 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Insomnia

Insomnia is a sleep disorder that is characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early and being unable to fall back asleep. Insomnia can be short-term (acute) or long-term (chronic) and can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, anxiety, depression, medication use, caffeine intake, and poor sleep habits.
Symptoms of insomnia may include difficulty falling asleep, waking up frequently during the night, waking up too early and being unable to fall back asleep, daytime fatigue or sleepiness, irritability, and difficulty concentrating or performing daily tasks.
Treatment for insomnia may depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In some cases, making lifestyle changes such as avoiding caffeine, establishing a regular sleep schedule, and practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation or yoga may be helpful. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a type of therapy that has been shown to be effective in treating insomnia by addressing negative thoughts and behaviors that may be interfering with sleep.
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help with sleep, such as over-the-counter sleep aids or prescription medications such as benzodiazepines or non-benzodiazepine sedative-hypnotics. However, these medications should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider, as they can have side effects and may be habit-forming.
Preventing insomnia may involve maintaining good sleep hygiene habits, such as establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, avoiding stimulants such as caffeine and nicotine, and engaging in regular exercise. Stress management techniques, such as relaxation exercises or therapy, may also be helpful in preventing insomnia.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Difficulty falling asleep at night
- Lack of sleep (Sleep apnea)
- Trouble sleep (insomnia)
- Not feeling well-rested after a night's sleep
- Anxiety
Disease Causes
Insomnia
Insomnia may be the primary problem, or it may be associated with other conditions.
Chronic insomnia is usually a result of stress, life events or habits that disrupt sleep. Treating the underlying cause can resolve the insomnia, but sometimes it can last for years.
Common causes of chronic insomnia include:
- Stress. Concerns about work, school, health, finances or family can keep your mind active at night, making it difficult to sleep. Stressful life events or trauma — such as the death or illness of a loved one, divorce, or a job loss — also may lead to insomnia.
- Travel or work schedule. Your circadian rhythms act as an internal clock, guiding such things as your sleep-wake cycle, metabolism and body temperature. Disrupting your body's circadian rhythms can lead to insomnia. Causes include jet lag from traveling across multiple time zones, working a late or early shift, or frequently changing shifts.
- Poor sleep habits. Poor sleep habits include an irregular bedtime schedule, naps, stimulating activities before bed, an uncomfortable sleep environment, and using your bed for work, eating or watching TV. Computers, TVs, video games, smartphones or other screens just before bed can interfere with your sleep cycle.
- Eating too much late in the evening. Having a light snack before bedtime is OK, but eating too much may cause you to feel physically uncomfortable while lying down. Many people also experience heartburn, a backflow of acid and food from the stomach into the esophagus after eating, which may keep you awake.
Chronic insomnia may also be associated with medical conditions or the use of certain drugs. Treating the medical condition may help improve sleep, but the insomnia may persist after the medical condition improves.
Additional common causes of insomnia include:
- Mental health disorders. Anxiety disorders, such as post-traumatic stress disorder, may disrupt your sleep. Awakening too early can be a sign of depression. Insomnia often occurs with other mental health disorders as well.
- Medications. Many prescription drugs can interfere with sleep, such as certain antidepressants and medications for asthma or blood pressure. Many over-the-counter medications — such as some pain medications, allergy and cold medications, and weight-loss products — contain caffeine and other stimulants that can disrupt sleep.
- Medical conditions. Examples of conditions linked with insomnia include chronic pain, cancer, diabetes, heart disease, asthma, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), overactive thyroid, Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease.
- Sleep-related disorders. Sleep apnea causes you to stop breathing periodically throughout the night, interrupting your sleep. Restless legs syndrome causes unpleasant sensations in your legs and an almost irresistible desire to move them, which may prevent you from falling asleep.
