 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Polycystic ovarian syndrome - Generics
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. PCOS is characterized by the presence of multiple cysts on the ovaries, irregular menstrual cycles, and high levels of male hormones (androgens).
Symptoms of PCOS can vary widely, but can include irregular periods or no periods at all, heavy bleeding, weight gain, acne, excessive hair growth on the face, chest, or back (hirsutism), thinning hair on the scalp, and infertility.
The exact cause of PCOS is not known, but it is believed to be related to insulin resistance and high levels of insulin in the body. Insulin resistance can cause the body to produce too much insulin, which can increase androgen levels and interfere with ovulation.
Treatment for PCOS typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medication. Lifestyle changes may include regular exercise, healthy eating habits, and weight loss, as excess weight can exacerbate PCOS symptoms.
Medications such as birth control pills or other hormonal contraceptives can help to regulate menstrual cycles and reduce androgen levels. Other medications may be used to treat specific symptoms of PCOS, such as insulin resistance or excess hair growth.
In cases where infertility is a concern, medications to induce ovulation or in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be recommended. It's important for women with PCOS to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan that meets their specific needs.

Atopic or contact dermato...
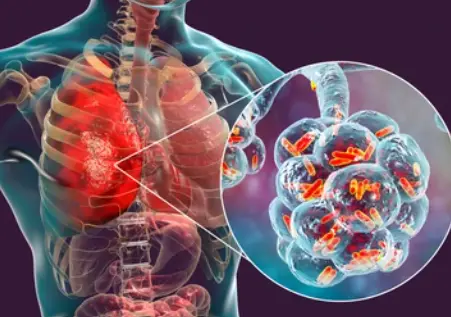
Bacteraemic pneumonia
PID

Severe metabolic acidosis

Angina

Hyperprolactinemia

Renal angiomyolipoma

Vitamin B12 deficiency
Polycystic ovarian syndrome, পলিসিস্টিক ওভারিয়ান সিনড্রোম
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.