 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Hysteria (Fainting) - Yoga remedies
Hysteria, also known as fainting or syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness that occurs when there is a sudden decrease in blood flow to the brain. It is a common condition that can be caused by various factors, such as dehydration, low blood sugar, or emotional stress.
Symptoms of hysteria typically include a sudden feeling of lightheadedness or dizziness, followed by a loss of consciousness. Other symptoms may include sweating, rapid heartbeat, and a feeling of nausea or weakness.
Some of the most common causes of hysteria include:
- Dehydration: A lack of fluids in the body can cause a drop in blood pressure, leading to fainting.
- Low blood sugar: Low blood sugar levels, also known as hypoglycemia, can cause weakness, dizziness, and fainting.
- Emotional stress: Extreme emotions, such as fear, anxiety, or excitement, can trigger a fainting episode.
- Blood pressure medications: Some medications used to treat high blood pressure can cause fainting as a side effect.
- Heart problems: Certain heart conditions, such as an irregular heartbeat or valve problems, can cause a sudden drop in blood pressure and lead to fainting.
Treatment for hysteria depends on the underlying cause. For mild cases, lying down and elevating the legs can help increase blood flow to the brain and prevent fainting. Drinking fluids and eating a small snack can also help in cases of dehydration or low blood sugar.
In more severe cases, medical treatment may be necessary. This may include administering fluids or medications to help regulate blood pressure, or treating an underlying heart condition.
Prevention of hysteria involves staying well-hydrated, maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, and avoiding triggers such as extreme emotions or prolonged standing.
In summary, hysteria or fainting is a temporary loss of consciousness caused by a sudden decrease in blood flow to the brain. Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may include lying down, drinking fluids, or medical intervention. Prevention involves staying hydrated, maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, and avoiding triggers. If you experience fainting or have concerns, it's important to consult with your healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.

Workforce reduction

Neuralgia

Nervousness
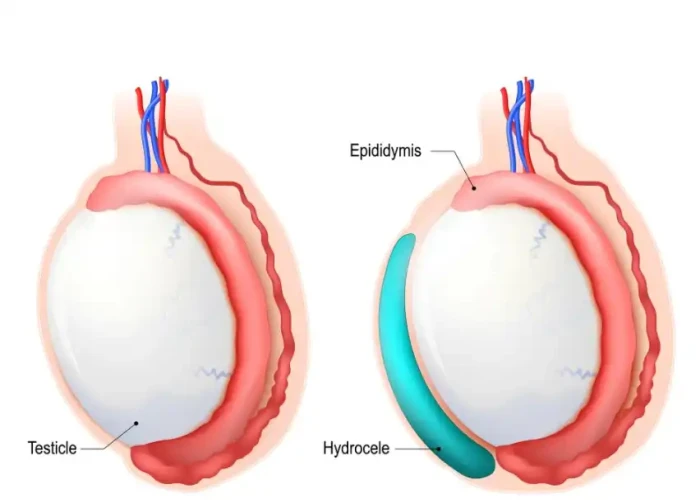
Hydrocele

Impotence
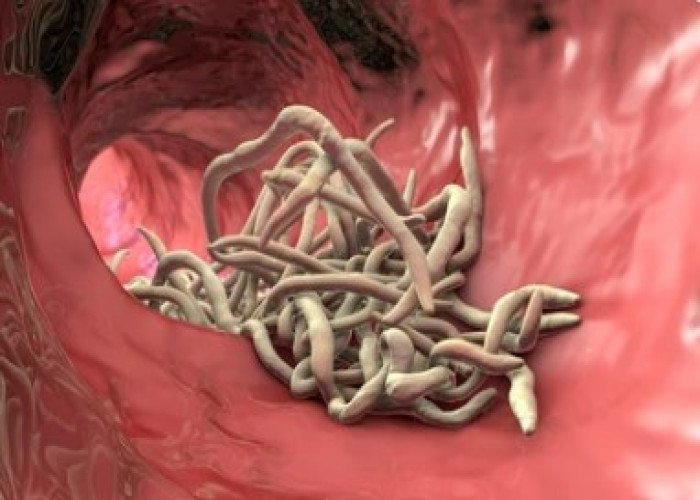
Worm

Inflammation of airways
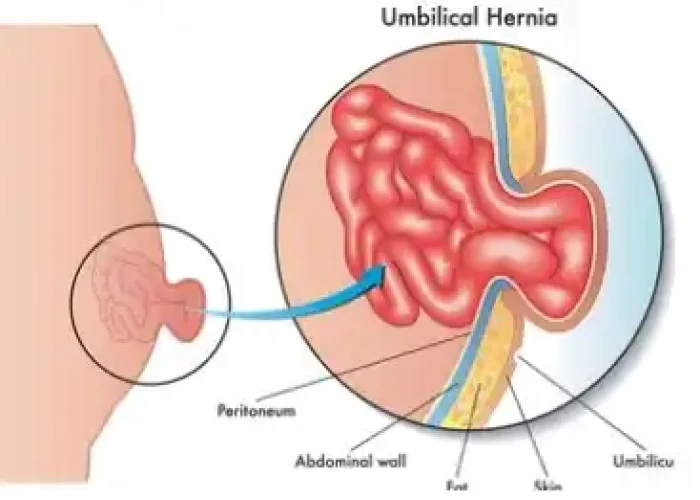
Hernia (Intestinal protru...
Hysteria, Fainting, হিষ্টিরিয়া, মূর্ছা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.