- Caffeine, nicotine and alcohol. Coffee, tea, cola and other caffeinated drinks are stimulants. Drinking them in the late afternoon or evening can keep you from falling asleep at night. Nicotine in tobacco products is another stimulant that can interfere with sleep. Alcohol may help you fall asleep, but it prevents deeper stages of sleep and often causes awakening in the middle of the night.
Insomnia and aging
Insomnia becomes more common with age. As you get older, you may experience:
- Changes in sleep patterns. Sleep often becomes less restful as you age, so noise or other changes in your environment are more likely to wake you. With age, your internal clock often advances, so you get tired earlier in the evening and wake up earlier in the morning. But older people generally still need the same amount of sleep as younger people do.
- Changes in activity. You may be less physically or socially active. A lack of activity can interfere with a good night's sleep. Also, the less active you are, the more likely you may be to take a daily nap, which can interfere with sleep at night.
- Changes in health. Chronic pain from conditions such as arthritis or back problems as well as depression or anxiety can interfere with sleep. Issues that increase the need to urinate during the night ―such as prostate or bladder problems ― can disrupt sleep. Sleep apnea and restless legs syndrome become more common with age.
- More medications. Older people typically use more prescription drugs than younger people do, which increases the chance of insomnia associated with medications.
Insomnia in children and teens
Sleep problems may be a concern for children and teenagers as well. However, some children and teens simply have trouble getting to sleep or resist a regular bedtime because their internal clocks are more delayed. They want to go to bed later and sleep later in the morning.
Disease Prevents
Insomnia
Good sleep habits can help prevent insomnia and promote sound sleep:
- Keep your bedtime and wake time consistent from day to day, including weekends.
- Stay active — regular activity helps promote a good night's sleep.
- Check your medications to see if they may contribute to insomnia.
- Avoid or limit naps.
- Avoid or limit caffeine and alcohol, and don't use nicotine.
- Avoid large meals and beverages before bedtime.
- Make your bedroom comfortable for sleep and only use it for sex or sleep.
- Create a relaxing bedtime ritual, such as taking a warm bath, reading or listening to soft music.
Disease Treatments
Changing your sleep habits and addressing any issues that may be associated with insomnia, such as stress, medical conditions or medications, can restore restful sleep for many people. If these measures don't work, your doctor may recommend cognitive behavioral therapy, medications or both, to help improve relaxation and sleep.
Cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia
Cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) can help you control or eliminate negative thoughts and actions that keep you awake and is generally recommended as the first line of treatment for people with insomnia. Typically, CBT-I is equally or more effective than sleep medications.
The cognitive part of CBT-I teaches you to recognize and change beliefs that affect your ability to sleep. It can help you control or eliminate negative thoughts and worries that keep you awake. It may also involve eliminating the cycle that can develop where you worry so much about getting to sleep that you can't fall asleep.
The behavioral part of CBT-I helps you develop good sleep habits and avoid behaviors that keep you from sleeping well. Strategies include, for example:
- Stimulus control therapy. This method helps remove factors that condition your mind to resist sleep. For example, you might be coached to set a consistent bedtime and wake time and avoid naps, use the bed only for sleep and sex, and leave the bedroom if you can't go to sleep within 20 minutes, only returning when you're sleepy.
- Relaxation techniques. Progressive muscle relaxation, biofeedback and breathing exercises are ways to reduce anxiety at bedtime. Practicing these techniques can help you control your breathing, heart rate, muscle tension and mood so that you can relax.
- Sleep restriction. This therapy decreases the time you spend in bed and avoids daytime naps, causing partial sleep deprivation, which makes you more tired the next night. Once your sleep has improved, your time in bed is gradually increased.
- Remaining passively awake. Also called paradoxical intention, this therapy for learned insomnia is aimed at reducing the worry and anxiety about being able to get to sleep by getting in bed and trying to stay awake rather than expecting to fall asleep.
- Light therapy. If you fall asleep too early and then awaken too early, you can use light to push back your internal clock. You can go outside during times of the year when it's light outside in the evenings, or you can use a light box. Talk to your doctor about recommendations.
