Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
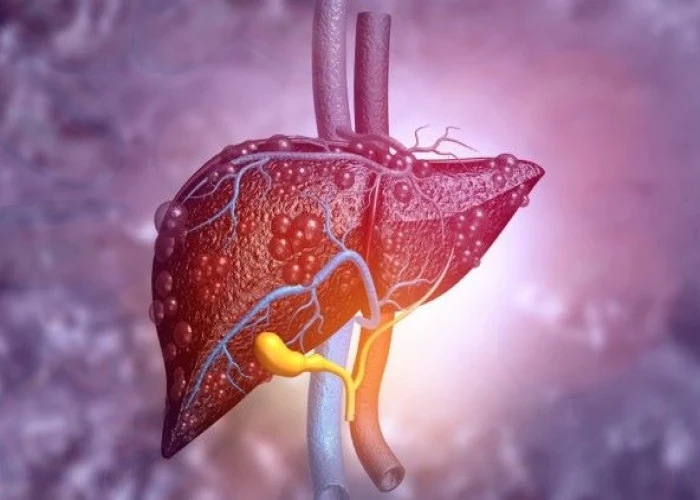
Liver disease

Liver disease refers to any condition or disorder that affects the normal functioning of the liver. The liver is an important organ responsible for a wide range of functions such as producing bile, storing glycogen, metabolizing drugs and toxins, and synthesizing proteins. When the liver is damaged, its ability to perform these functions is impaired, which can lead to a variety of symptoms and health problems.
There are many types of liver disease, including:
- Hepatitis: Inflammation of the liver caused by a viral infection (hepatitis A, B, C, D, or E).
- Cirrhosis: Scarring of the liver tissue caused by long-term liver damage. This can be caused by chronic hepatitis, alcoholism, or other factors.
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A condition in which fat accumulates in the liver, leading to inflammation and damage. This can be caused by obesity, diabetes, or high cholesterol.
- Autoimmune liver disease: A condition in which the immune system attacks the liver, causing inflammation and damage.
- Liver cancer: Cancer that originates in the liver.
- Genetic liver diseases: Inherited disorders that affect the liver, such as hemochromatosis or Wilson's disease.
Symptoms of liver disease can include fatigue, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), abdominal pain, swelling of the legs and ankles, and nausea. Treatment depends on the specific type of liver disease and may include medication, lifestyle changes, or surgery in some cases. It's important to see a healthcare provider if you are experiencing symptoms of liver disease or have concerns about your liver health.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Yellowing of skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea or vomiting
- Pale stool color
- Yellow urine color
- Dark urine color
- Itching
- Swollen feet and ankles (edema)
- Swollen leg
- Swollen abdomen (Ascites)
- Abdomen pain
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
Disease Causes
Liver disease
Liver disease has many causes.
Infection
Parasites and viruses can infect the liver, causing inflammation that reduces liver function. The viruses that cause liver damage can be spread through blood or semen, contaminated food or water, or close contact with a person who is infected. The most common types of liver infection are hepatitis viruses, including:
- Hepatitis A
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis C
Immune system abnormality
Diseases in which your immune system attacks certain parts of your body (autoimmune) can affect your liver. Examples of autoimmune liver diseases include:
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Primary biliary cholangitis
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis
Genetics
An abnormal gene inherited from one or both of your parents can cause various substances to build up in your liver, resulting in liver damage. Genetic liver diseases include:
- Hemochromatosis
- Wilson's disease
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
Cancer and other growths
Examples include:
- Liver cancer
- Bile duct cancer
- Liver adenoma
Other
Additional, common causes of liver disease include:
- Chronic alcohol abuse
- Fat accumulation in the liver (nonalcoholic fatty liver disease)
- Certain prescription or over-the-counter medications
- Certain herbal compounds
Disease Prevents
Liver disease
To prevent liver disease:
- Drink alcohol in moderation. For healthy adults, that means up to one drink a day for women and up to two drinks a day for men. Heavy or high-risk drinking is defined as more than eight drinks a week for women and more than 15 drinks a week for men.
- Avoid risky behavior. Use a condom during sex. If you choose to have tattoos or body piercings, be picky about cleanliness and safety when selecting a shop. Seek help if you use illicit intravenous drugs, and don't share needles to inject drugs.
- Get vaccinated. If you're at increased risk of contracting hepatitis or if you've already been infected with any form of the hepatitis virus, talk to your doctor about getting the hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines.
- Use medications wisely. Take prescription and nonprescription drugs only when needed and only in recommended doses. Don't mix medications and alcohol. Talk to your doctor before mixing herbal supplements or prescription or nonprescription drugs.
- Avoid contact with other people's blood and body fluids. Hepatitis viruses can be spread by accidental needle sticks or improper cleanup of blood or body fluids.
- Keep your food safe. Wash your hands thoroughly before eating or preparing foods. If traveling in a developing country, use bottled water to drink, wash your hands and brush your teeth.
- Take care with aerosol sprays. Make sure to use these products in a well-ventilated area, and wear a mask when spraying insecticides, fungicides, paint and other toxic chemicals. Always follow the manufacturer's instructions.
- Protect your skin. When using insecticides and other toxic chemicals, wear gloves, long sleeves, a hat and a mask so that chemicals aren't absorbed through your skin.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Obesity can cause nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Disease Treatments
Treatment for liver disease depends on your diagnosis. Some liver problems can be treated with lifestyle modifications, such as stopping alcohol use or losing weight, typically as part of a medical program that includes careful monitoring of liver function. Other liver problems may be treated with medications or may require surgery.
Treatment for liver disease that causes or has led to liver failure may ultimately require a liver transplant.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Liver disease and Learn More about Diseases

Lyme disease
Short bowel syndrome

Heat exhaustion

Toe walking in children

Snoring
Rheumatoid arthritis
Renal artery stenosis
Arteriovenous fistula
liver disease, যকৃতের রোগ
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.