 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Asthma

Asthma is a chronic lung disease characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, which can make breathing difficult. It affects people of all ages and can be caused by a variety of triggers, including allergens, irritants, exercise, and stress.
Symptoms of asthma include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath, especially during physical activity or exposure to triggers. In some cases, asthma symptoms can also be accompanied by increased production of mucus.
Diagnosis of asthma typically involves a medical history, physical examination, and lung function tests. Treatment for asthma may include medications, such as inhaled corticosteroids, bronchodilators, and leukotriene modifiers, to reduce inflammation and open up the airways. In some cases, allergy shots or immunotherapy may be recommended to help manage triggers.
It is important for people with asthma to work closely with their doctor to develop an asthma action plan, which can help them manage symptoms and prevent asthma attacks. This may include monitoring symptoms regularly, avoiding known triggers, and taking medications as prescribed. Regular exercise, good nutrition, and stress management can also help improve overall health and control asthma symptoms.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Chest tightness
- Asthma
- Wheezing when exhaling, which is a common sign of asthma in children
- Asthma signs and symptoms that are more frequent and bothersome
Disease Causes
Asthma
It isn't clear why some people get asthma and others don't, but it's probably due to a combination of environmental and inherited (genetic) factors.
Asthma triggers
Exposure to various irritants and substances that trigger allergies (allergens) can trigger signs and symptoms of asthma. Asthma triggers are different from person to person and can include:
- Airborne allergens, such as pollen, dust mites, mold spores, pet dander or particles of cockroach waste
- Respiratory infections, such as the common cold
- Physical activity
- Cold air
- Air pollutants and irritants, such as smoke
- Certain medications, including beta blockers, aspirin, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve)
- Strong emotions and stress
- Sulfites and preservatives added to some types of foods and beverages, including shrimp, dried fruit, processed potatoes, beer and wine
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), a condition in which stomach acids back up into your throat
Disease Prevents
Asthma
While there's no way to prevent asthma, you and your doctor can design a step-by-step plan for living with your condition and preventing asthma attacks.
- Follow your asthma action plan. With your doctor and health care team, write a detailed plan for taking medications and managing an asthma attack. Then be sure to follow your plan.
- Asthma is an ongoing condition that needs regular monitoring and treatment. Taking control of your treatment can make you feel more in control of your life.
- Get vaccinated for influenza and pneumonia. Staying current with vaccinations can prevent flu and pneumonia from triggering asthma flare-ups.
- Identify and avoid asthma triggers. A number of outdoor allergens and irritants — ranging from pollen and mold to cold air and air pollution — can trigger asthma attacks. Find out what causes or worsens your asthma, and take steps to avoid those triggers.
- Monitor your breathing. You may learn to recognize warning signs of an impending attack, such as slight coughing, wheezing or shortness of breath.
- But because your lung function may decrease before you notice any signs or symptoms, regularly measure and record your peak airflow with a home peak flow meter. A peak flow meter measures how hard you can breathe out. Your doctor can show you how to monitor your peak flow at home.
- Identify and treat attacks early. If you act quickly, you're less likely to have a severe attack. You also won't need as much medication to control your symptoms.
- When your peak flow measurements decrease and alert you to an oncoming attack, take your medication as instructed. Also, immediately stop any activity that may have triggered the attack. If your symptoms don't improve, get medical help as directed in your action plan.
- Take your medication as prescribed. Don't change your medications without first talking to your doctor, even if your asthma seems to be improving. It's a good idea to bring your medications with you to each doctor visit. Your doctor can make sure you're using your medications correctly and taking the right dose.
- Pay attention to increasing quick-relief inhaler use. If you find yourself relying on your quick-relief inhaler, such as albuterol, your asthma isn't under control. See your doctor about adjusting your treatment.
Disease Treatments
Prevention and long-term control are key to stopping asthma attacks before they start. Treatment usually involves learning to recognize your triggers, taking steps to avoid triggers and tracking your breathing to make sure your medications are keeping symptoms under control. In case of an asthma flare-up, you may need to use a quick-relief inhaler.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Phenobarbital
Mild asthma.
1 pill 2/3 times a day.
-
Salbutamol
Salbutamol can be given in all types of bronchospasm, bronchial or asthma, chronic bronchitis, status asthmaticus.
1/2 pill 3 times a day.
-
Theophylline
Theophylline-containing drugs in moderate asthma.
1 pill 3 times a day or Inicontin 1/2 2 times a day.
-
Salbutamol (Inhaler)
2 pumps of gas should be given in each mouth 3/4 times a day, 1 minute after the 1st time, the 2nd pump should be given.
-
Ketotifen Fumarate (Oral)
Taking ketotifen pills for a long time with gas consumption can reduce asthma or prevent asthma.
1 pill 2 times a day between meals or after meals.
-
Chlorpheniramine Maleate
Chlorpheniramine maleate syrup for allergic cold or cough or in children if allergic.
1 spoon 3 times a day.
-
Promethazine Hydrochloride
1/2 teaspoon 3 times a day.
-
Dexamethasone
In the case of status asthmaticus, i.e. if the patient has no previous medication or the breathing problem continues without interruption.
1+1+1+1 5 days or 2+2+2
-
Prednisolone
In the case of status asthmaticus, i.e. if the patient has no previous medication or the breathing problem continues without interruption.
1+1+1 5 days or 2+0+2
-
Betamethasone
In the case of status asthmaticus, i.e. if the patient has no previous medication or the breathing problem continues without interruption.
1+0+1 5 days or 1+0+1
-
Aminophylline
Medicines containing aminophylline can be given if breathing difficulties are not relieved by medicines containing salbutamol or theophylline.
1 pill 2/3 times a day or 1/2 a 350 mg pill twice a day 1/2 times a day.
-
Diazepam
Sedative drug diazepam.
1/2 or 1 pill 2/3 times a day according to age.
-
Clobazam
1/2, 1 pill 2/3 times a day.
-
Maprotiline Hydrochloride
Depression medications have benefits. 1+0+1
-
Amoxicillin Trihydrate
If there is secondary infection i.e. chest cough, phlegm or fever.
1 capsule 3 times a day for 7 days.
-
Cephalexin
250mg 1+1+1 or 500mg 1+1+1.
-
Cephradine
Syrup 1 tsp/ 1 cap every 6 hours or 500mg 2 times a day.
-
Sparfloxacin
1st day 2 pills. 1 pill daily from next day for 8-10 days.
-
Azithromycin Dihydrate
1/1 teaspoon daily for 5 days.
-
Cefuroxime Axetil
1+0+1 makes 10 days.
-
Diethylcarbamazine Citrate
If there is an increase in eosinophils, medication with diethylcarbamazine.
1, 2, 3 pills 3 times a day (3/4 weeks)
-
Ferrous Sulfate
for blood
1/2 teaspoon 2/3 times a day after meals.
-
Multivitamin [Pediatric Preparation]
For small children.
15/20 drops 2 times a day.
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Asthma and Learn More about Diseases

Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome

Nearsightedness
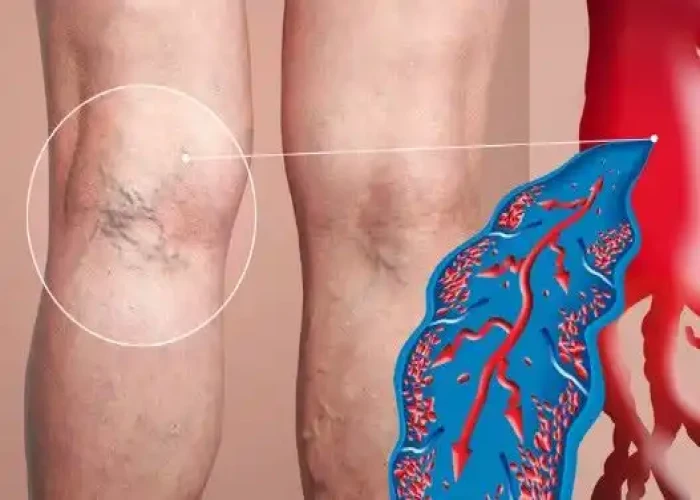
Varicose veins
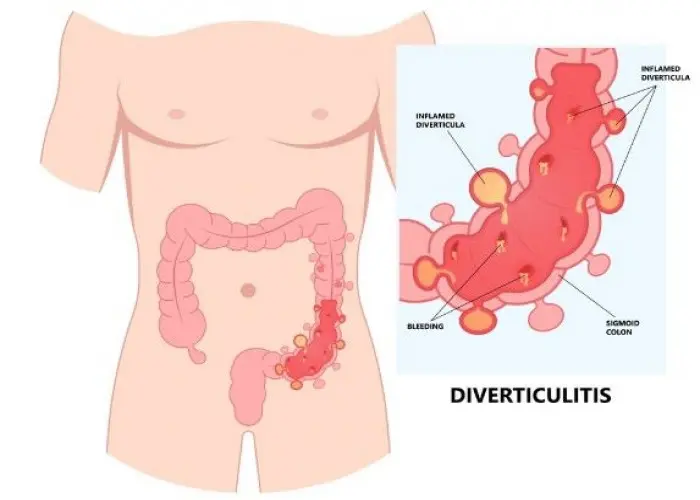
Fecal incontinence

Esophageal spasms
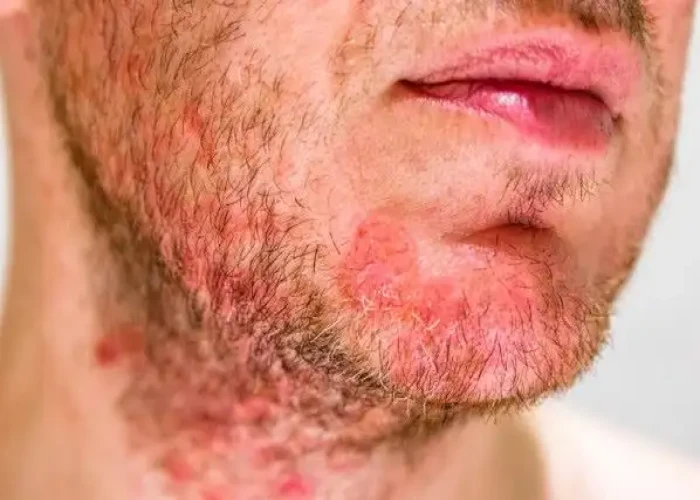
Seborrheic dermatitis

Giardial Dysentry

Child abuse
Asthma, Inhalers, Asthma symptoms, Peak flow meter, হাঁপানি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
