 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Generalized tonic-clonic seizures - Generics
Generalized tonic-clonic seizures, also known as grand mal seizures, are a type of seizure that involves the entire brain. They are characterized by a sudden loss of consciousness, followed by muscle rigidity and convulsions. These seizures can be caused by various factors, such as epilepsy, brain injury, infections, and metabolic imbalances.
During a generalized tonic-clonic seizure, the person typically falls to the ground and loses consciousness. The body stiffens (tonic phase) for several seconds, followed by rhythmic jerking of the limbs (clonic phase). The person may also bite their tongue, lose bladder or bowel control, and breathe abnormally. The seizure can last for several minutes, and the person may feel tired, confused, or sore afterward.
Treatment for generalized tonic-clonic seizures typically involves antiepileptic medications, which can help prevent seizures or reduce their frequency and severity. In some cases, surgery may be an option for people who do not respond to medications. Other treatments may include avoiding triggers that can cause seizures, such as stress or lack of sleep, and following a healthy lifestyle.
It is important to seek medical attention if you or someone you know experiences a generalized tonic-clonic seizure, especially if it is the first time. A healthcare provider can perform tests to determine the cause of the seizure and develop an appropriate treatment plan.

Dry Irritated eyes

Mild cystitis and spasmod...

Otitis externa

Reversal of neuromuscular...

Local pain relief

Osteogenic sarcoma
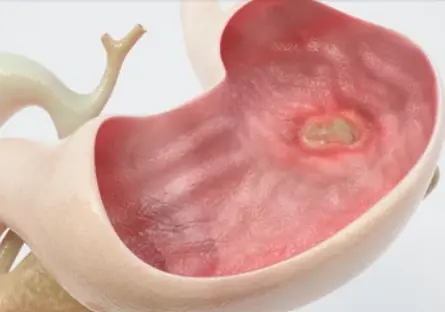
Peptic ulcer disease

Supraventricular arrhythm...
Generalized tonic-clonic seizures, সাধারণীকৃত টনিক-ক্লোনিক খিঁচুনি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.