Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
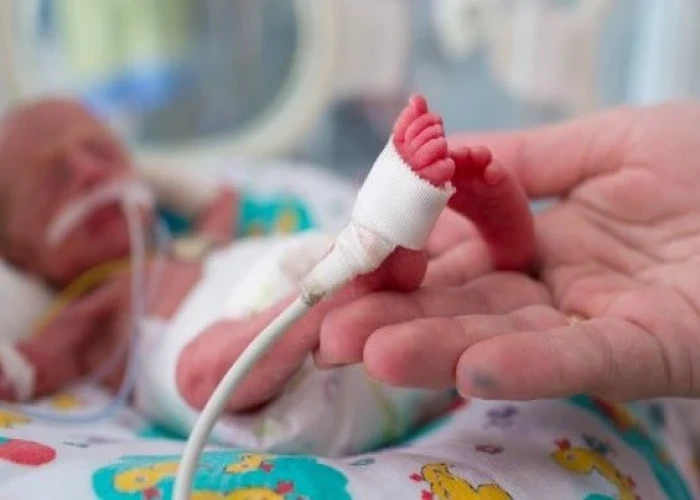
Premature birth

Premature birth, also known as preterm birth, is the birth of a baby before 37 weeks of gestation. Premature birth is a common and serious health problem that affects approximately 1 in 10 babies worldwide.
Babies who are born prematurely may be at risk for a range of health problems, including respiratory distress syndrome, feeding difficulties, infections, and neurological complications. Premature babies may also have long-term developmental and health problems, such as cerebral palsy, vision and hearing problems, and learning difficulties.
The causes of premature birth are not fully understood, but may include factors such as infections, multiple pregnancies, problems with the uterus or cervix, and lifestyle factors such as smoking and substance abuse.
Treatment for premature babies depends on their individual needs and may involve a range of interventions, such as respiratory support, feeding support, medication, and monitoring for complications. In some cases, premature babies may need to spend time in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) to receive specialized care and support.
Prevention of premature birth is an important public health priority. Prenatal care, including regular check-ups and monitoring, can help identify and manage risk factors for premature birth. Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and reducing stress, may also help reduce the risk of premature birth. In some cases, medications or interventions to address underlying medical conditions may be necessary to prevent premature birth.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Sharper looking, less rounded features than a full-term baby's features, due to a lack of fat stores
- Low body temperature, especially immediately after birth in the delivery room, due to a lack of stored body fat
- Lack of reflexes for sucking and swallowing, leading to feeding difficulties
- Premature birth
Disease Causes
Disease Prevents
Premature birth
Although the exact cause of preterm birth is often unknown, there are some things that can be done to help women — especially those who have an increased risk — to reduce their risk of preterm birth, including:
- Progesterone supplements. Women who have a history of preterm birth, a short cervix or both factors may be able to reduce the risk of preterm birth with progesterone supplementation.
- Cervical cerclage. This is a surgical procedure performed during pregnancy in women with a short cervix, or a history of cervical shortening that resulted in a preterm birth.
- During this procedure, the cervix is stitched closed with strong sutures that may provide extra support to the uterus. The sutures are removed when it's time to deliver the baby. Ask your doctor if you need to avoid vigorous activity during the remainder of your pregnancy.
Disease Treatments
The neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) or special care nursery provides round-the-clock care for your premature baby.
Supportive care
Specialized supportive care for your baby may include:
- Being placed in an incubator. Your baby will probably stay in an enclosed plastic bassinet (incubator) that's kept warm to help your baby maintain normal body temperature. Later on, NICU staff may show you a particular way to hold your baby — known as "kangaroo" care — with direct skin-to-skin contact.
- Monitoring of your baby's vital signs. Sensors may be taped to your baby's body to monitor blood pressure, heart rate, breathing and temperature. A ventilator may be used to help your baby breathe.
- Having a feeding tube. At first your baby may receive fluids and nutrients through an intravenous (IV) tube. Breast milk may be given later through a tube passed through your baby's nose and into his or her stomach (nasogastric, or NG, tube). When your baby is strong enough to suck, breast-feeding or bottle-feeding is often possible.
- Replenishing fluids. Your baby needs a certain amount of fluids each day, depending upon his or her age and medical conditions. The NICU team will closely monitor fluids, sodium and potassium levels to make sure that your baby's fluid levels stay on target. If fluids are needed, they'll be delivered through an IV line.
- Spending time under bilirubin lights. To treat infant jaundice, your baby may be placed under a set of lights — known as bilirubin lights — for a period of time. The lights help your baby's system break down excess bilirubin, which builds up because the liver can't process it all. While under the bilirubin lights, your baby will wear a protective eye mask to rest more comfortably.
- Receiving a blood transfusion. Your preterm baby may need a blood transfusion to raise blood volume — especially if your baby has had several blood samples drawn for various tests.
Medications
Medications may be given to your baby to promote maturing and to stimulate normal functioning of the lungs, heart and circulation. Depending on your baby's condition, medication may include:
- Surfactant, a medication used to treat respiratory distress syndrome
- Fine-mist (aerosolized) or IV medication to strengthen breathing and heart rate
- Antibiotics if infection is present or if there's a risk of possible infection
- Medicines that increase urine output (diuretics) to manage excess fluid
- An injection of medication into the eye to stop the growth of new blood vessels that could cause retinopathy of prematurity
- Medicine that helps close the heart defect known as patent ductus arteriosus
Surgery
Sometimes surgery is necessary to treat a number of conditions associated with prematurity. Talk with your baby's health care team to understand which complications may require surgery, and learn about the type of surgery that might be necessary to treat them.
Taking your baby home
Your baby is ready to go home when he or she:
- Can breathe without support
- Can maintain a stable body temperature
- Can breast- or bottle-feed
- Is gaining weight steadily
- Is free of infection
In some cases, a child may be allowed to go home before meeting one of these requirements — as long as the baby's medical team and family create and agree on a plan for home care and monitoring.
Your baby's health care team will help you learn how to care for your baby at home. Before dismissal from the hospital, your baby's nurse or a hospital discharge planner may ask you about:
- Living arrangements
- Other children in the household
- Adult relatives and friends who may assist you in caring for your baby
- Primary pediatric care
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Premature birth and Learn More about Diseases

Plantar warts

Latex allergy

Mood disorders
Myocardial ischemia
Ringworm (body)
Cradle cap
Heart attack
Posterior vaginal prolapse (Rectocele)
premature birth, সময়ের পূর্বে জন্ম
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.