Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
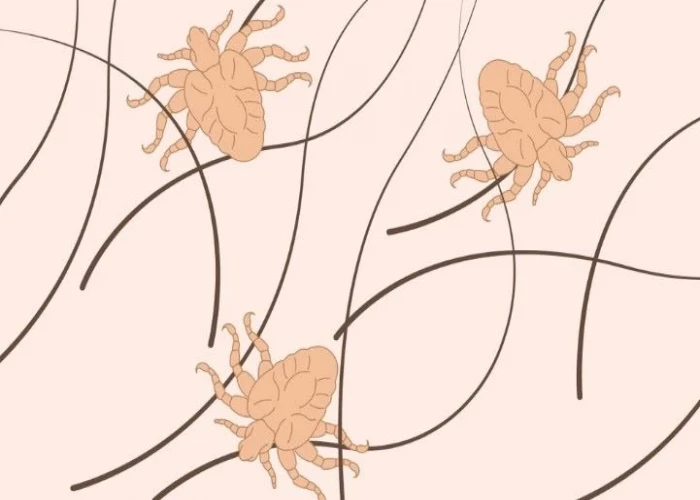
Pubic lice (crabs)

Pubic lice, also known as crabs, are tiny parasitic insects that infest the pubic hair and skin of the human body. They are typically spread through sexual contact, but can also be spread through close personal contact, sharing of clothing or bedding, or contact with infested objects.
Symptoms of pubic lice infestation include intense itching in the pubic area, visible lice or eggs (nits) in the hair, and small red or blue spots on the skin. Scratching of the affected area can lead to secondary infections.
Treatment for pubic lice infestation typically involves topical medications that are applied directly to the affected area. These medications may include permethrin, pyrethrins with piperonyl butoxide, or malathion. In some cases, oral medications may also be prescribed.
In addition to treatment, it is important to take steps to prevent the spread of pubic lice. This may include avoiding sexual contact until the infestation has been treated, washing all clothing, bedding, and towels in hot water, and thoroughly cleaning any objects that may have come into contact with the infested area.
While pubic lice infestations can be uncomfortable and embarrassing, they are not typically a serious medical condition and can be easily treated with proper care and attention. It is important to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or if there are signs of secondary infection.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Body lice
Disease Causes
Pubic lice (crabs)
Pubic lice are most commonly spread during sexual activity. You may also get pubic lice from infested sheets, blankets, towels or clothes.
Disease Prevents
Pubic lice (crabs)
To prevent pubic lice infestation, avoid having sexual contact or sharing bedding or clothing with anyone who has an infestation. If you are being treated for pubic lice, all sexual partners also must be treated.
Disease Treatments
If over-the-counter lotions or shampoos that have 1% permethrin (Nix) or pyrethrin don't kill your pubic lice, your doctor may prescribe stronger treatments, such as:
- Malathion. You apply this prescription lotion to the affected area and wash it off after eight to 12 hours.
- Ivermectin (Stromectol). This medication is taken as a single dose of two pills, with an option to take another dose in 10 days if the treatment isn't initially successful.
- Eyelash and eyebrow treatments. If pubic lice are found in eyelashes and eyebrows, you can treat them by carefully applying petroleum jelly with a cotton swab at night and washing it off in the morning. This treatment may need to be repeated for several weeks and can irritate the eyes if used incorrectly.
- If only a few live lice and nits are found, you may be able to remove them using a nit comb or your fingernails. If additional treatment is needed, your doctor may prescribe a topical ointment.
All hairy areas of the body should be thoroughly checked and treated because lice can move away from treated areas to other hairy parts of the body. Shaving won't get rid of pubic lice.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Pubic lice (crabs) and Learn More about Diseases

Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
Traumtic eye
Frozen shoulder
Pseudotumor cerebri (idiopathic intracranial hypertension)

Bell's palsy
Intestinal ischemia

Sickle cell anemia

Wilms' tumor
Pubic lice, crabs, পাবিক উকুন, কাঁকড়া
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.