Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Polycythemia vera
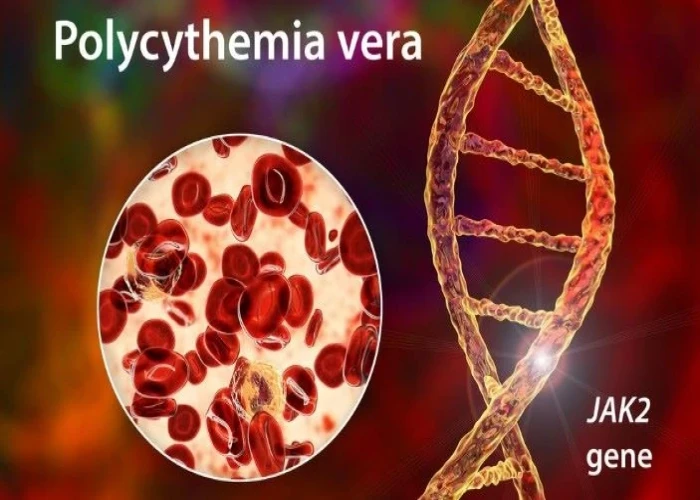
Polycythemia vera is a rare blood disorder that causes the bone marrow to produce too many red blood cells. This can lead to a thickening of the blood and increase the risk of blood clots, stroke, and heart attack.
Polycythemia vera is a type of myeloproliferative neoplasm, which is a group of disorders that cause abnormal growth of blood cells in the bone marrow. The exact cause of polycythemia vera is not known, but it is thought to be related to genetic mutations that affect the regulation of blood cell production.
Symptoms of polycythemia vera may include fatigue, headaches, blurred vision, itching, sweating, and dizziness. In some cases, the disorder may be discovered during routine blood tests, which may show elevated red blood cell counts and hemoglobin levels.
Treatment for polycythemia vera typically involves managing symptoms and reducing the risk of blood clots. This may include medications to reduce the number of red blood cells, such as hydroxyurea, or to prevent blood clots, such as aspirin or anticoagulants. In some cases, phlebotomy may be used to remove excess blood from the body.
While there is no cure for polycythemia vera, ongoing monitoring and management can help prevent complications and improve quality of life for those affected by the disorder. People with polycythemia vera should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan based on their individual needs and symptoms.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Itching
- A feeling of fullness soon after eating and bloating or pain in the left upper abdomen due to an enlarged spleen
- Numbness, tingling, burning, or weakness in your hands, feet, arms or legs
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Swollen joint
- Joint pain
- Bleeding from gums
- Nose bleeding
- Enlarged liver and spleen
- Fullness in abdomen
- Weakness and numbness in legs
- Weakness and numbness in arms
- Weakness
- Tingling sensation
- Numbness
- Unusual bleeding, such as a nosebleed or bleeding gums
Disease Causes
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Polycythemia vera and Learn More about Diseases

Restless legs syndrome

Throat cancer

Urinary incontinence

Wilson's disease
Liposarcoma
Stomatitis
Pediatric obstructive sleep apnea

HIV / AIDS
polycythemia vera, পলিসিথেমিয়া ভেরা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.