 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Candidal cystitis - Generics
Candidal cystitis is a type of urinary tract infection caused by the yeast Candida albicans. It is relatively rare compared to bacterial UTIs, but can occur in people with weakened immune systems, those who have recently taken antibiotics, or those who have had recent urinary tract procedures.
The symptoms of candidal cystitis are similar to those of bacterial UTIs, including painful urination, frequent urination, and a feeling of urgency to urinate. Additionally, people with candidal cystitis may experience pelvic pain or discomfort, and blood may be present in the urine.
Diagnosis of candidal cystitis typically involves a urine culture to identify the presence of Candida albicans. Treatment may involve antifungal medications, such as fluconazole or amphotericin B, which are taken orally or intravenously. It is also important to identify and address any underlying risk factors, such as diabetes or a weakened immune system.
Prevention of candidal cystitis includes maintaining good hygiene, staying hydrated, urinating after sexual activity, and avoiding irritating substances, such as bubble baths or feminine hygiene sprays. It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect that you have candidal cystitis or if your symptoms persist despite treatment.

Low back pain

Slit-lamp examination
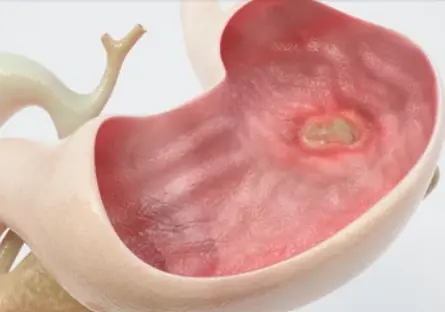
Ulcers

Functional rehabilitation...
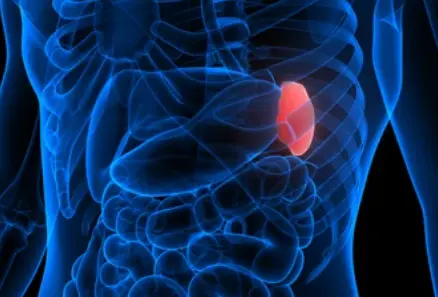
Spleen disorders

Pulmonary thromboembolism

Smoking cessation aid

Gingivitis
Candidal cystitis, ক্যান্ডিদাল সিস্টাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.