Your doctor may recommend other strategies related to your lifestyle and sleep environment to help you develop habits that promote sound sleep and daytime alertness.
Prescription medications
Prescription sleeping pills can help you get to sleep, stay asleep or both. Doctors generally don't recommend relying on prescription sleeping pills for more than a few weeks, but several medications are approved for long-term use.
Examples include:
- Eszopiclone (Lunesta)
- Ramelteon (Rozerem)
- Zaleplon (Sonata)
- Zolpidem (Ambien, Edluar, Intermezzo, Zolpimist)
Prescription sleeping pills can have side effects, such as causing daytime grogginess and increasing the risk of falling, or they can be habit-forming, so talk to your doctor about these medications and other possible side effects.
Over-the-counter sleep aids
Nonprescription sleep medications contain antihistamines that can make you drowsy, but they're not intended for regular use. Talk to your doctor before you take these, as antihistamines may cause side effects, such as daytime sleepiness, dizziness, confusion, cognitive decline and difficulty urinating, which may be worse in older adults.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Diazepam
New and old anxiety, mental restlessness, insomnia with anxiety or physical restlessness.
Take 1 pill half an hour before going to bed at night.
-
Nitrazepam
Insomnia without reason or short-term insomnia is a drug containing nitrizepam.
1 tablet of 5 mg at night if not sleeping. 1 tablet of 1mg if not sleepy.
-
Clobazam
Medicines containing clobazam for anxiety, stress, restlessness, agitation and sleep difficulties.
Consume 1 pill 3 times a day.
-
Trifluoperazine
Medicines containing trifluopyrazine for insomnia, anxiety, and restlessness.
Consume 1 pill 3 times a day.
-
Lorazepam
1 tablet of 1 mg 2 times a day and 2 mg at night or 2 mg + 2 mg + 2 mg. None of the above medicines will have permanent effect if the patient is debilitated. Note the treatment of 'psychosis' for this.
-
Paracetamol
Body or throat pain due to influenza.
1/2 pill 3 times a day.
-
Diclofenac Sodium
Medications with diclofene sodium for insomnia, trauma, strain, wounds and burns, renal colic, new rheumatic arthritis, severe toothache, migraine.
1 pill every night on a full stomach. If the pain is severe, 1 pill in the morning after food, 1 pill at night for 5 days.
-
Ranitidine Hydrochloride
So that the acid is not. 1 pill in the morning and 1 pill at night after food.
- Naproxen Sodium
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
-
Aurum metalicum
30 strength.
-
Camphor
6, 30 strength.
-
Lycopodium clavatum
Q strength.
-
Phosphorus
6, 30 strength.
-
Zincum metallicum
30 strength.
-
Sulphur
30 strength.
-
Coffea
6, 30 strength.
-
Chamomilla
6 strength.
-
Aconite
6, 30 strength.
-
Belladonna
30 strength.
-
Passiflora
Q strength.
-
Ignatia amara
30 strength.
-
Nux vomica
30, 200 strength.
-
Sepia
6, 30 strength.
-
Kali bromatum
6, 30 strength.
