 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Secondary hypertension

Secondary hypertension is high blood pressure that is caused by an underlying medical condition or a medication. Unlike primary hypertension, which has no identifiable cause, secondary hypertension can be attributed to a specific cause.
Some common causes of secondary hypertension include:
- Kidney disease or renal artery stenosis
- Endocrine disorders, such as hyperthyroidism or Cushing's syndrome
- Sleep apnea
- Medications, such as birth control pills, decongestants, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Coarctation of the aorta or other congenital heart defects
Diagnosis of secondary hypertension typically involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and various tests to identify the underlying cause. Treatment of secondary hypertension involves addressing the underlying condition or discontinuing the medication that is causing the high blood pressure. In some cases, medications may also be prescribed to help lower blood pressure.
It is important to properly diagnose and treat secondary hypertension, as it can increase the risk of serious health problems such as heart attack, stroke, and kidney failure.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- High blood pressure that doesn't respond to blood pressure medications (resistant hypertension)
- Sudden-onset high blood pressure before age 30 or after age 55
- No family history of high blood pressure
Disease Causes
Secondary hypertension
Many different diseases and health conditions can cause secondary hypertension. Several kidney diseases may cause secondary hypertension, including:
- Diabetes complications (diabetic nephropathy). Diabetes can damage your kidneys' filtering system, which can lead to high blood pressure.
- Polycystic kidney disease. In this inherited condition, cysts in your kidneys prevent the kidneys from working normally and can raise blood pressure.
- Glomerular disease. Your kidneys filter waste and sodium using microscopic filters called glomeruli that can sometimes become swollen. If the swollen glomeruli can't work normally, you may develop high blood pressure.
- Renovascular hypertension. This type of high blood pressure is caused by narrowing (stenosis) of one or both arteries leading to your kidneys.
- Renovascular hypertension is often caused by the same type of fatty plaques that can damage your coronary arteries (atherosclerosis) or a separate condition in which the muscle and fibrous tissues of the renal artery wall thicken and harden into rings (fibromuscular dysplasia).
Medical conditions affecting hormone levels also may cause secondary hypertension. These conditions may include:
- Cushing syndrome. In this condition, corticosteroid medications may cause secondary hypertension, or hypertension may be caused by a pituitary tumor or other factors that cause the adrenal glands to produce too much of the hormone cortisol.
- Aldosteronism. The adrenal glands produce too much of the hormone aldosterone. This makes your kidneys retain salt and water and lose too much potassium, which raises blood pressure.
- Pheochromocytoma. This rare tumor, usually found in an adrenal gland, produces too much of the hormones adrenaline and noradrenaline, which can lead to long-term high blood pressure or short-term spikes in blood pressure.
- Thyroid problems. When the thyroid gland doesn't produce enough thyroid hormone (hypothyroidism) or produces too much thyroid hormone (hyperthyroidism), high blood pressure can result.
- Hyperparathyroidism. The parathyroid glands control levels of calcium and phosphorus in your body. If the glands release too much parathyroid hormone, the amount of calcium in your blood rises — which triggers a rise in blood pressure.
Other possible causes of secondary hypertension include:
- Coarctation of the aorta. In this condition, present at birth, the body's main artery (aorta) is narrowed (coarctation). This forces the heart to pump harder to get blood through the aorta and to the rest of your body. As a result, blood pressure increases — particularly in your arms.
- Sleep apnea. In this condition, often marked by severe snoring, breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep, causing you to not get enough oxygen.
- Not getting enough oxygen may damage the lining of the blood vessel walls, which may make it harder for your blood vessels to control your blood pressure. In addition, sleep apnea causes part of the nervous system to be overactive and release certain chemicals that increase blood pressure.
- Obesity. As you gain weight, the amount of blood flowing through your body increases. This puts added pressure on your artery walls, increasing your blood pressure.
- Being overweight also increases the heart rate and makes it harder for your blood vessels to move blood. In addition, fat deposits can release chemicals that raise blood pressure.
- Pregnancy. Pregnancy can make existing high blood pressure worse or cause high blood pressure to develop (pregnancy-induced hypertension or preeclampsia).
- Medications and supplements. Various prescription medications — such as pain relievers, birth control pills, antidepressants and drugs used after organ transplants — can cause or worsen high blood pressure in some people.
- Over-the-counter decongestants and certain herbal supplements, including ginseng, licorice and ephedra (ma-huang), may have the same effect. Many illegal drugs, such as cocaine and methamphetamine, also increase blood pressure.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Treatment for secondary hypertension involves treating the underlying medical condition with medications or surgery. Once the underlying condition is treated, your blood pressure might decrease or return to normal.
You may need to continue to take blood pressure medication as well, and any underlying medical condition you have may affect your doctor's choice of medication.
Possible drug choices include:
- Thiazide diuretics. Diuretics, sometimes called water pills, are medications that help your kidneys eliminate sodium and water. Thiazide diuretics are often the first — but not the only — choice in high blood pressure medications.
