 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Myocarditis
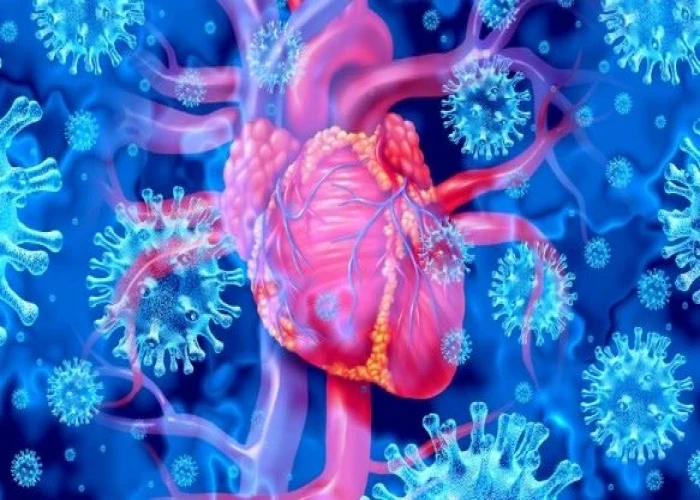
Myocarditis is a condition in which the heart muscle (myocardium) becomes inflamed, usually due to a viral infection. The inflammation can weaken the heart muscle, interfere with its ability to pump blood effectively, and cause other complications such as arrhythmias, heart failure, and sudden cardiac death.
In addition to viral infections, myocarditis can also be caused by bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infections, exposure to certain drugs or toxins, autoimmune disorders, and other medical conditions.
Symptoms of myocarditis may include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, fatigue, fever, palpitations, and swelling in the legs or abdomen. In some cases, myocarditis may not cause any symptoms at all, particularly in people with mild or asymptomatic infections.
Diagnosis of myocarditis may involve a physical exam, blood tests to check for signs of inflammation or infection, electrocardiogram (ECG) to evaluate heart function, imaging tests such as echocardiography or cardiac MRI to look for signs of inflammation or damage to the heart muscle, and in some cases, a heart biopsy to examine a sample of heart tissue for signs of inflammation or infection.
Treatment options for myocarditis depend on the severity of the condition and may include rest, medications (such as anti-inflammatory drugs or immunosuppressants), supportive care (such as oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation), and in some cases, heart transplantation for people with severe heart damage or failure.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath, at rest or during physical activity
- Rapid breathing
- Diarrhea
- Sore throat
- Fever
- Joint pain
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Irregular heartbeats (arrhythmia)
- Fluid retention with swelling of your legs, ankles and feet
Disease Causes
Myocarditis
Often, the cause of myocarditis isn't identified. There are many potential causes but the risk of developing myocarditis is rare.
Potential causes of myocarditis include:
- Viruses. Many viruses are commonly associated with myocarditis, including the viruses that cause the common cold (adenovirus); COVID-19; hepatitis B and C; parvovirus, which causes a mild rash, usually in children (fifth disease); and herpes simplex virus.
- Gastrointestinal infections (echoviruses), mononucleosis (Epstein-Barr virus) and German measles (rubella) also can cause myocarditis. It's also common in people with HIV, the virus that causes AIDS.
- Bacteria. Bacteria that can cause myocarditis include staphylococcus, streptococcus, the bacterium that causes diphtheria and the tick-borne bacterium responsible for Lyme disease.
- Parasites. Among these are such parasites as Trypanosoma cruzi and toxoplasma, including some that are transmitted by insects and can cause a condition called Chagas disease. Chagas disease is much more common in Central and South America than in the United States, but it can occur in travelers and in immigrants from that part of the world.
- Fungi. Yeast infections, such as candida; molds, such as aspergillus; and other fungi, such as histoplasma, often found in bird droppings, can sometimes cause myocarditis, particularly in people with weakened immune systems.
Myocarditis also sometimes occurs if you're exposed to:
- Medications or illegal drugs that might cause an allergic or toxic reaction. These include drugs used to treat cancer; antibiotics, such as penicillin and sulfonamide drugs; some anti-seizure medications; and some illegal substances, such as cocaine.
- Chemicals or radiation. Exposure to certain chemicals, such as carbon monoxide, and radiation can sometimes cause myocarditis.
- Other diseases. These include disorders such as lupus, Wegener's granulomatosis, giant cell arteritis and Takayasu's arteritis.
Disease Prevents
Myocarditis
There's no specific prevention for myocarditis. However, taking these steps to prevent infections might help:
- Avoid people who have a viral or flu-like illness until they've recovered. If you're sick with symptoms of a viral infection, try to avoid exposing others.
- Follow good hygiene. Regular hand-washing can help prevent spreading illness.
- Avoid risky behaviors. To reduce your chances of getting an HIV-related myocardial infection, practice safe sex and don't use illegal drugs.
- Minimize exposure to ticks. If you spend time in tick-infested areas, wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants to cover as much of your skin as possible. Apply tick or insect repellents that contain DEET.
- Get your vaccines. Stay up to date on the recommended vaccines, including those that protect against COVID-19, rubella and influenza — diseases that can cause myocarditis. Rarely, the COVID-19 vaccine can cause inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis) and inflammation of the outer heart lining (pericarditis), especially in males ages 12 through 17. Talk to your health care provider about the benefits and risks of vaccines.
Disease Treatments
In many people, myocarditis improves on its own or with treatment, leading to a complete recovery. Myocarditis treatment focuses on the cause and the symptoms, such as heart failure.
Medications
People with mild myocarditis may only need rest and medication.
- Corticosteroids. Certain rare types of viral myocarditis, such as giant cell and eosinophilic myocarditis, may improve with corticosteroids or other medications to suppress your immune system.
- Heart medications. If myocarditis is causing heart failure or arrhythmias, you may need to stay in the hospital. Your doctor will prescribe drugs or other treatments, depending on your signs and symptoms. For example, if you have certain irregular heart rhythms or severe heart failure, you may be given medications to reduce the risk of blood clots forming in your heart.
- If your heart is weak, your doctor might prescribe blood pressure medications to reduce the strain on your heart or help your body remove excess fluid. These medications may include diuretics, beta blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs).
- Medications to treat chronic conditions. If myocarditis is caused by a chronic illnesses, such as lupus, treatment is directed at the underlying disease.
Surgeries and procedures
If you have severe myocarditis, you will need aggressive treatment, which might include:
- IV medications. Medications given through a vein are used to quickly improve your heart's ability to pump.
- Ventricular assist devices (VAD). A VAD is a device that helps pump blood from the lower chambers of your heart (the ventricles) to the rest of your body. VADs are used in people who have weakened hearts or heart failure. This treatment may be used to allow your heart to recover or while you're waiting for other treatments, such as a heart transplant.
- Intra-aortic balloon pump. The doctor inserts a thin tube (catheter) into a blood vessel in your leg and guides it to your heart using X-ray imaging. A balloon attached to the end of the catheter inflates and deflates in the main artery leading out to the body from the heart (aorta). An intra-aortic pump helps increase blood flow and decrease the strain on your heart.
- Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). An ECHO machine mimics the function of the lungs. It removes carbon dioxide and adds oxygen to the blood. If you have severe heart failure, this device can provide oxygen to your body. During ECMO, blood is removed from the body, passed through the ECMO machine and then returned to the body.
- The ECMO machine takes over the work of your heart. This treatment may be used to allow the heart to recover or while waiting for other treatments, such as a heart transplant.
- Heart transplant. If you have very severe myocarditis, your doctor might recommend urgent heart transplantation.
Some people with myocarditis might have chronic and irreversible damage to the heart muscle requiring lifelong medications, while other people need medications for just a few months and then recover completely. Either way, your doctor is likely to recommend regular follow-up appointments, including tests to evaluate your condition.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Myocarditis and Learn More about Diseases

