 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Staph infections

Staphylococcus aureus (staph) is a type of bacteria that is commonly found on the skin and in the nose. While many people carry staph without any symptoms, sometimes the bacteria can cause an infection. Staph infections can range from minor skin infections to life-threatening infections that affect the bloodstream or organs.
Symptoms of a staph infection depend on the type of infection but may include redness, swelling, pain, and warmth at the site of the infection, as well as fever, chills, and fatigue in more severe cases. Staph infections can also cause boils, impetigo, cellulitis, and other skin infections.
Treatment of a staph infection typically involves antibiotics, which may be given orally or intravenously, depending on the severity of the infection. In some cases, surgical drainage of an abscess may also be necessary.
Prevention of staph infections can be done by practicing good hygiene, washing hands regularly, keeping cuts and scrapes clean and covered, avoiding sharing personal items like towels or razors, and avoiding close contact with people who have a staph infection.
It is important for individuals with a suspected staph infection to seek medical attention to receive an appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan. A healthcare provider can help determine the severity of the infection and recommend appropriate treatment options to promote healing and prevent the further spread of the bacteria.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Red skin
- Abdomen pain
- Muscle pain
- Confusion (Hallucinations)
- Fever
- Low blood pressure (hypotension)
- Diarrhea
- Nausea or vomiting
- Blisters
- Swollen skin
- Skin boils
- Swollen joint
Disease Causes
Staph infections
Many people carry staph bacteria and never develop staph infections. However, if you develop a staph infection, there's a good chance that it's from bacteria you've been carrying around for some time.
These bacteria can also be transmitted from person to person. Because staph bacteria are so hardy, they can live on objects such as pillowcases or towels long enough to transfer to the next person who touches them.
Staph bacteria are able to survive:
- Drying
- Extremes of temperature
- Stomach acid
Disease Prevents
Staph infections
These commonsense precautions can help lower your risk of developing staph infections:
- Wash your hands. Careful hand-washing is your best defense against germs. Wash your hands with soap and water briskly for at least 20 seconds. Then dry them with a disposable towel and use another towel to turn off the faucet. If your hands aren't visibly dirty, you can use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
- Wash your hands with soap and water regularly, such as before, during and after making food; after handling raw meat or poultry; before eating; after using the bathroom; and after touching an animal or animal waste.
- Keep wounds covered. Keep cuts and abrasions clean and covered with sterile, dry bandages until they heal. The pus from infected sores often contains staph bacteria, and keeping wounds covered will help keep the bacteria from spreading.
- Reduce tampon risks. Toxic shock syndrome is caused by staph bacteria. Tampons left in for long periods can be a breeding ground for staph bacteria. You can reduce your chances of getting toxic shock syndrome by changing your tampon frequently — at least every four to eight hours. Use the lowest absorbency tampon you can. Try to alternate tampons with sanitary napkins whenever possible.
- Keep personal items personal. Avoid sharing personal items such as towels, sheets, razors, clothing and athletic equipment. Staph infections can spread on objects, as well as from person to person.
- Wash clothing and bedding in hot water. Staph bacteria can survive on clothing and bedding that isn't properly washed. To get bacteria off clothing and sheets, wash them in hot water whenever possible.
- Also, use bleach on any bleach-safe materials. Drying in the dryer is better than air-drying, but staph bacteria may survive the clothes dryer.
- Take food safety precautions. Wash your hands before handling food. If food will be out for a while, make sure that hot foods stay hot — above 140 F (60 C) — and that cold foods stay at 40 F (4.4 C) or below. Refrigerate leftovers as soon as possible. Wash cutting boards and counters with soap and water.
Disease Treatments
Treatment of a staph infection may include:
- Antibiotics. Your doctor may perform tests to identify the staph bacteria behind your infection, and to help choose the antibiotic that will work best. Antibiotics commonly prescribed to treat staph infections include certain cephalosporins such as cefazolin; nafcillin or oxacillin; vancomycin; daptomycin (Cubicin); telavancin (Vibativ); or linezolid (Zyvox).
- Vancomycin increasingly is required to treat serious staph infections because so many strains of staph bacteria have become resistant to other traditional medicines. But vancomycin and some other antibiotics have to be given intravenously.
- If you're given an oral antibiotic, be sure to take it as directed, and to finish all of the medication prescribed by your doctor. Ask your doctor what signs and symptoms you should watch for that might indicate your infection is worsening.
- Wound drainage. If you have a skin infection, your doctor will likely make an incision into the sore to drain fluid that has collected there.
- Device removal. If your infection involves a device or prosthetic, prompt removal of the device is needed. For some devices, removal might require surgery.
Antibiotic resistance
Staph bacteria are very adaptable, and many varieties have become resistant to one or more antibiotics. For example, only about 5% of today's staph infections can be cured with penicillin.
The emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains of staph bacteria — often described as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains — has led to the use of IV antibiotics, such as vancomycin or daptomycin, with the potential for more side effects.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Staph infections and Learn More about Diseases