- Diuretics are often generic and tend to be less expensive than other high blood pressure medications. If you're not taking a diuretic and your blood pressure remains high, talk to your doctor about adding one or replacing a drug you currently take with a diuretic. Possible side effects of diuretics include weakness, leg cramps and a higher risk of sexual dysfunction.
- Beta blockers. These medications reduce the workload on your heart and open your blood vessels, causing your heart to beat slower and with less force. When prescribed alone, beta blockers don't work as well in Black people — but they're effective when combined with a thiazide diuretic.
- Possible side effects include fatigue, sleep problems, a slowed heart rate, and cold hands and feet. In addition, beta blockers generally aren't prescribed for people with asthma, as they can increase muscle spasms in the lungs.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. These medications help relax blood vessels by blocking the formation of a natural chemical that narrows blood vessels. ACE inhibitors may be especially important in treating high blood pressure in people with coronary artery disease, heart failure or kidney failure.
- Like beta blockers, ACE inhibitors don't work as well in Black people when prescribed alone, but they're effective when combined with a thiazide diuretic. Possible side effects include dizziness and coughing. ACE inhibitors should not be taken during pregnancy.
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers. These medications help relax blood vessels by blocking the action — not the formation — of a natural chemical that narrows blood vessels. Like ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers often are useful for people with coronary artery disease, heart failure or kidney failure.
- These medications have fewer potential side effects than do ACE inhibitors. Angiotensin II receptor blockers should not be used during pregnancy.
- Calcium channel blockers. These medications help relax the muscles of your blood vessels or slow your heart rate. Calcium channel blockers may work better for some people than ACE inhibitors or beta blockers alone. Possible side effects include water retention, dizziness and constipation.
- Grapefruit juice interacts with some calcium channel blockers, increasing levels of the medication in your blood and putting you at a higher risk of side effects. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if your medication is affected by grapefruit juice.
- Direct renin inhibitors. These medications relax and widen the arteries by prevention the action of a protein (enzyme) called renin. Renin is released by your kidneys and helps control blood pressure. An example of a direct renin inhibitor is as aliskiren (Tekturna).
- Common side effects of aliskiren include dizziness and diarrhea. If you have diabetes or moderate to severe kidney problems, you shouldn't use aliskiren in combination with ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers.
- Treatment for secondary hypertension can sometimes be complicated. You may need more than one medication combined with lifestyle changes to control your high blood pressure. Your doctor will want to see you more frequently — possibly as often as once a month — until your blood pressure is controlled. Your doctor may also recommend that you keep track of your blood pressure at home.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Secondary hypertension and Learn More about Diseases
Nephrotic syndrome
Lichen nitidus

Sleep apnea
Contact dermatitis
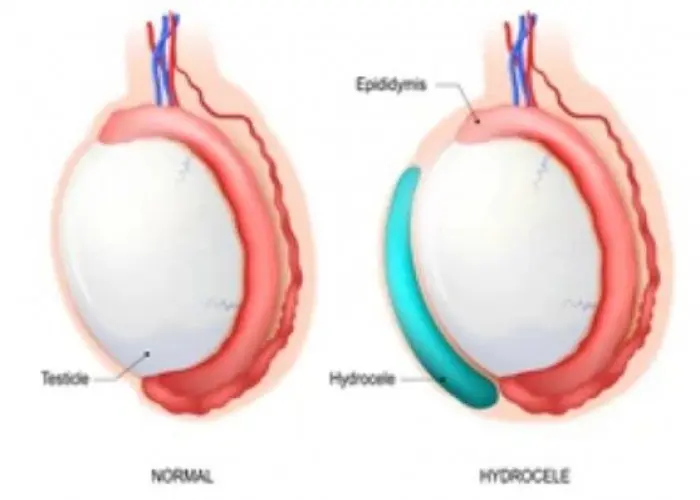
Hydrocele
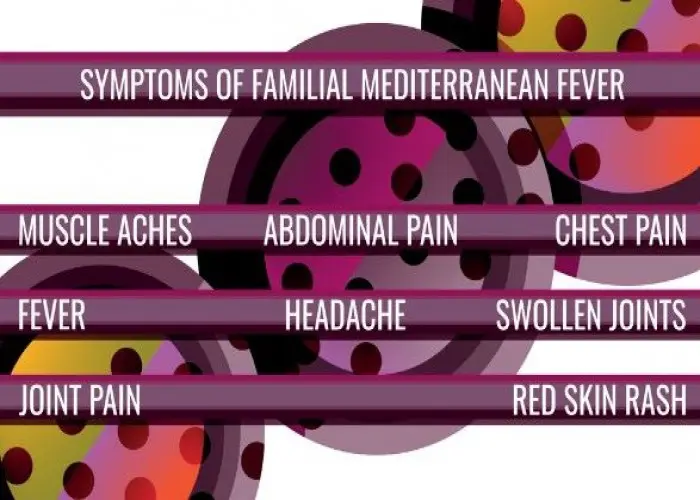
Familial Mediterranean fever
Miscarriage (Abortion)
Epilepsy
secondary hypertension, সেকেন্ডারি হাইপারটেনশন
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
