 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Schizophrenia - Generics
Schizophrenia is a serious mental illness that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. It is a chronic condition that usually develops in late adolescence or early adulthood and affects approximately 1% of the population. The exact cause of schizophrenia is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and brain chemistry factors.
The symptoms of schizophrenia can be divided into positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms. Positive symptoms include hallucinations, delusions, and disordered thinking. Negative symptoms include reduced emotional expression, reduced motivation and interest in daily activities, and difficulty in communicating with others. Cognitive symptoms include problems with memory, attention, and decision-making.
Diagnosis of schizophrenia involves a thorough evaluation by a mental health professional, including a medical history, physical examination, and psychiatric evaluation. Treatment of schizophrenia usually involves a combination of medications and therapy. Antipsychotic medications are often used to manage the positive symptoms of schizophrenia, while therapy can help individuals learn coping strategies, improve communication and social skills, and manage stress.
While there is no cure for schizophrenia, treatment can help manage symptoms and improve the overall quality of life for individuals with this condition. It is important to seek treatment early, as early intervention has been shown to improve outcomes for individuals with schizophrenia.

Hemophilia B or Christmas...

Urothelial toxicity

Recurrent miscarriage

Infected wounds & ulcers

Rheumatic fever

Surgical wounds

Post-operative pain
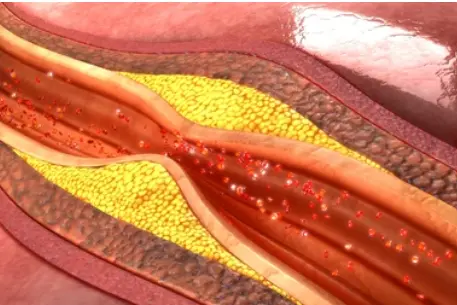
Pulmonary arterial hypert...
Schizophrenia, সিজোফ্রেনিয়া
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.