 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Urinary incontinence

Urinary incontinence is a common medical condition characterized by the involuntary leakage of urine. It can affect people of all ages, but it is more common in older adults and women who have given birth.
Urinary incontinence can be caused by various factors, such as weak pelvic floor muscles, damage to the nerves that control the bladder, certain medications, or medical conditions such as diabetes or urinary tract infections.
Symptoms of urinary incontinence can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Some people may experience only occasional leakage, while others may have more frequent and severe episodes of incontinence. Types of urinary incontinence include stress incontinence, urge incontinence, overflow incontinence, and mixed incontinence.
Diagnosis of urinary incontinence typically involves a medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as a urine analysis, bladder diary, and urodynamic testing. Treatment options for urinary incontinence may include lifestyle changes, such as pelvic floor exercises and dietary modifications, medications, or medical devices such as catheters or pessaries. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat the underlying cause of the incontinence.
The prognosis for urinary incontinence can vary depending on the cause and severity of the condition, as well as the person's overall health and age. However, with proper diagnosis and treatment, many people can effectively manage or even cure their incontinence.
If you are experiencing symptoms of urinary incontinence, it is important to consult a medical professional to discuss appropriate treatment options and prevent potential complications.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Burning during urination
- Urinary incontinence
Disease Causes
Urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence can be caused by everyday habits, underlying medical conditions or physical problems. A thorough evaluation by your doctor can help determine what's behind your incontinence.
Temporary urinary incontinence
Certain drinks, foods and medications may act as diuretics — stimulating your bladder and increasing your volume of urine. They include:
- Alcohol
- Caffeine
- Carbonated drinks and sparkling water
- Artificial sweeteners
- Chocolate
- Chili peppers
- Foods that are high in spice, sugar or acid, especially citrus fruits
- Heart and blood pressure medications, sedatives, and muscle relaxants
- Large doses of vitamin C
Urinary incontinence may also be caused by an easily treatable medical condition, such as:
- Urinary tract infection. Infections can irritate your bladder, causing you to have strong urges to urinate and, sometimes, incontinence.
- Constipation. The rectum is located near the bladder and shares many of the same nerves. Hard, compacted stool in your rectum causes these nerves to be overactive and increase urinary frequency.
Persistent urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence can also be a persistent condition caused by underlying physical problems or changes, including:
- Pregnancy. Hormonal changes and the increased weight of the fetus can lead to stress incontinence.
- Childbirth. Vaginal delivery can weaken muscles needed for bladder control and damage bladder nerves and supportive tissue, leading to a dropped (prolapsed) pelvic floor. With prolapse, the bladder, uterus, rectum or small intestine can get pushed down from the usual position and protrude into the vagina. Such protrusions may be associated with incontinence.
- Changes with age. Aging of the bladder muscle can decrease the bladder's capacity to store urine. Also, involuntary bladder contractions become more frequent as you get older.
- Menopause. After menopause, women produce less estrogen, a hormone that helps keep the lining of the bladder and urethra healthy. Deterioration of these tissues can aggravate incontinence.
- Enlarged prostate. Especially in older men, incontinence often stems from enlargement of the prostate gland, a condition known as benign prostatic hyperplasia.
- Prostate cancer. In men, stress incontinence or urge incontinence can be associated with untreated prostate cancer. But more often, incontinence is a side effect of treatments for prostate cancer.
- Obstruction. A tumor anywhere along your urinary tract can block the normal flow of urine, leading to overflow incontinence. Urinary stones — hard, stonelike masses that form in the bladder — sometimes cause urine leakage.
- Neurological disorders. Multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, a stroke, a brain tumor or a spinal injury can interfere with nerve signals involved in bladder control, causing urinary incontinence.
Disease Prevents
Urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence isn't always preventable. However, to help decrease your risk:
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Practice pelvic floor exercises
- Avoid bladder irritants, such as caffeine, alcohol and acidic foods
- Eat more fiber, which can prevent constipation, a cause of urinary incontinence
- Don't smoke, or seek help to quit if you're a smoker
Disease Treatments
Treatment for urinary incontinence depends on the type of incontinence, its severity and the underlying cause. A combination of treatments may be needed. If an underlying condition is causing your symptoms, your doctor will first treat that condition.
Your doctor may recommend less invasive treatments to start with and move on to other options if these techniques fail to help you.
Behavioral techniques
Your doctor may recommend:
- Bladder training, to delay urination after you get the urge to go. You may start by trying to hold off for 10 minutes every time you feel an urge to urinate. The goal is to lengthen the time between trips to the toilet until you're urinating only every 2.5 to 3.5 hours.
- Double voiding, to help you learn to empty your bladder more completely to avoid overflow incontinence. Double voiding means urinating, then waiting a few minutes and trying again.
- Scheduled toilet trips, to urinate every two to four hours rather than waiting for the need to go.
- Fluid and diet management, to regain control of your bladder. You may need to cut back on or avoid alcohol, caffeine or acidic foods. Reducing liquid consumption, losing weight or increasing physical activity also can ease the problem.
Pelvic floor muscle exercises
Your doctor may recommend that you do these exercises frequently to strengthen the muscles that help control urination. Also known as Kegel exercises, these techniques are especially effective for stress incontinence but may also help urge incontinence.
To do pelvic floor muscle exercises, imagine that you're trying to stop your urine flow. Then:
- Tighten (contract) the muscles you would use to stop urinating and hold for five seconds, and then relax for five seconds. (If this is too difficult, start by holding for two seconds and relaxing for three seconds.)
- Work up to holding the contractions for 10 seconds at a time.
- Aim for at least three sets of 10 repetitions each day.
To help you identify and contract the right muscles, your doctor may suggest that you work with a pelvic floor physical therapist or try biofeedback techniques.
Medications
Medications commonly used to treat incontinence include:
- Anticholinergics. These medications can calm an overactive bladder and may be helpful for urge incontinence. Examples include oxybutynin (Ditropan XL), tolterodine (Detrol), darifenacin (Enablex), fesoterodine (Toviaz), solifenacin (Vesicare) and trospium chloride.
- Mirabegron (Myrbetriq). Used to treat urge incontinence, this medication relaxes the bladder muscle and can increase the amount of urine your bladder can hold. It may also increase the amount you are able to urinate at one time, helping to empty your bladder more completely.
- Alpha blockers. In men who have urge incontinence or overflow incontinence, these medications relax bladder neck muscles and muscle fibers in the prostate and make it easier to empty the bladder. Examples include tamsulosin (Flomax), alfuzosin (Uroxatral), silodosin (Rapaflo), and doxazosin (Cardura).
- Topical estrogen. Applying low-dose, topical estrogen in the form of a vaginal cream, ring or patch may help tone and rejuvenate tissues in the urethra and vaginal areas.
Electrical stimulation
Electrodes are temporarily inserted into your rectum or vagina to stimulate and strengthen pelvic floor muscles. Gentle electrical stimulation can be effective for stress incontinence and urge incontinence, but you may need multiple treatments over several months.
Medical devices
Devices designed to treat women with incontinence include:
- Urethral insert, a small, tampon-like disposable device inserted into the urethra before a specific activity, such as tennis, that can trigger incontinence. The insert acts as a plug to prevent leakage and is removed before urination.
- Pessary, a flexible silicone ring that you insert into your vagina and wear all day. The device is also used in women with vaginal prolapse. The pessary helps support the urethra, to prevent urine leakage.
Interventional therapies
Interventional therapies that may help with incontinence include:
- Bulking material injections. A synthetic material is injected into tissue surrounding the urethra. The bulking material helps keep the urethra closed and reduce urine leakage. This procedure is for the treatment of stress incontinence and is generally less effective than more-invasive treatments such as surgery. It may need to be repeated more than once.
- OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox). Injections of Botox into the bladder muscle may benefit people who have an overactive bladder and urge incontinence. Botox is generally prescribed to people only if other treatments haven't been successful.
- Nerve stimulators. There are two types of devices that use painless electrical pulses to stimulate the nerves involved in bladder control (sacral nerves). One type is implanted under your skin in your buttock and connected to wires on the lower back. The other type is a removable plug that is inserted into the vagina. Stimulating the sacral nerves can control overactive bladder and urge incontinence if other therapies haven't worked.
Surgery
If other treatments aren't working, several surgical procedures can treat the problems that cause urinary incontinence:
- Sling procedures. Synthetic material (mesh) or strips of your body's tissue are used to create a pelvic sling underneath your urethra and the area of thickened muscle where the bladder connects to the urethra (bladder neck). The sling helps keep the urethra closed, especially when you cough or sneeze. This procedure is used to treat stress incontinence.
- Bladder neck suspension. This procedure is designed to provide support to your urethra and bladder neck — an area of thickened muscle where the bladder connects to the urethra. It involves an abdominal incision, so it's done during general or spinal anesthesia.
- Prolapse surgery. In women who have pelvic organ prolapse and mixed incontinence, surgery may include a combination of a sling procedure and prolapse surgery. Repair of pelvic organ prolapse alone does not routinely improve urinary incontinence symptoms.
- Artificial urinary sphincter. A small, fluid-filled ring is implanted around the bladder neck to keep the urinary sphincter shut until there's a need to urinate. To urinate, you press a valve implanted under your skin that causes the ring to deflate and allows urine from your bladder to flow.
Absorbent pads and catheters
If medical treatments can't eliminate your incontinence, you can try products that help ease the discomfort and inconvenience of leaking urine:
- Pads and protective garments. Most products are no more bulky than normal underwear and can be easily worn under everyday clothing. Men who have problems with dribbles of urine can use a drip collector — a small pocket of absorbent padding that's worn over the penis and held in place by close-fitting underwear.
- Catheter. If you're incontinent because your bladder doesn't empty properly, your doctor may recommend that you learn to insert a soft tube (catheter) into your urethra several times a day to drain your bladder. You'll be instructed on how to clean these catheters for safe reuse.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Urinary incontinence and Learn More about Diseases

