 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome - Generics
Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a severe and potentially life-threatening medical condition that can occur in adults who have experienced acute lung injury or other serious medical conditions. ARDS is characterized by the sudden onset of severe breathing difficulty, low oxygen levels, and lung inflammation, which can lead to respiratory failure and require mechanical ventilation.
The causes of ARDS can include direct lung injury, such as from pneumonia or inhaling toxic substances, or indirect lung injury, such as from sepsis or severe trauma. Risk factors for ARDS include smoking, alcohol abuse, obesity, and a history of chronic lung disease.
Diagnosis of ARDS typically involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests, such as chest X-rays and CT scans. Blood tests may also be performed to evaluate oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood.
Treatment for ARDS typically involves supportive care, such as mechanical ventilation to help with breathing, supplemental oxygen, and medications to help reduce inflammation in the lungs. In some cases, medications to treat the underlying cause of ARDS may also be necessary, such as antibiotics to treat pneumonia.
Prognosis for ARDS depends on the underlying cause, the severity of the condition, and how quickly treatment is initiated. In some cases, individuals with ARDS may require long-term mechanical ventilation or rehabilitation to recover their lung function.

Pneumococcal pneumonia

Fever blisters

Obesity

Peritoneal Dialysis
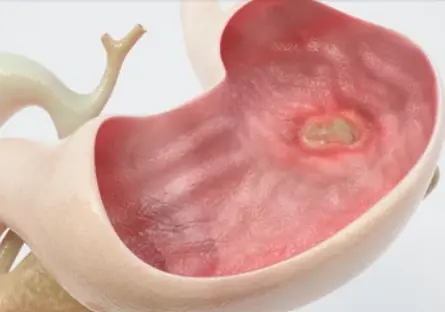
Duodenal ulcer
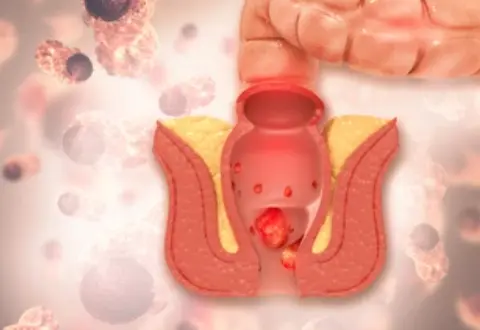
Hemorrhoids (piles)

Hypereosinophilic syndrom...

Swine flu
Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome, অ্যাডাল্ট রেসপিরেটরি ডিস্রেস সিনড্রোম
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.