Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Aspergillosis
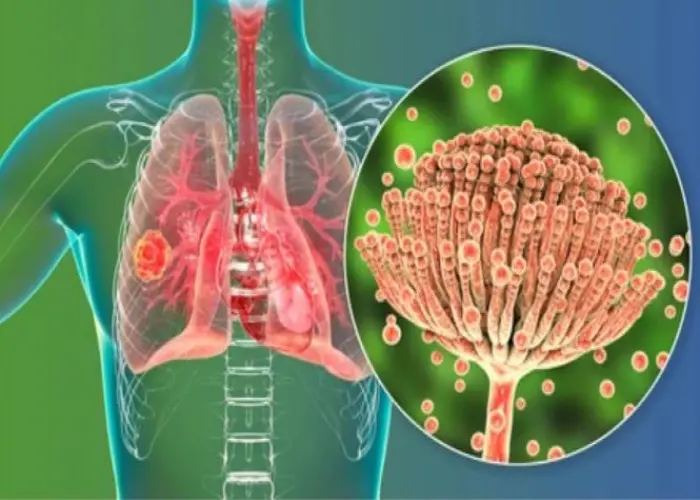
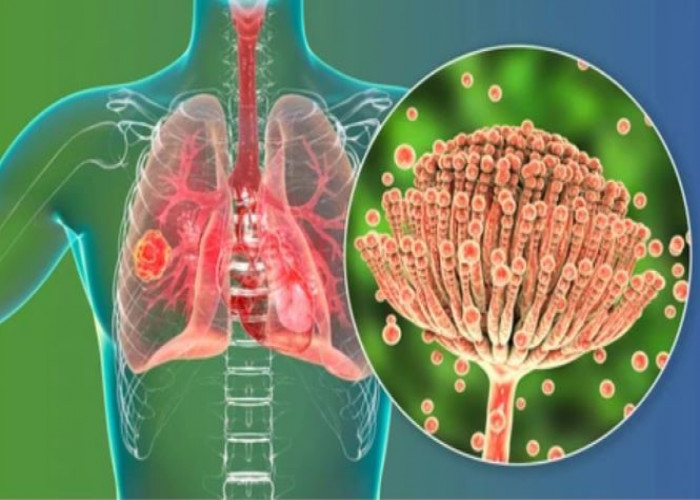
Aspergillosis is a type of fungal infection that can affect the lungs and other parts of the body. The fungus that causes aspergillosis, Aspergillus, is commonly found in the environment and typically only causes illness in people with weakened immune systems.
There are several types of aspergillosis, including invasive aspergillosis (which affects the lungs and other organs), allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (which causes an allergic reaction in the lungs), and aspergilloma (which is a type of fungal ball that grows in a cavity in the lung).
Symptoms of aspergillosis can vary depending on the type of infection but may include cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue, and fever.
Diagnosis of aspergillosis may involve a combination of imaging tests, such as a CT scan or chest x-ray, and laboratory tests to identify the presence of Aspergillus in the body.
Treatment for aspergillosis typically involves antifungal medications, and in some cases, surgical removal of the infected tissue. If you have a weakened immune system, taking steps to improve your immune function and reduce your exposure to Aspergillus can help reduce your risk of developing aspergillosis.
If you have symptoms of aspergillosis or are at increased risk for the disease, it's important to talk to your doctor about your medical history and any steps you can take to reduce your risk. With proper treatment and care, many people with aspergillosis are able to manage their symptoms and prevent the disease from progressing.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Fever
- Skin lesions
- Headaches
- Chest pain
- Joint pain
- Fever and chills
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Weight loss
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Shortness of breath with cough
- Asthma
- Blood with cough
- A cough that often brings up blood (hemoptysis)
Disease Causes
Aspergillosis
Aspergillus mold is unavoidable. Outdoors, it's found in decaying leaves and compost and on plants, trees and grain crops.
Everyday exposure to aspergillus is rarely a problem for people with healthy immune systems. When mold spores are inhaled, immune system cells surround and destroy them. But people who have a weakened immune system from illness or immunosuppressant medications have fewer infection-fighting cells. This allows aspergillus to take hold, invading the lungs and, in the most serious cases, other parts of the body.
Aspergillosis is not contagious from person to person.
Disease Prevents
Aspergillosis
It's nearly impossible to avoid exposure to aspergillus, but if you have had a transplant or are undergoing chemotherapy, try to stay away from places where you're likely to encounter mold, such as construction sites, compost piles and buildings that store grain. If you have a weakened immune system, your doctor may advise you to wear a face mask to avoid being exposed to aspergillus and other airborne infectious agents.
Disease Treatments
Aspergillosis treatments vary with the type of disease. Possible treatments include:
- Observation. Simple, single aspergillomas often don't need treatment, and medications aren't usually effective in treating these fungal masses. Instead, aspergillomas that don't cause symptoms may simply be closely monitored by chest X-ray. If the condition progresses, then antifungal medications may be recommended.
- Oral corticosteroids. The goal in treating allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis is to prevent existing asthma or cystic fibrosis from worsening. The best way to do this is with oral corticosteroids. Antifungal medications by themselves aren't helpful for allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, but they may be combined with corticosteroids to reduce the dose of steroids and improve lung function.
- Antifungal medications. These drugs are the standard treatment for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. The most effective treatment is a newer antifungal drug, voriconazole (Vfend). Amphotericin B is another option.
- All antifungal drugs can have serious side effects, including kidney and liver damage. Interactions between antifungal drugs and other medications are also common.
- Surgery. Because antifungal medications don't penetrate an aspergilloma very well, surgery to remove the fungal mass is the first-choice treatment when an aspergilloma causes bleeding in the lungs.
- Embolization. This procedure stops lung bleeding caused by an aspergilloma. A radiologist injects a material through a catheter that has been guided into an artery feeding a lung cavity where an aspergilloma is causing blood loss. The injected material hardens, blocking the blood supply to the area and stopping the bleeding. This treatment works temporarily, but the bleeding is likely to start again.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Aspergillosis and Learn More about Diseases

Delayed sleep phase

Grand mal seizure
Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)
Amoebic Dysentry
Rotator cuff injury
Soft palate cancer

Common variable immunodeficiency

Bronchitis
Aspergillosis, Aspergillus fumigatus, Invasive aspergillosis, অ্যাস্পারগিলোসিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.