 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Poisonings - Generics
Poisoning occurs when a person is exposed to a substance that can cause harm or damage to the body. The severity of poisoning can range from mild symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, or vomiting to severe symptoms such as seizures, coma, or even death.
Poisonings can occur through ingestion, inhalation, injection, or absorption through the skin. Common substances that can cause poisoning include drugs, chemicals, pesticides, household cleaners, and even certain foods or plants.
Symptoms of poisoning can vary depending on the substance involved, the amount of exposure, and the age and health of the person affected. In some cases, symptoms may not appear immediately and may take several hours or even days to develop.
Treatment for poisoning depends on the type and severity of the poisoning. In some cases, the person may need to be hospitalized for observation and treatment. Treatment may involve administering medications to counteract the effects of the poison, providing supportive care such as oxygen or fluids, or performing emergency procedures such as gastric lavage or dialysis.
Prevention is key in avoiding poisoning. This can involve taking precautions such as reading product labels, storing chemicals and medications properly, and keeping harmful substances out of reach of children and pets. If a poisoning occurs, seeking prompt medical attention can help to minimize the harm caused and improve the chances of a full recovery.

Nutritional supplement

Gastroparesis

Chemotherapy-induced neut...
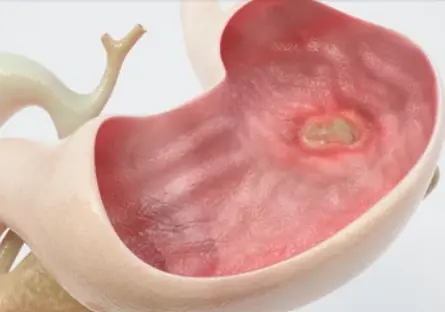
Ulcerative colitis

Urethritis
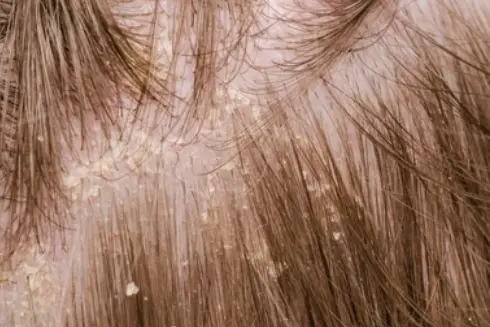
Scalp and non-scalp psori...

Anaphylactic shock

Inflammatory joint diseas...
Poisonings, বিষ
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.