 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Hyperprolactinemia - Generics
Hyperprolactinemia is a condition where there is an excessive amount of prolactin, a hormone that is produced by the pituitary gland, in the blood. This condition can affect both men and women.
The most common cause of hyperprolactinemia is a benign tumor called a prolactinoma that develops on the pituitary gland. Other causes include medications, such as antipsychotics, antidepressants, and blood pressure medications, as well as certain medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism, kidney disease, and liver disease.
Symptoms of hyperprolactinemia can include irregular menstrual periods, decreased libido, erectile dysfunction in men, breast milk production in women who are not pregnant or nursing, and infertility.
Treatment for hyperprolactinemia depends on the underlying cause. If a medication is causing the condition, switching to a different medication may help. In cases where a prolactinoma is causing the condition, medications, such as dopamine agonists, are usually prescribed to reduce the amount of prolactin in the blood and shrink the tumor. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the tumor.
It is important to work with a healthcare provider to manage hyperprolactinemia, as untreated cases can lead to complications such as osteoporosis, infertility, and loss of vision.

Hypokalaemia

Atopic eczema
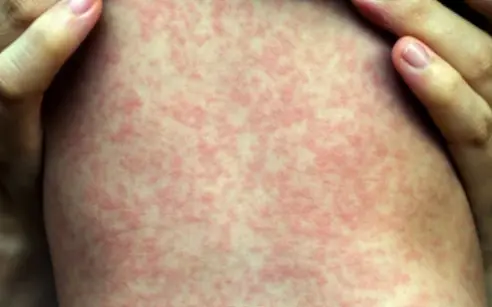
Prevention of measles

Bacterial ear infections

lodine deficiency

Electrolyte replenisher

Roughness and fine wrinkl...

Bacterial or fungal vagin...
Hyperprolactinemia, হাইপারপ্রোলাক্টিনেমিয়া
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.