 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Renal cancers - Generics
Renal cancer, also known as kidney cancer, is a type of cancer that originates in the cells of the kidney. There are several types of renal cancer, the most common of which is renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
The exact causes of renal cancer are not well understood, but certain risk factors have been identified. These include smoking, obesity, high blood pressure, family history of renal cancer, and certain genetic conditions such as von Hippel-Lindau syndrome.
Symptoms of renal cancer may include blood in the urine, pain or discomfort in the side or back, a mass or lump in the abdomen, weight loss, fatigue, and fever. However, many people with renal cancer may not experience any symptoms until the cancer has progressed to an advanced stage.
Diagnosis of renal cancer typically involves a physical exam, blood and urine tests, imaging studies such as a CT scan or MRI, and a biopsy to confirm the presence of cancer cells. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and chemotherapy, depending on the stage and type of cancer.
The prognosis for renal cancer depends on several factors, including the stage of the cancer at diagnosis, the patient's age and overall health, and the type of cancer. Early detection and treatment can improve the chances of a successful outcome, so it is important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms or risk factors for renal cancer.

Psychogenic amenorrhea

Analgesia

Hair loss

Bacterial Pneumonia cause...

Trophoblastic neoplasms
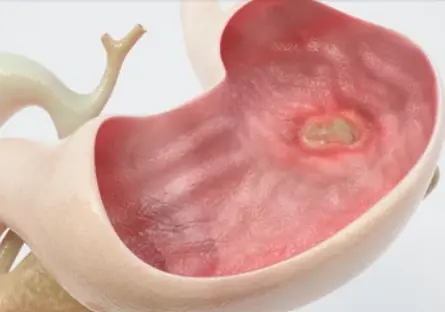
Ulcerative colitis

Tonic-clonic status epile...

lodine deficiency
Renal cancers, রেনাল ক্যান্সার
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.