Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Rosacea

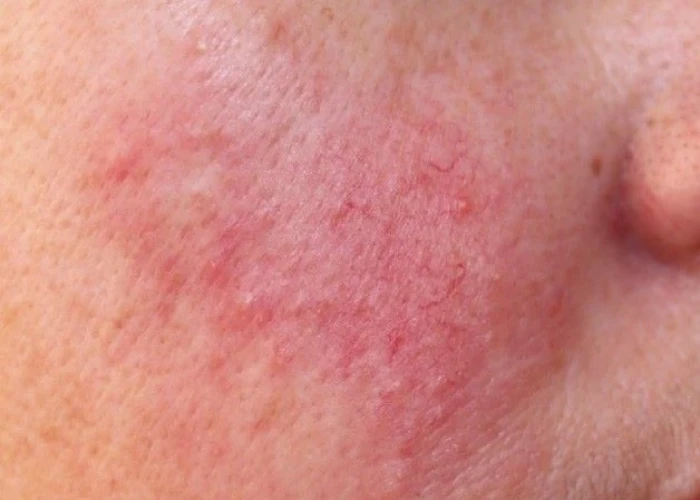
Rosacea is a common, chronic skin condition that primarily affects the face. It is characterized by redness, flushing, and the development of small, red, pus-filled bumps, as well as visible blood vessels in the affected area.
The exact cause of rosacea is not fully understood, but it is thought to be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors, such as exposure to sunlight, stress, and certain foods.
Symptoms of rosacea may include:
- Redness on the cheeks, nose, chin, or forehead
- Visible blood vessels on the face
- Swollen, red bumps or pimples on the face
- Eye problems, including dryness, irritation, and redness
While there is no cure for rosacea, there are several treatment options that can help manage the symptoms. These may include topical medications, such as creams and gels, as well as oral antibiotics, which can help reduce inflammation and control the growth of bacteria on the skin. In some cases, laser therapy may also be recommended to help reduce the appearance of visible blood vessels.
In addition to medical treatments, there are several self-care measures that can help manage the symptoms of rosacea. These may include avoiding triggers, such as sunlight, spicy foods, and alcohol, and using gentle skincare products that are fragrance-free and do not contain alcohol or other irritants.
Overall, the prognosis for rosacea is generally good, and most people are able to manage their symptoms with appropriate treatment and self-care measures. However, it is important to seek medical attention if symptoms are severe or do not respond to treatment, as this may indicate an underlying medical condition.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Black skin
- In some people, the eye symptoms precede the skin symptoms.
- This is known as ocular rosacea.
- Many people with rosacea also experience dry, irritated, swollen eyes and red, swollen eyelids.
- Many people with rosacea also develop pimples on their faces that resemble acne.
- Small blood vessels on the nose and cheeks often swell and become visible.
- Rosacea usually causes a persistent redness in the central part of the face.
- Enlarged nose
- Swollen nose
- Swollen eye (Conjunctivitis)
- Eye pain or burning
- Visible veins
- Over time, rosacea can thicken the skin on the nose, causing the nose to appear bulbous (rhinophyma).
Disease Causes
Rosacea
The cause of rosacea is unknown, but it could be due to an overactive immune system, heredity, environmental factors or a combination of these. Rosacea is not caused by poor hygiene and it's not contagious.
Flare-ups might be triggered by:
- Hot drinks and spicy foods
- Red wine and other alcoholic beverages
- Temperature extremes
- Sun or wind
- Emotions
- Exercise
- Drugs that dilate blood vessels, including some blood pressure medications
- Some cosmetic, skin or hair care products
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Treatment for rosacea focuses on controlling signs and symptoms. Most often this requires a combination of good skin care and prescription drugs.
The duration of your treatment depends on the type and severity of your signs and symptoms. Recurrence is common.
Medications
New rosacea medications have been developed in recent years. The type of medication your doctor prescribes depends on which signs and symptoms you're experiencing. You may need to try different options or a combination of drugs to find a treatment that works for you.
Prescription drugs for rosacea include:
- Topical drugs that reduce flushing. For mild to moderate rosacea, your doctor may prescribe a cream or gel that you apply to the affected skin. Brimonidine (Mirvaso) and oxymetazoline (Rhofade) reduce flushing by constricting blood vessels. You may see results within 12 hours after use. The effect on the blood vessels is temporary, so the medication needs to be applied regularly to maintain improvements.
- Other topical products help control the pimples of mild rosacea. These drugs include azelaic acid (Azelex, Finacea), metronidazole (Metrogel, Noritate, others) and ivermectin (Soolantra). With azelaic acid and metronidazole, noticeable improvements generally don't appear for two to six weeks. Ivermectin may take even longer to improve skin, but it results in a longer remission than does metronidazole.
- Oral antibiotics. Your doctor may prescribe an oral antibiotic such as doxycycline (Oracea, others) for moderate to severe rosacea with bumps and pimples.
- Oral acne drug. If you have severe rosacea that doesn't respond to other therapies, your doctor may suggest isotretinoin (Amnesteem, Claravis, others). It's a powerful oral acne drug that also helps clear up acnelike lesions of rosacea. Don't use this drug during pregnancy as it can cause serious birth defects.
Laser therapy
Laser therapy can make enlarged blood vessels less visible. Because the laser targets visible veining, it's most effective on skin that isn't tanned, brown or black.
Talk with your doctor about the risks and benefits of laser therapy. Side effects of laser therapy for rosacea include swelling and bruising that might last for several days. Icing and gentle skin care will be needed during the recovery period. On brown or black skin, laser treatment might cause long-term or permanent discoloration of the treated skin.
The full effect of the treatment might not be noticeable for weeks. Repeat treatments may be needed periodically to maintain the improved appearance of your skin.
Laser treatment for rosacea is usually considered a cosmetic procedure, which insurance typically doesn't cover.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Rosacea and Learn More about Diseases

