 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Denture sores - Generics
Denture sores, also known as denture stomatitis, is a common condition that affects many denture wearers. It is characterized by redness, inflammation, and irritation of the oral tissues that come into contact with the dentures. The condition is caused by a variety of factors, including poor oral hygiene, ill-fitting dentures, and the accumulation of bacteria and other microorganisms on the denture surface.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of denture sores may vary from person to person, and the severity of the symptoms may depend on the underlying cause. Some of the most common symptoms of denture sores include:
- Redness and inflammation of the oral tissues
- Pain or discomfort in the mouth
- Swelling of the gums or other oral tissues
- Formation of small, red bumps or sores on the gums or other oral tissues
- Dryness or cracking of the lips or corners of the mouth
- Bad breath or a foul taste in the mouth.
Causes:
Denture sores can be caused by a number of factors, including:
- Poor oral hygiene: Failure to properly clean and maintain dentures can result in the accumulation of bacteria and other microorganisms on the denture surface, leading to inflammation and irritation of the oral tissues.
- Ill-fitting dentures: Dentures that do not fit properly can cause friction and pressure on the gums and other oral tissues, leading to irritation, inflammation, and the development of sores.
- Allergic reactions: Some people may be allergic to the materials used to make dentures or to the adhesives used to secure them in place, resulting in an allergic reaction that can cause inflammation, irritation, and other symptoms.
- Candidiasis: A fungal infection caused by the overgrowth of Candida albicans, which is commonly found in the mouth, can lead to the development of denture sores.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antibiotics and corticosteroids, can increase the risk of developing denture sores by altering the balance of bacteria in the mouth or suppressing the immune system.
Prevention:
- Proper oral hygiene: Regular brushing and cleaning of dentures is essential to preventing the accumulation of bacteria and other microorganisms on the denture surface.
- Proper denture fit: Ensuring that dentures fit properly and are adjusted as needed can help to reduce the risk of irritation, inflammation, and the development of sores.
- Good nutrition: A diet that is rich in nutrients, including vitamins and minerals, can help to maintain healthy oral tissues and reduce the risk of infection.
- Regular dental checkups: Regular checkups with a dentist or dental hygienist can help to identify and address potential problems before they become more serious.
Treatment:
The treatment of denture sores may depend on the underlying cause and the severity of the symptoms. Some common treatments may include:
- Oral hygiene: Improving oral hygiene through regular brushing and cleaning of dentures can help to reduce inflammation and irritation of the oral tissues.
- Antifungal medication: If denture sores are caused by a fungal infection, antifungal medication may be prescribed to treat the underlying infection.
- Adjustments to dentures: If denture sores are caused by ill-fitting dentures, adjustments may be needed to ensure that the dentures fit properly and do not cause friction or pressure on the gums and other oral tissues.
- Medications: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help reduce inflammation and other symptoms associated with denture sores.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove damaged tissue or to correct structural problems with the jaw or oral tissues.
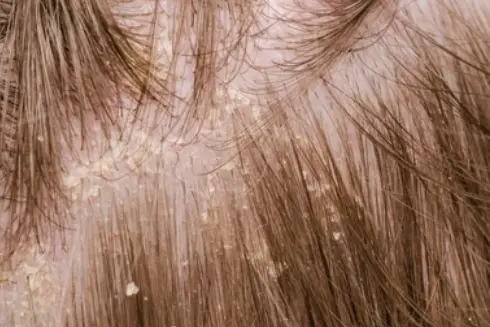
Scalp psoriasis

Hemolytic Disease of the...

Susceptible infections

Iron deficiency

Hyperkeratosis

Corticosteroid-responsive...

Acute otitis media

Surgery
Denture sores, দাঁত ঘা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.