 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Perennial or seasonal allergic rhinitis - Generics
Allergic rhinitis is a common condition that causes inflammation and irritation of the nasal passages due to an allergic reaction. There are two main types of allergic rhinitis: perennial and seasonal.
Perennial allergic rhinitis is a year-round condition caused by allergens that are present throughout the year, such as dust mites, pet dander, or mold. Symptoms of perennial allergic rhinitis can include sneezing, congestion, runny nose, and itchy or watery eyes.
Seasonal allergic rhinitis, also known as hay fever, is caused by allergens that are present during certain times of the year, such as pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds. Symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis can include sneezing, congestion, runny nose, itchy or watery eyes, and sometimes fatigue or headaches.
Treatment for allergic rhinitis typically involves avoiding the allergen when possible and using medications to relieve symptoms. Medications may include antihistamines, decongestants, and nasal corticosteroids. In some cases, allergy shots, also known as immunotherapy, may be recommended to help desensitize the immune system to specific allergens.
Prevention of allergic rhinitis involves avoiding exposure to known allergens when possible and taking steps to reduce indoor allergens, such as dust mites and pet dander. Keeping windows and doors closed during peak pollen seasons and wearing a mask when outdoors can also help reduce exposure to allergens.
If you are experiencing symptoms of allergic rhinitis, it is important to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment. Left untreated, allergic rhinitis can lead to complications such as sinus infections and ear infections.

Reproductive tract infect...

Congenital ichthyosis

Fungal skin infections

Streptococcal pharyngitis

VTB

Chorea
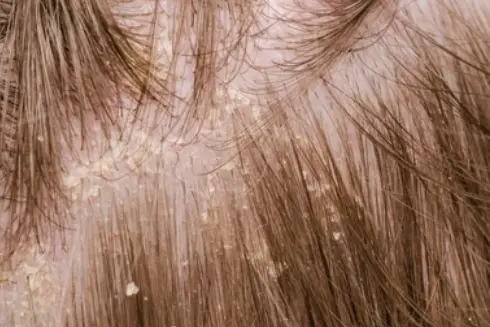
Scaly or itchy scalps

CAPD-associated peritonit...
Perennial or seasonal allergic rhinitis, বহুবর্ষজীবী বা মৌসুমী অ্যালার্জিক রাইনাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.