Disease yoga
Insomnia and Learn More about Diseases

Interstitial cystitis
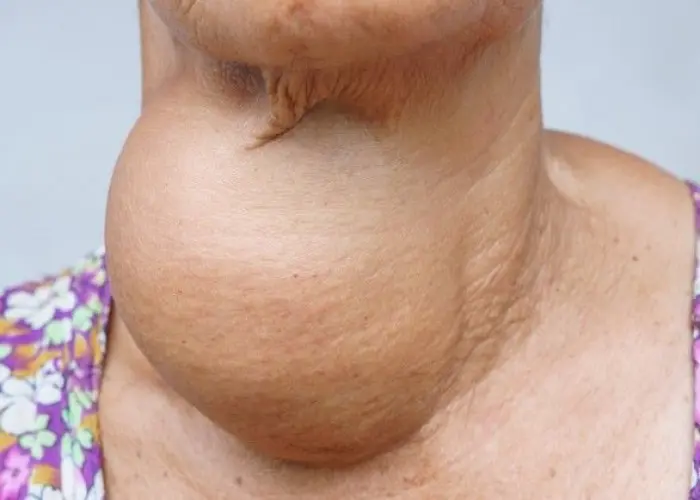
Goiter

Common cold in babies
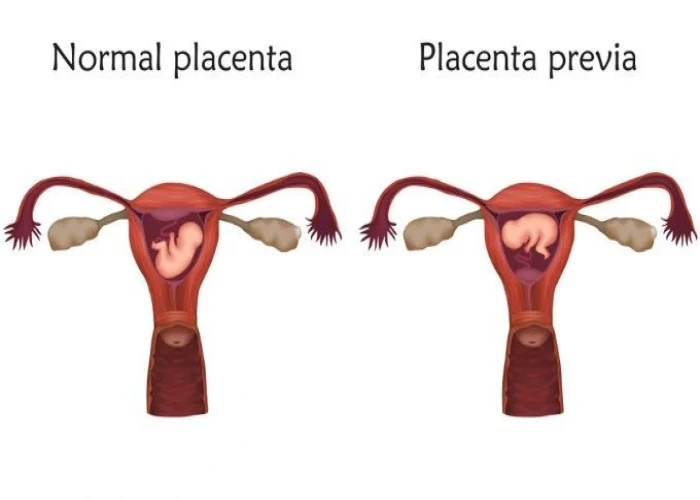
Placenta previa

Selective IgA deficiency

Hair loss
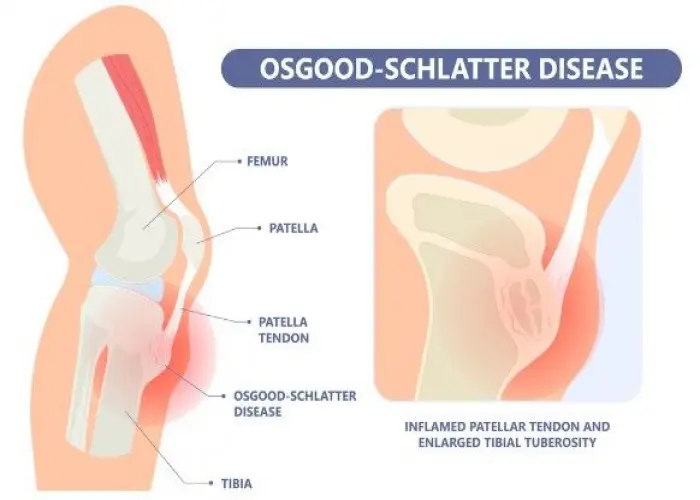
Growth plate fractures
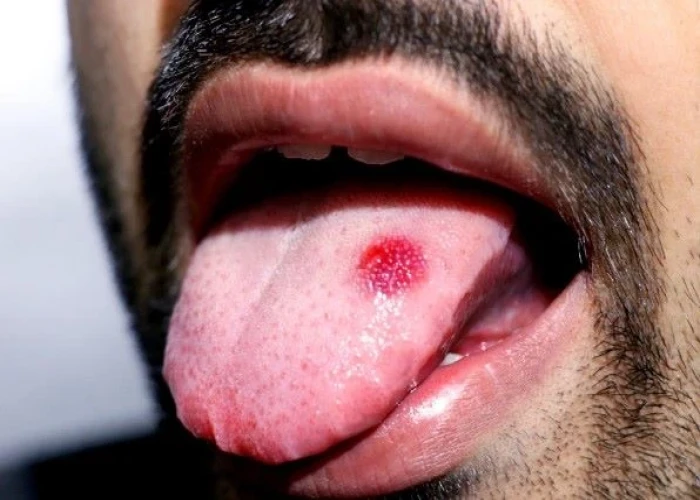
Leukoplakia
insomnia, অনিদ্রা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
