Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Tinnitus
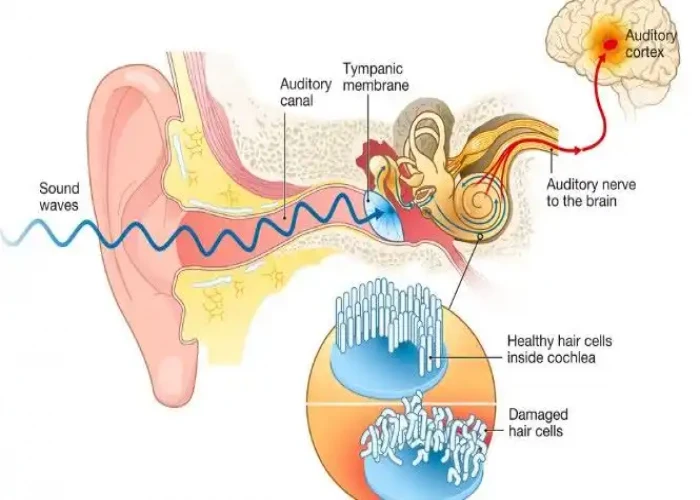
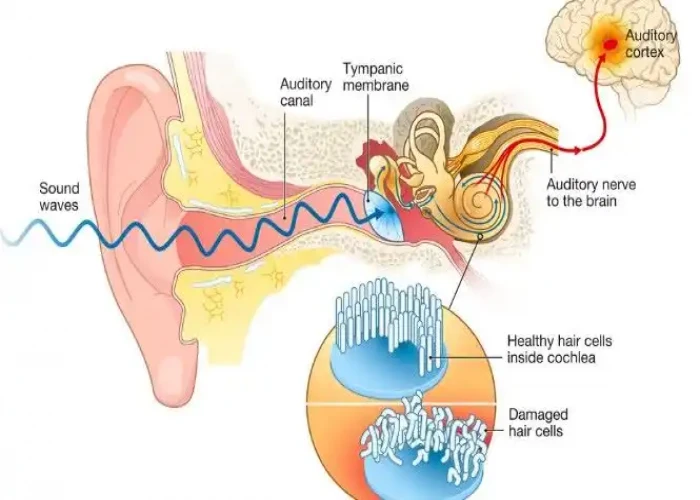
Tinnitus is when you experience ringing or other noises in one or both of your ears. The noise you hear when you have tinnitus isn't caused by an external sound, and other people usually can't hear it. Tinnitus is a common problem. It affects about 15% to 20% of people and is especially common in older adults.
Tinnitus is usually caused by an underlying condition, such as age-related hearing loss, an ear injury, or a problem with the circulatory system. For many people, tinnitus improves with treatment of the underlying cause or with other treatments that reduce or mask the noise, making tinnitus less noticeable.
Some common treatment options for tinnitus include:
- Sound therapy: This involves using white noise, music, or other sounds to mask or distract from the tinnitus noise.
- Counseling: This may involve cognitive behavioral therapy or other forms of counseling to help manage the emotional and psychological impact of tinnitus.
- Medication: Certain medications, such as antidepressants or anti-anxiety drugs, may be prescribed to help manage the symptoms of tinnitus.
- Medical interventions: In some cases, medical interventions, such as surgery or the use of cochlear implants, may be necessary to treat underlying conditions or severe cases of tinnitus.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent ringing or noise in the ears or head, as early diagnosis and treatment can help manage the symptoms and improve your quality of life.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Ringing in ears (tinnitus)
Disease Causes
Tinnitus
A number of health conditions can cause or worsen tinnitus. In many cases, an exact cause is never found.
Common causes of tinnitus
In many people, tinnitus is caused by one of the following:
- Hearing loss. There are tiny, delicate hair cells in your inner ear (cochlea) that move when your ear receives sound waves. This movement triggers electrical signals along the nerve from your ear to your brain (auditory nerve). Your brain interprets these signals as sound.
- If the hairs inside your inner ear are bent or broken — this happens as you age or when you are regularly exposed to loud sounds — they can "leak" random electrical impulses to your brain, causing tinnitus.
- Ear infection or ear canal blockage. Your ear canals can become blocked with a buildup of fluid (ear infection), earwax, dirt or other foreign materials. A blockage can change the pressure in your ear, causing tinnitus.
- Head or neck injuries. Head or neck trauma can affect the inner ear, hearing nerves or brain function linked to hearing. Such injuries usually cause tinnitus in only one ear.
- Medications. A number of medications may cause or worsen tinnitus. Generally, the higher the dose of these medications, the worse tinnitus becomes. Often the unwanted noise disappears when you stop using these drugs.
- Medications known to cause tinnitus include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and certain antibiotics, cancer drugs, water pills (diuretics), antimalarial drugs and antidepressants.
Other causes of tinnitus
Less common causes of tinnitus include other ear problems, chronic health conditions, and injuries or conditions that affect the nerves in your ear or the hearing center in your brain.
- Meniere's disease. Tinnitus can be an early indicator of Meniere's disease, an inner ear disorder that may be caused by abnormal inner ear fluid pressure.
