 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Pericardial effusion
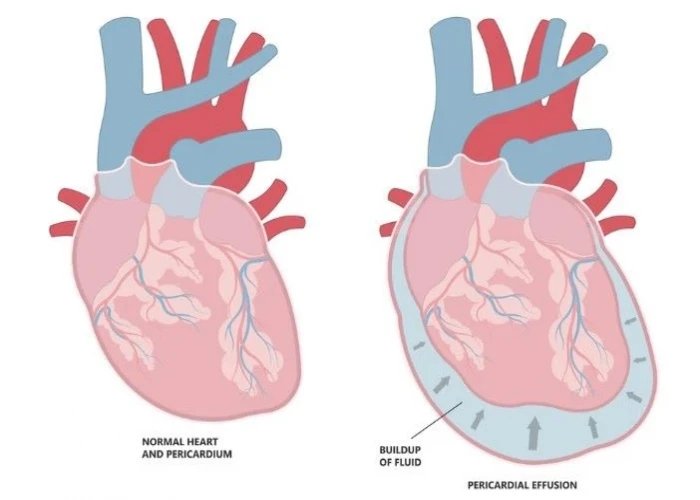
Pericardial effusion is a medical condition in which there is an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pericardial sac, which is the sac surrounding the heart. The pericardial sac normally contains a small amount of fluid that lubricates the heart and allows it to beat smoothly. However, if the amount of fluid increases, it can put pressure on the heart and affect its ability to pump blood effectively.
Pericardial effusion can have a number of causes, including:
- Infections (such as viral, bacterial, or fungal infections)
- Autoimmune disorders (such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis)
- Cancer or metastases
- Trauma or injury to the chest
- Kidney failure
- Certain medications
- Idiopathic (unknown cause)
Symptoms of pericardial effusion can vary depending on the amount of fluid and the rate at which it accumulates. Some people may have no symptoms, while others may experience chest pain, shortness of breath, cough, palpitations, fatigue, and swelling in the legs or abdomen.
Diagnosis of pericardial effusion usually involves a physical exam, imaging tests (such as echocardiography or CT scan), and blood tests. Treatment depends on the underlying cause and the severity of symptoms. In some cases, pericardial effusion may not require any treatment, and the fluid may be reabsorbed by the body over time. However, if the effusion is causing significant pressure on the heart or causing symptoms, treatment may include:
- Drainage of the fluid (pericardiocentesis)
- Medications to reduce inflammation or treat the underlying cause
- Surgery to remove the pericardium (pericardiectomy)
Prompt diagnosis and treatment of pericardial effusion is important to prevent serious complications, such as cardiac tamponade (a life-threatening condition in which the pressure on the heart becomes too high, preventing it from pumping blood effectively).
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Difficulty breathing (dyspnea)
- Chest pain
- Chest fullness
- Dizziness, lightheadedness or faintness
- Swollen abdomen (Ascites)
- Discomfort when breathing while lying down (orthopnea)
- Chest pain, usually behind the breastbone or on the left side of the chest
- The pain usually occurs behind the breastbone or in the left side of the chest.
Disease Causes
Pericardial effusion
Pericardial effusion can result from inflammation of the pericardium (pericarditis) after an illness or injury. In some settings, large effusions may be caused by certain cancers. A blockage of pericardial fluids or a collection of blood within the pericardium also can lead to this condition.
Sometimes the cause can't be determined (idiopathic pericarditis).
Causes of pericardial effusion may include:
- Autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus
- Cancer of the heart or pericardium
- Spread of cancer (metastasis), particularly lung cancer, breast cancer or Hodgkin's lymphoma
- Radiation therapy for cancer if the heart was in the area of the radiation
- Chest trauma
- Inflammation of the pericardium following a heart attack or after heart surgery or a procedure where the heart's lining is injured
- Underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism)
- Use of certain drugs or exposure to toxins
- Viral, bacterial, fungal or parasitic infections
- Waste products in the blood due to kidney failure (uremia)
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Treatment for pericardial effusion depends on:
- The amount of fluid buildup
- The cause of pericardial effusion
- The presence or risk of cardiac tamponade
Medications
If you don't have cardiac tamponade or there's no immediate threat of cardiac tamponade, your health care provider might prescribe one of the following medications to treat inflammation of the pericardium:
- Aspirin
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others)
- Colchicine (Colcrys, Mitigare)
- A corticosteroid, such as prednisone
Surgery or other procedures
Your health care provider may recommend procedures to drain a pericardial effusion or prevent future fluid buildup if:
- Medications don't correct the pericardial effusion
- A large effusion is causing symptoms and increasing the risk of cardiac tamponade
- You have cardiac tamponade
Drainage procedures or surgery to treat pericardial effusion may include:
- Fluid drainage (pericardiocentesis). A health care provider uses a needle to enter the pericardial space and then inserts a small tube (catheter) to drain the fluid. Imaging techniques, typically echocardiography, are used to guide the work. Usually, the catheter is left in place to drain the pericardial space for a few days to help prevent future fluid buildup. The catheter is taken out when all the fluid has drained and isn't re-accumulating.
- Open-heart surgery. If there's bleeding into the pericardium, especially due to recent heart surgery or other complicating factors, open-heart surgery may be done to drain the pericardium and repair any damage. Sometimes, a surgeon may create a passageway that allows fluid to drain as needed into the abdominal cavity, where it can be absorbed.
- Removal of the pericardium (pericardiectomy). If pericardial effusions continue to occur despite drainage procedures, a surgeon may recommend removing all or part of the pericardium.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Pericardial effusion and Learn More about Diseases
Pulmonary hypertension
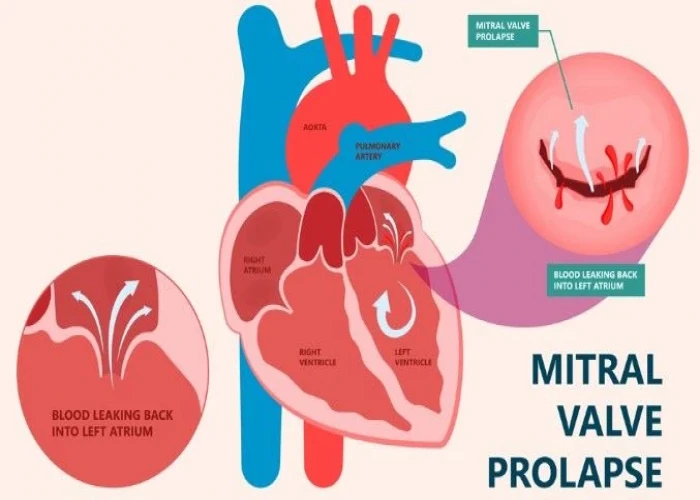
Mitral valve regurgitation
Stroke
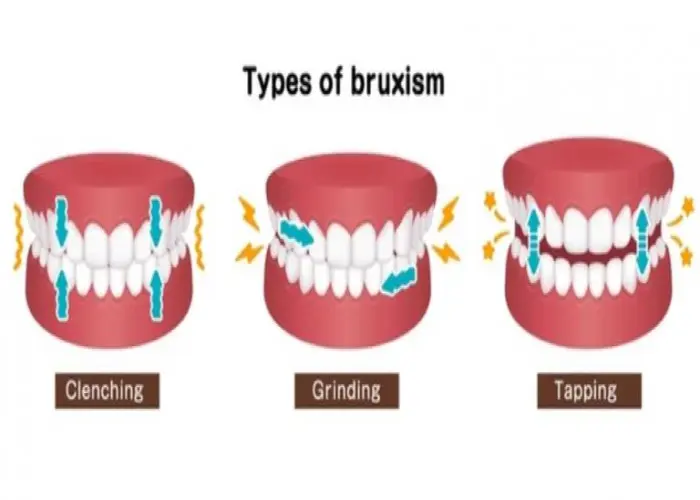
Bruxism (teeth grinding)

