 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Lichen nitidus
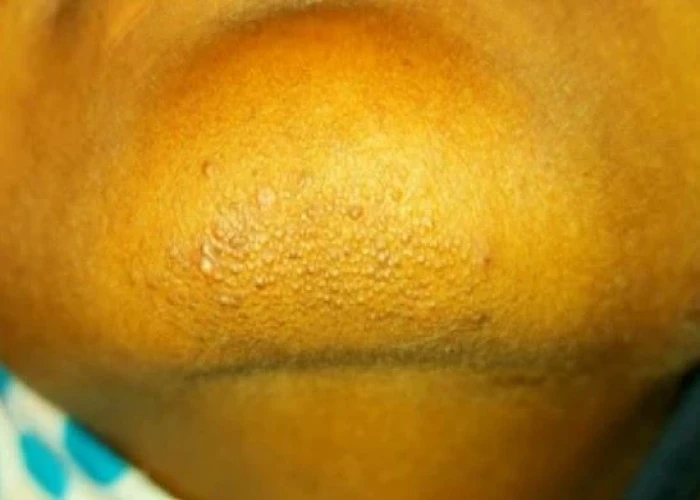
Lichen nitidus is a rare, benign skin condition that appears as small, shiny, flat-topped papules (bumps) on the skin. The papules are typically 1-2 mm in diameter and may be skin-colored, pink, or red. They usually appear on the wrists, forearms, ankles, genitals, and lower abdomen, but can occur on any part of the body.
The cause of lichen nitidus is unknown, but it is thought to be an inflammatory disorder of the skin. It can occur in people of any age, but is most common in children and young adults.
Lichen nitidus does not usually cause symptoms, but in some cases it may be itchy or painful. The condition is usually self-limiting and may resolve on its own within a few months to a few years. However, in some cases it may persist for many years.
Treatment options for lichen nitidus include topical steroids, phototherapy, or systemic medications such as retinoids or immunomodulators. However, treatment is not always necessary as the condition may resolve on its own.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Itching
- Fever
- Skin rash
- Itchy, blistery skin rash (dermatitis herpetiformis)
- Lichen nitidus may clear up at one site on the body but then appear at another.
- In rare cases, the bumps of lichen nitidus may itch, sometimes intensely.
- Purplish, flat bumps, most often on the inner forearm, wrist or ankle, and sometimes the genitals
- Blisters that break to form scabs or crusts
- Lacy white patches in the mouth or on the lips or tongue
Disease Causes
Lichen nitidus
The cause of lichen nitidus is unknown. The papules that appear are the result of inflammation controlled by white blood cells called T lymphocytes. Normally, these cells work to heal disease or injury, such as a cut on your finger. Doctors and researchers don't know what prompts T lymphocytes to be activated in lichen nitidus.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
For most people, lichen nitidus lasts for a few months to a year. The condition usually clears up on its own without treatment. After it clears up, the appearance of the skin is usually normal with no scarring or permanent change to skin color.
If lichen nitidus causes itching or if you have concerns about your appearance or your child's appearance, your doctor may prescribe one of the following treatments:
- Corticosteroids may reduce inflammation associated with lichen nitidus. The side effects vary depending on whether it's used as an ointment applied directly to the skin (topical) or taken as a pill (oral). Long-term use of topical corticosteroids can cause thinning of the skin, a lessening of the treatment effect and other skin problems. Long-term use of oral corticosteroids can cause weakening of the bones (osteoporosis), diabetes, high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels.
- Retinoid is a synthetic version of vitamin A that can be a topical or oral treatment. The topical treatment doesn't cause the side effects associated with corticosteroids, but it may irritate the skin.
- Because retinoid can cause birth defects, it shouldn't be used by women who are pregnant or who might become pregnant. Your doctor can advise you on necessary precautions.
- Other topical medications. A topical drug called tacrolimus (Protopic) helps to suppress the immune response and may be helpful for lichen nitidus. Possible side effects include stinging, burning and itching at the site where the medication is applied. This medication can't be used in conjunction with phototherapy. Limit sun exposure while using tacrolimus and don't use tanning beds during treatment.
- Antihistamines act against a protein called histamine that is involved in inflammatory activity. An oral or topical antihistamine may relieve itching associated with lichen nitidus.
- Phototherapy, a type of light therapy, may help clear up lichen nitidus. One type uses ultraviolet A (UVA) light, which penetrates deep into the skin. This therapy is usually used in combination with a drug that makes the skin more sensitive to UVA light. Another type uses narrow band ultraviolet B (UVB) light. It's important to avoid sun exposure for a couple of days after having phototherapy. Also, you need to wear special UV-absorbing sunglasses for a couple of days to protect your eyes.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Lichen nitidus and Learn More about Diseases
Lymphoma

Hay fever

Airplane ear
Chilblains
Vaginal cancer

Migraine with aura

Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)
Obstructive sleep apnea
lichen nitidus, লিকেন নাইটিডাস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
