 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Candidiasis - Generics
Candidiasis is a type of fungal infection caused by the overgrowth of Candida species, particularly Candida albicans, in the body. Candida is a type of yeast that is normally present in the body, but can become pathogenic and cause infections under certain conditions, such as a weakened immune system, poor hygiene, or the use of antibiotics or corticosteroids.
Candidiasis can affect different parts of the body, including the mouth, throat, esophagus, vagina, skin, and bloodstream. The symptoms of candidiasis vary depending on the location and severity of the infection, but may include redness, itching, swelling, and pain in the affected area. Candidiasis can also cause white patches or discharge in the mouth or vagina, and can lead to fever and chills if it spreads to the bloodstream.
Treatment for candidiasis depends on the location and severity of the infection. Topical antifungal medications, such as creams or ointments, may be used to treat skin or vaginal infections. Oral antifungal medications, such as fluconazole or itraconazole, may be used to treat more severe or systemic infections. In addition to medication, maintaining good hygiene, avoiding irritating substances, and addressing underlying risk factors, such as diabetes or a weakened immune system, can help prevent and manage candidiasis.
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect that you have candidiasis or if your symptoms persist despite treatment. Candidiasis can be a chronic or recurring condition, and in some cases, it can lead to serious complications, especially in people with weakened immune systems.

Lower urinary tract infec...
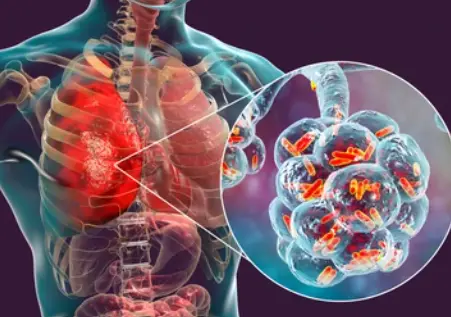
Mycoplasma pneumonia

Acute nonspecific gastroe...
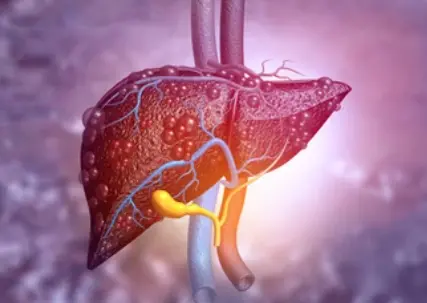
Primary biliary cirrhosis

Non-gonococcal urethritis

Aspiration pneumonia
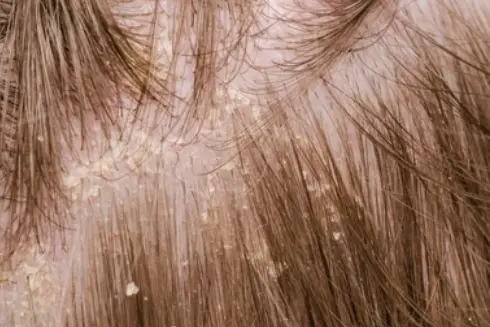
Scalp and non-scalp psori...

Xerophthalmia
Candidiasis, ক্যানডিয়াডিসিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.