Age spots (liver spots)

Lazy eye (amblyopia)
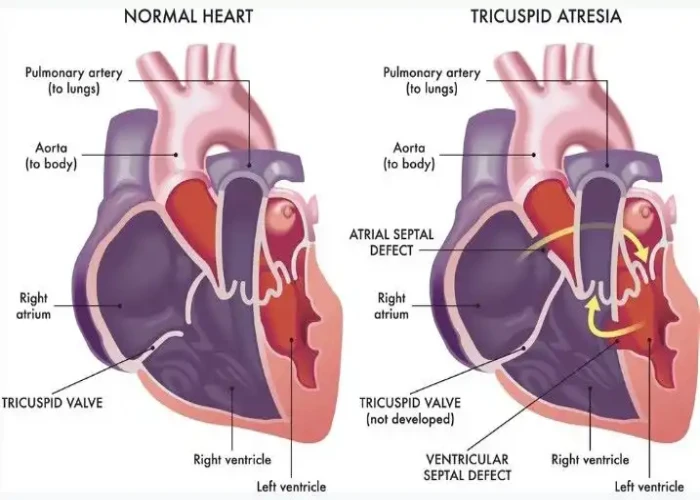
Tricuspid atresia

Bad breath
Sore throat
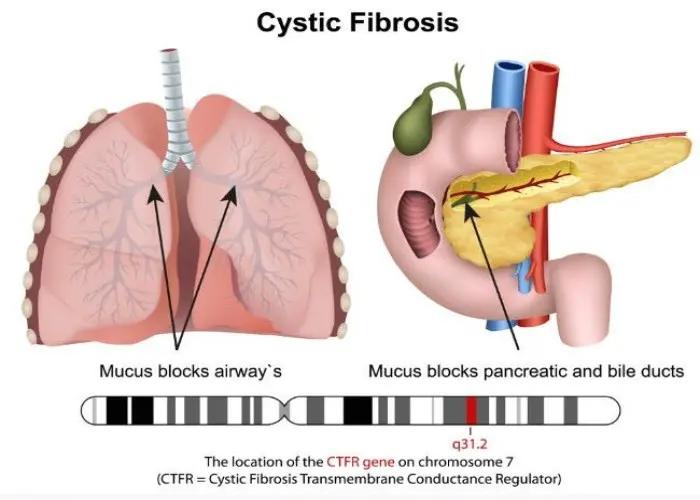
Cystic fibrosis
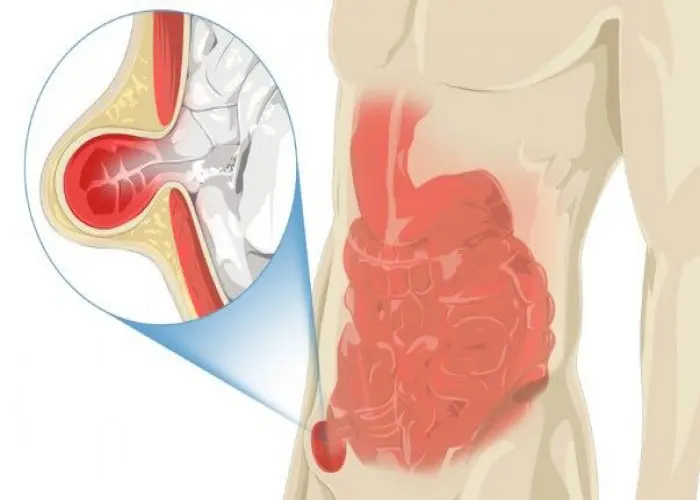
Inguinal hernia
Vasovagal syncope
staph infections, স্ট্যাফ সংক্রমণ, স্ট্যাফ ইনফেকশন
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