Airplane ear

Patent foramen ovale
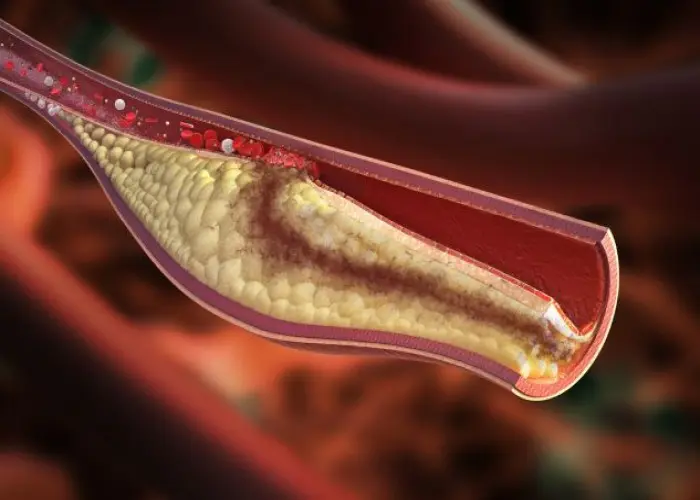
Acute coronary syndrome

Corns and calluses
pericardial effusion, পেরিকার্ডিয়াল ইফিউশন
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
