Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Sprains
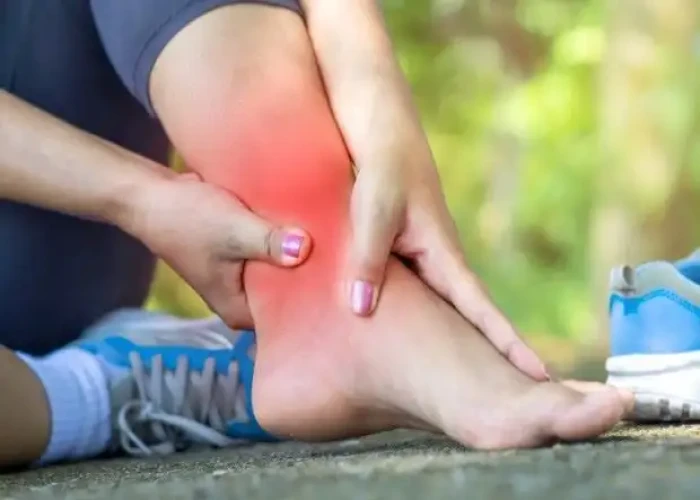
A sprain is an injury to a ligament, which is the tough, fibrous tissue that connects bones to each other and supports joints. Sprains are common and can occur in any joint, but are most commonly seen in the ankle, wrist, and knee. They can be caused by a sudden twist or wrenching of a joint, or by overuse of the joint.
Symptoms of a sprain include pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty moving the joint. In more severe cases, the joint may be unstable or visibly deformed.
The treatment of a sprain typically involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE therapy) to reduce pain and swelling. Over-the-counter pain medication can also be used to manage pain. In more severe cases, a healthcare provider may recommend physical therapy or a brace to help stabilize the joint during healing.
Prevention of sprains can be done by warming up before exercise, practicing good technique during physical activity, and wearing appropriate protective gear or footwear.
It is important for individuals with a suspected sprain to seek medical attention to receive an appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan. A healthcare provider can help determine the severity of the injury and recommend appropriate treatment options to promote healing and prevent further damage to the joint.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Ankle problems
- Joint pain
- Joint stiffness
- Swollen joint
- Hearing or feeling a "pop" in joint at the time of injury
- Limited ability to move the affected joint
Disease Causes
Sprains
A sprain occurs when you overextend or tear a ligament while severely stressing a joint. Sprains often occur in the following circumstances:
- Ankle — Walking or exercising on an uneven surface, landing awkwardly from a jump
- Knee — Pivoting during an athletic activity
- Wrist — Landing on an outstretched hand during a fall
- Thumb — Skiing injury or overextension when playing racquet sports, such as tennis
Children have areas of softer tissue, called growth plates, near the ends of their bones. The ligaments around a joint are often stronger than these growth plates, so children are more likely to experience a fracture than a sprain.
Disease Prevents
Sprains
Regular stretching and strengthening exercises for your sport, fitness or work activity, as part of an overall physical conditioning program, can help to minimize your risk of sprains. Try to be in shape to play your sport; don't play your sport to get in shape. If you have a physically demanding occupation, regular conditioning can help prevent injuries.
You can protect your joints in the long term by working to strengthen and condition the muscles around the joint that has been injured. The best brace you can give yourself is your own "muscle brace." Ask your doctor about appropriate conditioning and stability exercises. Also, use footwear that offers support and protection.
Disease Treatments
For immediate self-care of a sprain, try the R.I.C.E. approach — rest, ice, compression, elevation:
- Rest. Avoid activities that cause pain, swelling or discomfort. But don't avoid all physical activity.
- Ice. Even if you're seeking medical help, ice the area immediately. Use an ice pack or slush bath of ice and water for 15 to 20 minutes each time and repeat every two to three hours while you're awake for the first few days after the injury.
- Compression. To help stop swelling, compress the area with an elastic bandage until the swelling stops. Don't wrap it too tightly or you may hinder circulation. Begin wrapping at the end farthest from your heart. Loosen the wrap if the pain increases, the area becomes numb or swelling is occurring below the wrapped area.
- Elevation. Elevate the injured area above the level of your heart, especially at night, which allows gravity to help reduce swelling.
Over-the-counter pain medications such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) also can be helpful.
After the first two days, gently begin to use the injured area. You should see a gradual, progressive improvement in the joint's ability to support your weight or your ability to move without pain. Recovery from sprains can take days to months.
A physical therapist can help you to maximize stability and strength of the injured joint or limb. Your doctor may suggest that you immobilize the area with a brace or splint. For some injuries, such as a torn ligament, surgery may be considered.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Sprains and Learn More about Diseases

Heat rash
Paget's disease of bone

Swollen lymph nodes
Tooth abscess

Anal itching
Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors
Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome
Ringworm (body)
sprains, স্প্রেনস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.