- Eustachian tube dysfunction. In this condition, the tube in your ear connecting the middle ear to your upper throat remains expanded all the time, which can make your ear feel full.
- Ear bone changes. Stiffening of the bones in your middle ear (otosclerosis) may affect your hearing and cause tinnitus. This condition, caused by abnormal bone growth, tends to run in families.
- Muscle spasms in the inner ear. Muscles in the inner ear can tense up (spasm), which can result in tinnitus, hearing loss and a feeling of fullness in the ear. This sometimes happens for no explainable reason, but can also be caused by neurologic diseases, including multiple sclerosis.
- Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders. Problems with the TMJ, the joint on each side of your head in front of your ears, where your lower jawbone meets your skull, can cause tinnitus.
- Acoustic neuroma or other head and neck tumors. Acoustic neuroma is a noncancerous (benign) tumor that develops on the cranial nerve that runs from your brain to your inner ear and controls balance and hearing. Other head, neck or brain tumors can also cause tinnitus.
- Blood vessel disorders. Conditions that affect your blood vessels — such as atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, or kinked or malformed blood vessels — can cause blood to move through your veins and arteries with more force. These blood flow changes can cause tinnitus or make tinnitus more noticeable.
- Other chronic conditions. Conditions including diabetes, thyroid problems, migraines, anemia, and autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus have all been associated with tinnitus.
Disease Prevents
Tinnitus
In many cases, tinnitus is the result of something that can't be prevented. However, some precautions can help prevent certain kinds of tinnitus.
- Use hearing protection. Over time, exposure to loud sounds can damage the nerves in the ears, causing hearing loss and tinnitus. Try to limit your exposure to loud sounds. And if you cannot avoid loud sounds, use ear protection to help protect your hearing. If you use chain saws, are a musician, work in an industry that uses loud machinery or use firearms (especially pistols or shotguns), always wear over-the-ear hearing protection.
- Turn down the volume. Long-term exposure to amplified music with no ear protection or listening to music at very high volume through headphones can cause hearing loss and tinnitus.
- Take care of your cardiovascular health. Regular exercise, eating right and taking other steps to keep your blood vessels healthy can help prevent tinnitus linked to obesity and blood vessel disorders.
- Limit alcohol, caffeine and nicotine. These substances, especially when used in excess, can affect blood flow and contribute to tinnitus.
Disease Treatments
Treatment for tinnitus depends on whether your tinnitus is caused by an underlying health condition. If so, your doctor may be able to reduce your symptoms by treating the underlying cause. Examples include:
- Earwax removal. Removing an earwax blockage can decrease tinnitus symptoms.
- Treating a blood vessel condition. Underlying blood vessel conditions may require medication, surgery or another treatment to address the problem.
- Hearing aids. If your tinnitus is caused by noise-induced or age-related hearing loss, using hearing aids may help improve your symptoms.
- Changing your medication. If a medication you're taking appears to be the cause of tinnitus, your doctor may recommend stopping or reducing the drug, or switching to a different medication.
Noise suppression
Many times, tinnitus can't be cured. But there are treatments that can help make your symptoms less noticeable. Your doctor may suggest using an electronic device to suppress the noise. Devices include:
- White noise machines. These devices, which produce a sound similar to static, or environmental sounds such as falling rain or ocean waves, are often an effective treatment for tinnitus. You may want to try a white noise machine with pillow speakers to help you sleep. Fans, humidifiers, dehumidifiers and air conditioners in the bedroom also produce white noise and may help make tinnitus less noticeable at night.
- Masking devices. Worn in the ear and similar to hearing aids, these devices produce a continuous, low-level white noise that suppresses tinnitus symptoms.
Counseling
Behavioral treatment options aim to help you live with tinnitus by helping you change the way you think and feel about your symptoms. Over time, your tinnitus may bother you less. Counseling options include:
- Tinnitus retraining therapy (TRT). TRT is an individualized program that is usually administered by an audiologist or at a tinnitus treatment center. TRT combines sound masking and counseling from a trained professional. Typically, you wear a device in your ear that helps mask your tinnitus symptoms while you also receive directive counseling. Over time, TRT may help you notice tinnitus less and feel less distressed by your symptoms.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) or other forms of counseling. A licensed mental health professional or psychologist can help you learn coping techniques to make tinnitus symptoms less bothersome. Counseling can also help with other problems often linked to tinnitus, including anxiety and depression. Many mental health professionals offer CBT for tinnitus in individual or group sessions, and CBT programs are also available online.
Medications
Drugs can't cure tinnitus, but in some cases they may help reduce the severity of symptoms or complications. To help relieve your symptoms, your doctor may prescribe medication to treat an underlying condition or to help treat the anxiety and depression that often accompany tinnitus.
Potential future treatments
Researchers are investigating whether magnetic or electrical stimulation of the brain can help relieve symptoms of tinnitus. Examples include transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and deep brain stimulation.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Tinnitus and Learn More about Diseases
Neuroblastoma
Giardia infection (Giardiasis)
Bone metastasis

Jet lag disorder

Body dysmorphic disorder
Intestinal ischemia
Primary progressive aphasia
Aspergillosis
tinnitus, টিনিটাস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.