Greenstick fractures
Brain metastases

Alcohol poisoning

Progeria
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO)

Factor V Leiden

Indigestive Diarrhoea
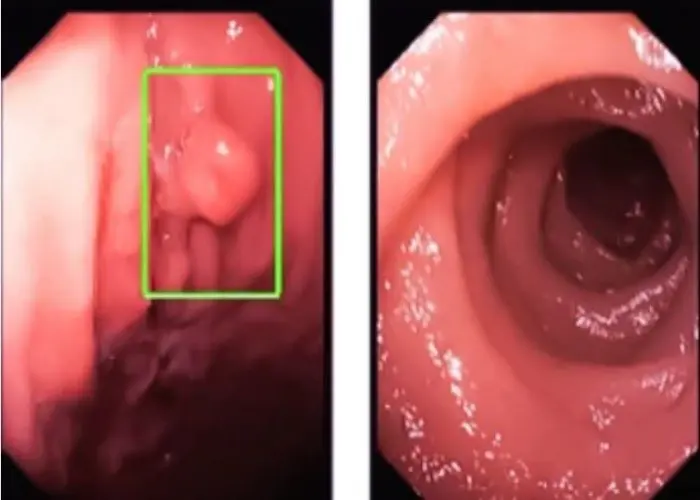
Colon polyps
myocarditis, মায়োকার্ডাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
