 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Psychotic disorders - Generics
Psychotic disorders are a group of mental illnesses characterized by the presence of psychotic symptoms, which include delusions, hallucinations, disorganized thinking, and abnormal behavior. These symptoms can be severe and can greatly affect a person's ability to function in daily life.
Some of the most common psychotic disorders include schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, and delusional disorder. Schizophrenia is a chronic and severe mental disorder that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. Schizoaffective disorder is a condition that combines symptoms of both schizophrenia and a mood disorder such as depression or bipolar disorder. Delusional disorder involves persistent, non-bizarre delusions that are not accompanied by other symptoms of psychosis.
Psychotic disorders can have a variety of causes, including genetics, brain chemistry, and environmental factors. Treatment for these disorders typically involves a combination of medications, such as antipsychotics and mood stabilizers, and psychotherapy, such as cognitive behavioral therapy and family therapy. In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary to stabilize symptoms and provide intensive treatment.
Early intervention is important in the treatment of psychotic disorders, as early treatment can improve outcomes and reduce the severity of symptoms. Family support and education can also be beneficial for individuals with psychotic disorders, as well as for their loved ones.
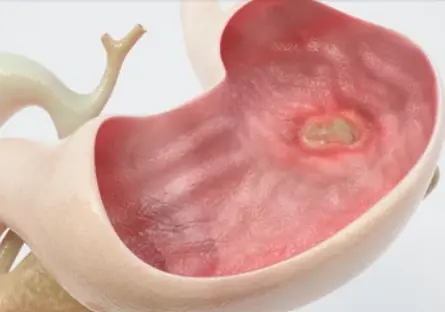
Ulcerative colitis

Functional diarrhea
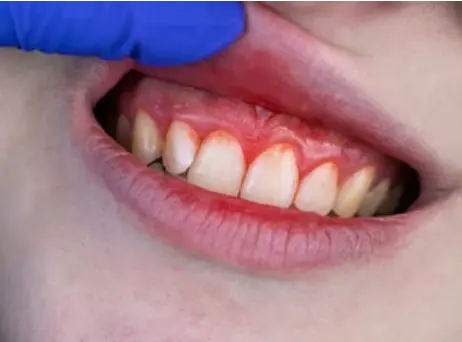
Scurvy
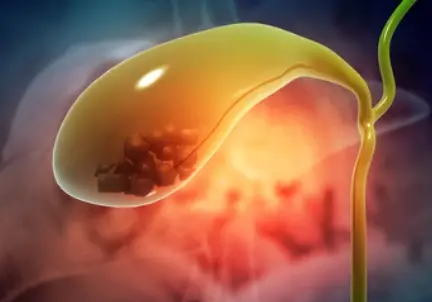
Cholecystography

Dyslipidemia

Migraine prophylaxis
Acute psychosis
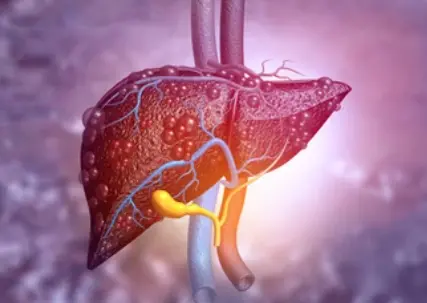
Liver cirrhosis
Psychotic disorders, মানসিক ব্যাধি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.