 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Menopausal HRT - Generics
Menopausal hormone therapy (HRT) involves the use of medications that contain female hormones such as estrogen and progesterone to help alleviate symptoms associated with menopause, such as hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and mood changes.
There are different types of HRT, including estrogen-only therapy (ET) and combined estrogen-progestin therapy (EPT). ET is typically recommended for women who have had a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus), while EPT is recommended for women who still have their uterus.
HRT can be administered in different forms, such as pills, patches, gels, creams, and vaginal rings. The choice of form depends on individual preferences and medical history.
While HRT can be effective in reducing menopausal symptoms, it is not without risks. Long-term use of HRT has been associated with an increased risk of breast cancer, heart disease, stroke, and blood clots. Therefore, it is important to discuss the potential benefits and risks of HRT with a healthcare professional to make an informed decision about its use.
It is also important to note that HRT should not be used as a long-term solution for other health conditions, such as osteoporosis, as there are other medications and lifestyle changes that can be more effective and have fewer risks.
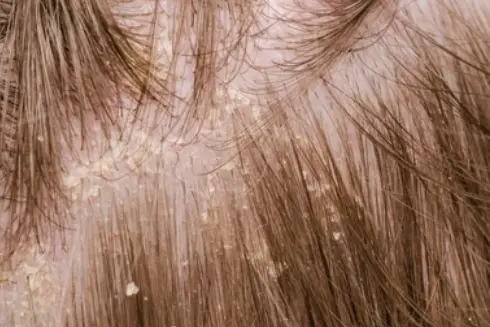
Seborrheic dermatitis of...

Pregnancy-associated naus...

Herpes simplex keratitis

Meningioma

Cushings disease

Episcleritis
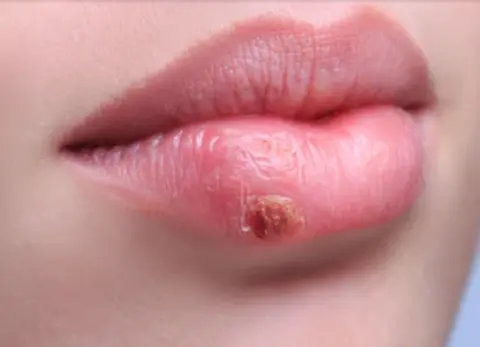
Sore lips

Dermatomycoses
Menopausal HRT, মেনোপজাল এইচআরটি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.