 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Midbrain Brainstem - Diseases
The midbrain is a part of the brainstem, which is the lower part of the brain that connects the brain to the spinal cord. It is located above the pons and below the thalamus, and it is divided into two parts, the tectum and the tegmentum.
The tectum of the midbrain is responsible for processing visual and auditory information. It contains two pairs of bumps called colliculi, the superior colliculi for processing visual information and the inferior colliculi for processing auditory information.
The tegmentum of the midbrain is involved in controlling several important functions, including eye movements, posture, and movement. It contains several nuclei, including the red nucleus, which is involved in controlling limb movement, and the substantia nigra, which is involved in the production of dopamine and plays a role in movement and reward.
Damage to the midbrain can result in a variety of neurological symptoms, depending on the location and extent of the damage. These can include problems with movement, sensation, vision, and hearing, among others.

Thymus

Mouth
Memory
Jaw
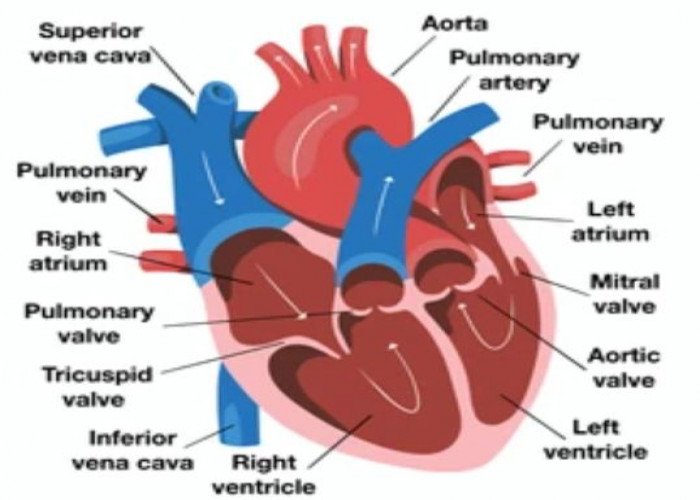
Heart

Nose
Muscles of breathing

Back
Midbrain Brainstem, মিডব্রেন ব্রেনস্টেম
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.