 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
ARDS
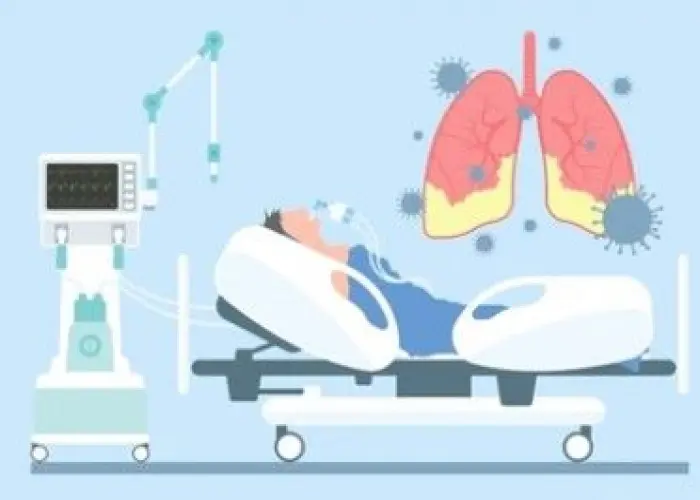
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a life-threatening condition that affects the lungs and can make it difficult for the body to get enough oxygen. ARDS occurs when fluid builds up in the air sacs of the lungs, making it difficult for oxygen to pass into the bloodstream. This can lead to a low oxygen level in the blood, known as hypoxemia, which can be life-threatening.
ARDS can be caused by a variety of factors, including severe infections, severe injuries such as burns or crush injuries, and complications from surgery or other medical procedures. In some cases, the cause of ARDS is unknown.
Symptoms of ARDS can include sudden shortness of breath, rapid breathing, and a decreased level of consciousness. The condition can also cause complications such as pneumonia, low blood pressure, and a decreased ability to fight infections.
Treatment for ARDS depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. In most cases, treatment involves supporting the patient's breathing with a ventilator and providing oxygen as needed. In severe cases, treatment may also involve medications to improve lung function and reduce inflammation, as well as support for other organs, such as the heart and kidneys, if they are also affected.
It is important to seek medical attention if you or a loved one experiences symptoms of ARDS, as prompt treatment can help prevent serious complications and improve outcomes. Your doctor can perform tests to determine the cause and severity of the condition and recommend the best course of treatment for you.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Rapid breathing
- Low blood pressure (hypotension)
- Confusion (Hallucinations)
Disease Causes
ARDS
The mechanical cause of ARDS is fluid leaked from the smallest blood vessels in the lungs into the tiny air sacs where blood is oxygenated. Normally, a protective membrane keeps this fluid in the vessels. Severe illness or injury, however, can cause damage to the membrane, leading to the fluid leakage of ARDS.
Underlying causes of ARDS include:
- Sepsis. The most common cause of ARDS is sepsis, a serious and widespread infection of the bloodstream.
- Inhalation of harmful substances. Breathing high concentrations of smoke or chemical fumes can result in ARDS, as can inhaling (aspirating) vomit or near-drowning episodes.
- Severe pneumonia. Severe cases of pneumonia usually affect all five lobes of the lungs.
- Head, chest or other major injury. Accidents, such as falls or car crashes, can directly damage the lungs or the portion of the brain that controls breathing.
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). People who have severe COVID-19 may develop ARDS.
- Others. Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas), massive blood transfusions and burns.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
The first goal in treating ARDS is to improve the levels of oxygen in your blood. Without oxygen, your organs can't function properly.
Oxygen
To get more oxygen into your bloodstream, your doctor will likely use:
- Supplemental oxygen. For milder symptoms or as a temporary measure, oxygen may be delivered through a mask that fits tightly over your nose and mouth.
- Mechanical ventilation. Most people with ARDS will need the help of a machine to breathe. A mechanical ventilator pushes air into your lungs and forces some of the fluid out of the air sacs.
Fluids
Carefully managing the amount of intravenous fluids is crucial. Too much fluid can increase fluid buildup in the lungs. Too little fluid can put a strain on your heart and other organs and lead to shock.
Medication
People with ARDS usually are given medication to:
- Prevent and treat infections
- Relieve pain and discomfort
- Prevent blood clots in the legs and lungs
- Minimize gastric reflux
- Sedate
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
ARDS and Learn More about Diseases
Colon cancer
Fibromyalgia

Ingrown toenails
Impotency

Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS)

Yeast infection (vaginal)

Solitary rectal ulcer syndrome
Diabetic coma
ARDS, ARDS full form এআরডিএস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
