vitamin B complex
1 capsule 2 times a day after meals or as directed by the physician.
- Vitamin B1, B2 & B6
- Vitamin B1 + B6 + B12
-
Clobazam
Medication with clobazam for pain, difficulty sleeping and mental restlessness.
1 pill at night.
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Gout and Learn More about Diseases

Sprained ankle

Membranous nephropathy

Myoclonus
CSF leak (Cerebrospinal fluid leak)
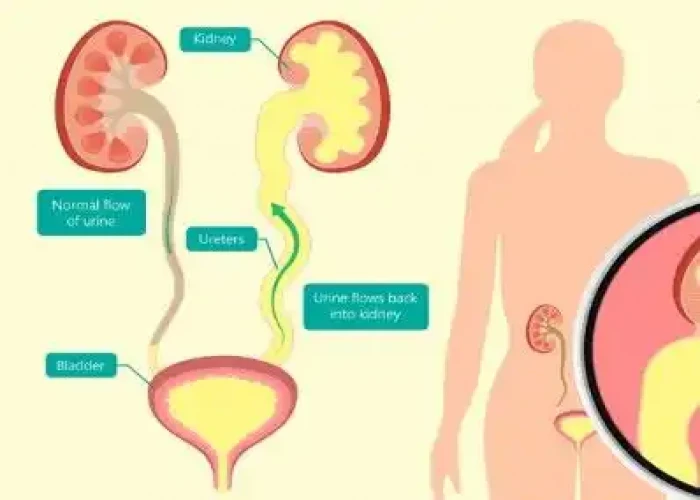
Vesicoureteral reflux

Hay fever
Diabetic neuropathy
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
gout, বাত
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.