 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Appendicitis - Homeopathic remedies
Appendicitis is a condition in which the appendix, a small tube-shaped organ attached to the large intestine, becomes inflamed and swollen. It is a common condition that affects people of all ages, but it is most commonly seen in people between the ages of 10 and 30.
Symptoms of Appendicitis:
The symptoms of appendicitis can vary, but they often include:
- Abdominal pain, usually starting near the navel and shifting to the lower right side of the abdomen
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Low-grade fever
- Swelling and tenderness in the abdomen
- Painful urination
Causes of Appendicitis:
The exact cause of appendicitis is not fully understood, but it is thought to be the result of blockage of the appendix by stool, a foreign body, or a tumor. When the appendix becomes blocked, bacteria can grow and multiply, causing inflammation and swelling of the appendix.
Treatment of Appendicitis:
The treatment for appendicitis typically involves surgery to remove the appendix, a procedure known as an appendectomy. In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to reduce the risk of infection or to treat a mild case of appendicitis. Surgery is usually performed as soon as possible after the diagnosis of appendicitis is made to prevent the appendix from rupturing, which can lead to a more serious infection.
Prevention of Appendicitis:
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent appendicitis, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk. These include:
- Maintaining a healthy diet with plenty of fiber to prevent constipation
- Staying hydrated with plenty of water and fluids
- Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption
- Practicing good hygiene to reduce the risk of infection
- Seeking prompt medical attention if symptoms of appendicitis arise
Appendicitis is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention. If you suspect you or someone you know may have appendicitis, it is important to seek medical attention immediately to prevent complications and ensure a full recovery.

Boil
Glandular swelling

Dizziness
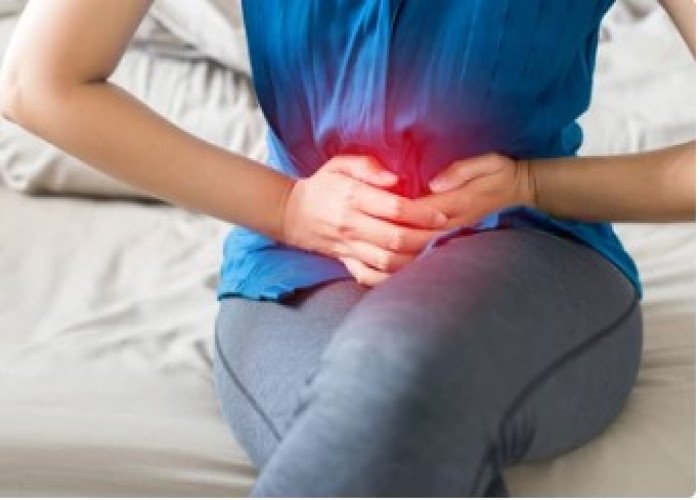
Colic

Irregular menstruation

Short periods

Vitiligo

Depressed
Appendicitis, এপিন্ডিসাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.