Balance problems
Sarcoidosis

Nail fungus

Nonmelanoma skin cancer
Bile reflux

Radiation sickness
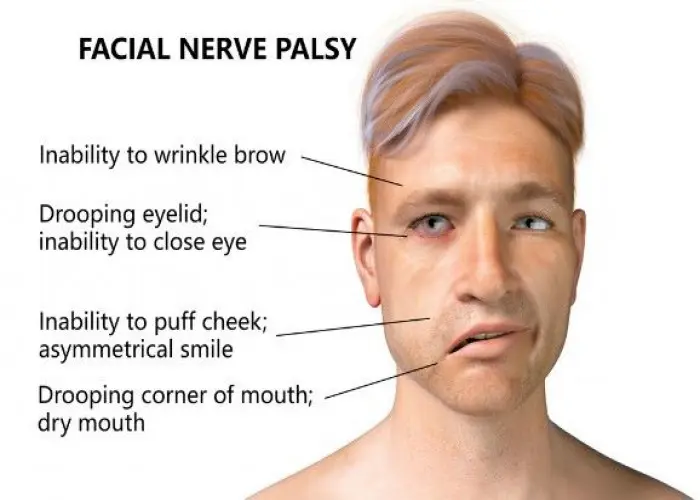
Facial palsy
Buerger's disease
urinary incontinence, প্রস্রাবে অসংযম
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