Rosacea
Vitamin deficiency anemia

Mosquito bites
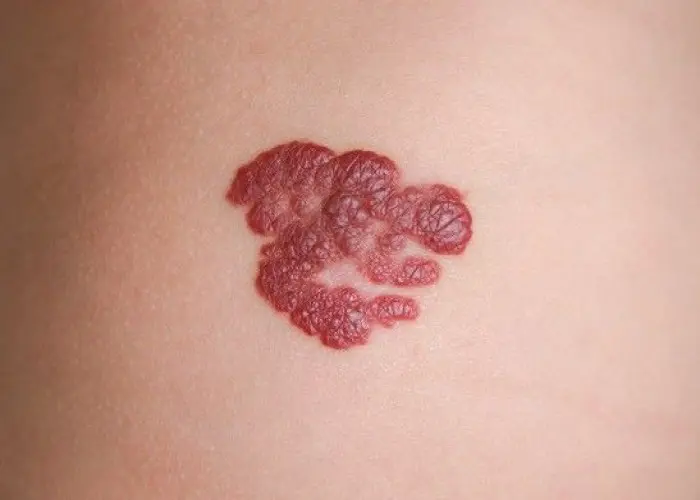
Hemangioma
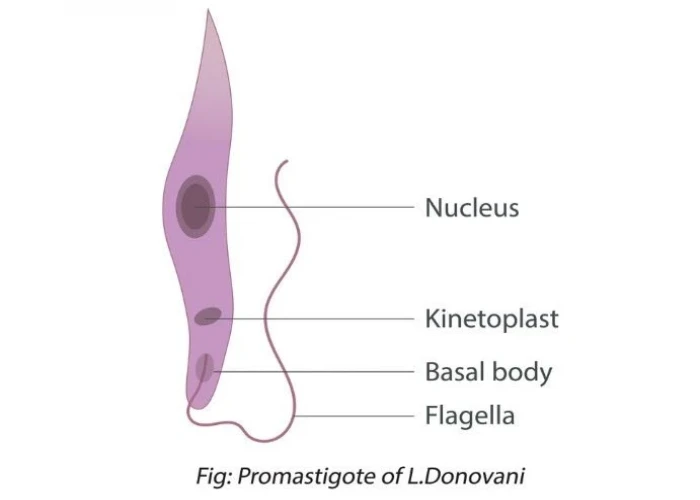
Kala Azar

Schizotypal personality disorder
Fever

Scorpion sting
rosacea, রোসেসিয়া
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.